19 Jul Neo-Liberalism in International Relations
Neo-Liberalism in International Relations – A Crucial IR Theory for UPSC CSE
Neo-Liberalism, also known as Neo-Liberal Institutionalism, emerged prominently in International Relations during the late 20th century as a direct response to Neo-Realism. For UPSC Civil Services aspirants preparing for GS Paper 2, Neo-Liberalism provides valuable insights into international cooperation, institutions, and global governance.
What is Neo-Liberalism?
Neo-Liberalism argues that international institutions significantly influence state behavior, fostering cooperation even in an anarchic international system. Unlike classical Liberalism, Neo-Liberalism emphasizes structured institutional frameworks rather than pure idealism, aligning itself more closely with realism’s rational actor model.
Core Assumptions of Neo-Liberalism
- Anarchy Managed by Institutions: While acknowledging anarchy, Neo-Liberalism argues institutions mitigate its effects.
- States are Rational Actors: Similar to Neo-Realism, it accepts that states act rationally to maximize their benefits.
- Absolute Gains Over Relative Gains: States prefer mutual benefits and are less concerned with unequal gains.
- Interdependence Promotes Cooperation: Economic interdependence and globalization facilitate cooperation.
- Institutions Matter: International organizations reduce uncertainty, promote transparency, and foster repeated interactions.
Historical Development and Key Thinkers
The intellectual foundation of Neo-Liberalism is traced back to scholars like Robert Keohane and Joseph Nye. Their theory of Complex Interdependence argued that growing global interconnectedness increases the scope for cooperation. In “After Hegemony,” Keohane notably highlighted the persistence of cooperation post-hegemony due to institutions.
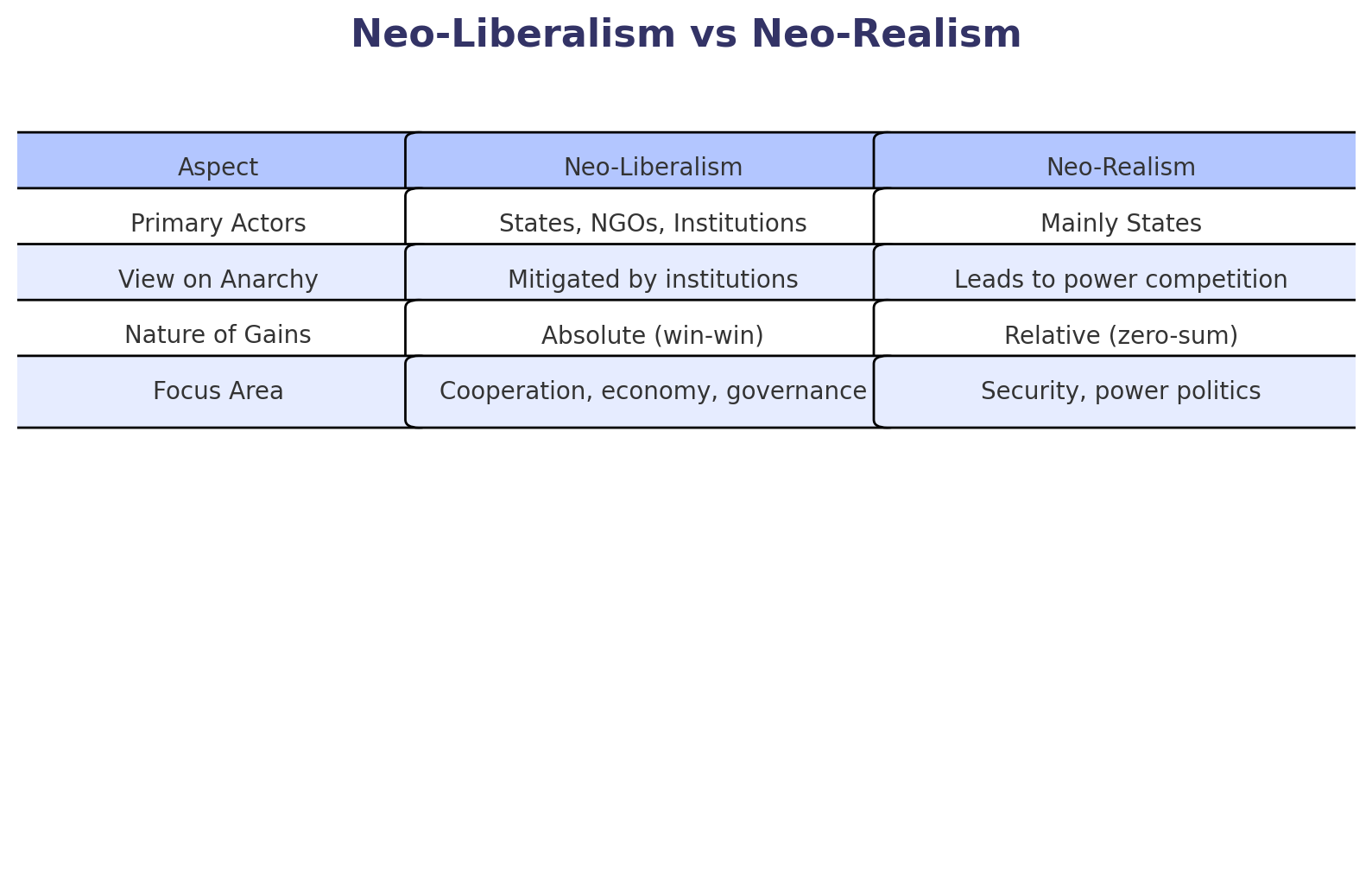
Neo-Liberalism vs Neo-Realism
| Aspect | Neo-Realism | Neo-Liberalism |
|---|---|---|
| View on Anarchy | Anarchy drives competition and conflict | Anarchy can be mitigated by institutions |
| Primary Actor | States only | States, institutions, NGOs, IGOs, MNCs |
| Cooperation | Limited by relative gains | Enhanced by absolute gains |
| Focus | Security and power | Economic interdependence and governance |
| International Institutions | Marginal significance | Central role |
Applications of Neo-Liberalism in India’s Foreign Policy
- Multilateral Trade and Economic Forums: India’s proactive role in WTO, G20, and BRICS illustrates institutional engagement.
- Climate Agreements: India’s active participation in the Paris Agreement and leadership in the International Solar Alliance.
- Global Health Initiatives: India’s vaccine diplomacy (Vaccine Maitri) demonstrates global cooperation for mutual benefit.
