
19 Jul Liberalism in International Relations
Liberalism in International Relations – A Key IR Theory for UPSC CSE
Liberalism is one of the core theories in International Relations (IR) and plays a significant role in understanding diplomacy, peacebuilding, trade relations, and international institutions. For aspirants preparing for the UPSC Civil Services Examination, especially GS Paper 2, Liberalism provides a balanced counterpoint to Realism. It emphasizes the possibility of cooperation in an otherwise anarchic international system and is essential for interpreting India’s multilateral engagements, climate diplomacy, and trade strategies.
Core Assumptions of Liberalism
- Pluralism: Multiple actors beyond the state, such as international organizations, NGOs, and MNCs, influence global affairs.
- Cooperation is Possible: Contrary to Realism, Liberalism believes states can cooperate based on shared interests.
- Rule of Law: International institutions and norms regulate state behavior.
- Economic Interdependence: Trade and economic integration reduce the likelihood of war.
- Democratic Peace Theory: Democracies are less likely to go to war with one another.
Flowchart: Core Assumptions of Liberalism
Historical Evolution
Liberalism has its roots in the Enlightenment, where philosophers like Immanuel Kant envisioned a peaceful global federation of republics. In the 20th century, U.S. President Woodrow Wilson promoted the League of Nations after World War I, reflecting liberal ideals. In modern times, scholars like Robert Keohane and Joseph Nye emphasized “Complex Interdependence” as an alternative to Realist power politics.
Key Thinkers
- Immanuel Kant: Advocated for perpetual peace and democratic governance.
- Woodrow Wilson: Promoted international organizations for peace.
- Keohane & Nye: Introduced concepts like soft power, institutions, and interdependence.
Liberalism in Practice – India’s Foreign Policy
India has increasingly adopted liberal principles in its external engagement. Some illustrations include:
- Multilateralism: Active participation in UN, WTO, WHO, and IAEA.
- Climate Diplomacy: Leadership in International Solar Alliance and Paris Agreement.
- Vaccine Diplomacy: India’s “Vaccine Maitri” initiative to supply COVID-19 vaccines globally.
- Trade Relations: Engaging with EU, UK, Australia, ASEAN through FTAs and dialogues.
- Peacekeeping: India’s significant role in UN peacekeeping missions worldwide.
Infographic: Liberalism in Indian Foreign Policy
Strengths and Criticisms of Liberalism
Strengths
- Explains cooperation and global governance structures.
- Highlights the role of international institutions and law.
- Focuses on peace, development, and democracy.
- Supports India’s identity as a responsible global actor.
Criticisms
- Underestimates power politics and conflict.
- Too idealistic about institutional efficiency.
- Fails to explain aggressive behaviors of democracies.
- Overlooks hegemonic influence in global institutions.
Previous Year UPSC Questions Related to “Liberalism”
- 2022: Examine India’s changing role in multilateral institutions.
- 2019: Has India shifted from non-alignment to multilateral engagement?
- 2017: Discuss India’s leadership in global climate action.
- 2015: Is international law an effective tool in foreign policy today?
Probable Questions on Liberalism for UPSC Mains
- Explain the core tenets of Liberalism in International Relations and evaluate its relevance in India’s foreign policy.
- Critically examine the role of international institutions in shaping India’s multilateral strategy.
- How does economic interdependence influence India’s relations with neighboring countries?
- Do democratic values shape India’s global diplomacy? Substantiate with examples.
- Assess the limitations of Liberalism in a world witnessing increasing polarization.
liberalism vs realism for UPSC CSE
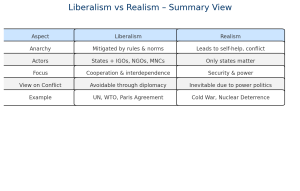
Liberalism vs Realism: A Comparative Glance
| Aspect | Liberalism | Realism |
|---|---|---|
| View on Anarchy | Mitigated by rules and institutions | Leads to self-help and conflict |
| Actors | States + NGOs + IGOs + MNCs | Primarily states |
| Focus | Cooperation, peace, norms | Power, security, national interest |
| Conflict View | Preventable through engagement | Inevitable and recurring |
| Example | UN, WTO, Paris Agreement | Nuclear deterrence, balance of power |
Why UPSC Aspirants Should Study Liberalism
Liberalism equips aspirants with the tools to analyze multilateral diplomacy, global governance, and international development. It enriches answer writing for GS2, essay topics, and even ethics case studies where values like cooperation and international justice are emphasized.

liberalism in indian foreign policy for UPSC CSE
Conclusion
Liberalism remains a relevant and powerful lens through which India’s global diplomacy, trade policy, and institutional engagements can be examined. While Realism explains strategic constraints, Liberalism reflects India’s aspirations for a peaceful, rule-based international order. A nuanced understanding of both is essential for a well-rounded UPSC answer.
Keywords: Liberalism in IR, IR theories UPSC, India multilateral diplomacy, UPSC GS Paper 2 IR notes




No Comments