12 Sep Global Biofuel Alliance
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the Topic details “Global Biofuel Alliance”. This Topic has relevance in the Economy section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
About Global Biofuel Alliance?
For Mains:
GS 2: Economy
Objectives of Global Biofuel Alliance?
Significance for India?
Challenges for Global Biofuel Alliance?
Why in the news:
During the G20 summit, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the Global Biofuel Alliance with President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva of Brazil and President Joe Biden of the United States.
About Global Biofuel Alliance:
- The Global Biofuel Alliance, founded by India, Brazil, and the United States, collectively responsible for 85% of global ethanol production, is an international initiative to foster collaboration in the biofuel sector. The alliance aspires to influence the global energy landscape and work toward achieving the net-zero emissions target.
- India, Brazil, and the United States are collectively responsible for 85% of global ethanol production
Membership:
- The core members of the Global Biofuel Alliance are India, Brazil, and the United States.
- To broaden its reach and impact, the Global Biofuel Alliance allows other countries to become members by endorsing its foundational document. The GBA welcomes participation from all interested nations. Currently, 19 additional countries, apart from the founding members, have expressed interest in joining, including nations such as Italy, Kenya, and the UAE.
- The membership structure of the Global Biofuel Alliance comprises three categories: member countries, partner organizations, and industries, to bring together diverse stakeholders to collaborate in advancing biofuel initiatives.
Objectives of Global Biofuel Alliance:
- Foster international collaboration and cooperation to promote the adoption and utilisation of biofuels on a global scale.
- Establish robust markets for biofuels and facilitate international trade in biofuels.
- Promote the widespread use of sustainable biofuels within the transportation sector.
- Provide policy guidance and technical support to assist national biofuels programs worldwide, promoting knowledge sharing and capacity building.
- Highlight and build upon the successful best practices and case studies already implemented in biofuels.
- Complement and collaborate with relevant existing regional and international agencies and initiatives focused on bioenergy, the bioeconomy, and energy transition, further enhancing global efforts in these areas.
Significance for India:
- Increased Technology Transfers: GBA allows India to access advanced technologies and international climate funds.
- Higher Blending of Petrol with Ethanol: India’s goal of achieving E-20 (20% ethanol blending with petrol) by 2025-26 can benefit from insights and experiences shared by countries like Brazil, which have achieved higher ethanol blending levels (E-85).
- Flex Fuel Vehicle Introduction: India can utilise GBA to collaborate with Brazil in adopting flex fuel vehicle technologies. These vehicles can use a wide range of fuel blends, reducing emissions and curbing India’s crude oil import bills.
- Global Climate Action: By being a part of GBA, India positions itself at the forefront of global climate action. It strengthens India’s role in combating climate change and demonstrates its commitment to sustainability.
- Promotion of Biofuel Exports: GBA can aid India in increasing its share of biofuel production, potentially making it a major exporter of biofuels globally.
- Greater Energy Independence: GBA supports India’s pursuit of greater energy independence by promoting the use of biofuels and reducing reliance on foreign crude oil.
- Financial Support for Farmers: Biofuel production has already provided financial relief to sugarcane farmers. GBA can further support farmers, especially those struggling with low sugar prices, by expanding opportunities in the biofuel sector.
Challenges for Global Biofuel Alliance:
- Technology Transfer: GBA may encounter challenges related to the transfer of advanced biofuel technologies, as countries, particularly the United States, have historically been cautious about sharing proprietary technology, potentially impeding the alliance’s objectives.
- Geopolitical Friction: The GBA may face resistance from countries like China and Russia, which may be averse to participating in a platform led by Western countries. China’s debt-trap diplomacy and foreign policy influence could pose a hurdle to expanding membership and international cooperation.
- Financial Sustainability: A robust funding mechanism is imperative for GBA’s projects. Economic downturns in the US and resource constraints faced by global institutions like the World Bank and IMF may challenge the alliance’s efforts to secure sustainable financing.
- Trade Barriers: Import restrictions on biofuels, such as those outlined in India’s National Biofuels Policy 2018, present a significant hurdle for developing a global biofuels market. GBA must focus on eliminating protectionist policies to promote cross-border biofuel trade.
- Environmental Impact: The production of biofuels, particularly ethanol derived from crops like sugar, carries substantial environmental consequences. This includes high water consumption, potential shifts in crop patterns, and impacts on water-scarce regions in Africa. Addressing these environmental concerns is vital for GBA to ensure sustainable biofuel production practices.

SOURCE:https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/energy/g20-summit-india-launches-global-biofuel-alliance-91659
plutus ias current affairs eng med 12th Sep 2023
Q.1 Consider the following Countries:
- India
- Russia
- China
- USA
- Brazil
Which of the above countries are founding members of the Global Biofuel Alliance?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 3, 4 and 5
(c) 1, 4 and 5
(d) 1, 3, 4 and 5
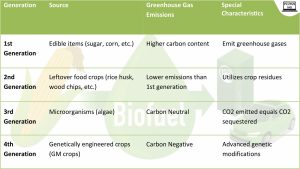
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Biofuels:
- Biofuels are carbon neutral but can not be carbon negative.
- India, Brazil, and the United States control over two-thirds of global ethanol production.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
.
Q.3 Discuss the significance and challenges of the Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA) in the context of global energy sustainability and the transition to a low-carbon economy.



No Comments