- Connectivity and Infrastructure: Institutional frameworks guiding connectivity projects like INSTC, BIMSTEC corridors.
Strengths of Neo-Liberalism
- Explains sustained international cooperation despite the absence of global governance.
- Highlights the importance and effectiveness of international institutions.
- Accounts for the growth of global economic interdependence.
- Aligns closely with India’s diplomatic approach towards multilateralism.
Criticism of Neo-Liberalism
- Overly optimistic about international institutions.
- Ignores underlying power dynamics influencing institutions.
- Assumes states prioritize absolute gains over security concerns.
- Institutions may reinforce inequalities between developed and developing nations.
Previous Year UPSC Questions Related to Neo-Liberalism
- 2021: Examine India’s role in international economic institutions.
- 2019: How far do international institutions influence India’s foreign policy choices?
- 2017: Discuss India’s engagement with global climate governance.
- 2014: Evaluate the effectiveness of multilateral diplomacy in contemporary international politics.
Probable UPSC Questions on Neo-Liberalism
- Critically evaluate Neo-Liberalism’s assumption that institutions significantly influence state behavior in international politics.
- How does Neo-Liberalism explain India’s increasing reliance on multilateral platforms?
- Discuss the relevance of Neo-Liberal Institutionalism in addressing global issues like climate change and pandemics.
- Analyze the limits of international institutions in overcoming geopolitical conflicts, with examples from recent events.
Neo-Liberalism and India’s Strategic Future
India’s approach towards global issues strongly resonates with Neo-Liberalism, reflecting its emphasis on global governance, multilateral solutions, and institutional cooperation. India’s efforts in promoting cooperative frameworks for issues such as climate change, global health, trade, and connectivity reflect Neo-Liberal principles. Future diplomats and administrators must thus deeply understand this theoretical framework.
Conclusion
Neo-Liberalism is crucial for understanding contemporary international relations, especially the role of institutions and cooperation. While not ignoring the constraints of power politics, it demonstrates that structured international cooperation can yield mutual benefits. For UPSC aspirants, grasping Neo-Liberalism provides essential analytical tools to interpret India’s foreign policy and global diplomacy strategies effectively.
Keywords: Neo-Liberalism, Neo-Liberal Institutionalism, UPSC IR theories, International Institutions, Global Governance, India Multilateralism




No Comments