20 Oct Appointment and Transfer of Judges of High Courts
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “Appointment and Transfer of Judges of High Courts”. This topic has relevance in the “Polity and Governance” section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
What are the procedure and criteria for the appointment of High Courts Judges?
For Mains:
GS2: Polity and Governance
Issues related to High Courts
Why in the news?
The central government has recently issued a notification regarding the transfer of 16 high court judges and the appointment of 17 new judges in different high courts.
Background Information
The High Courts of India play a crucial role in the country’s judicial system, serving as the second-highest judicial authority below the Supreme Court of India. These courts are essential pillars of the nation’s federal structure and are established under Part VI, Chapter V, of the Indian Constitution. The High Courts are responsible for administering justice at the state or union territory level, depending on their jurisdiction.
Appointment of Judges of HCs
The appointment of judges in the High Courts is primarily governed by the Indian Constitution, specifically under Articles 217 and 224. These articles lay down the framework for the appointment, eligibility, and terms of High Court judges.
- Eligibility Criteria:
-
- The candidate must be a citizen of India.
- The candidate must have attained the age of 35 years.
- The candidate must have been a judge of a subordinate court in India for at least 10 years or an advocate of a High Court for at least 10 years.
- Appointment: By the President of India, after consultation with
- Chief Justice of India
- Governor of the state (or the administrator of the Union Territory, as applicable)
- Chief Justice of the concerned High Court.
- Oath: before the state’s Governor or their designate.
- Tenure and terms of service:
-
- HC Judges serve until the age of 62.
- They may resign by writing to the President.
- Removal by the President requires a Parliament recommendation.
- Judges leave office when appointed to the Supreme Court or transferred to another High Court.
Transfer of HC Judges:
- Article 222 of the Constitution allows for the relocation of a Judge, including the Chief Justice, from one High Court to another High Court.
- After consulting the Chief Justice of India, the President can transfer a High Court judge. Upon transfer, they receive additional compensatory allowance as determined by Parliament.
- In 1977, the Supreme Court ruled that transfers should be exceptional, based on public interest rather than punishment.
- In 1994, the Supreme Court stressed the need for judicial review to prevent arbitrary transfers, but only the transferred judge can challenge it.
Challenges associated with High Courts of India
- Vacancies: As of 2023, there are 347 vacant positions in the High Courts across India against a total strength of 1,114.
- Caseload: The High Courts are overburdened with cases. In 2022-23, the High Courts disposed of 5.3 million cases, but the pendency of cases remains high. As of August 4, 2023, there are 6.2 million pending cases in the High Courts.
- Infrastructure: The High Courts are facing a shortage of infrastructure, including courtrooms, chambers, and libraries. This makes it difficult for judges to discharge their duties effectively.
- Technology: The High Courts are not fully equipped with the latest technology. This makes it difficult for judges to manage their work efficiently.
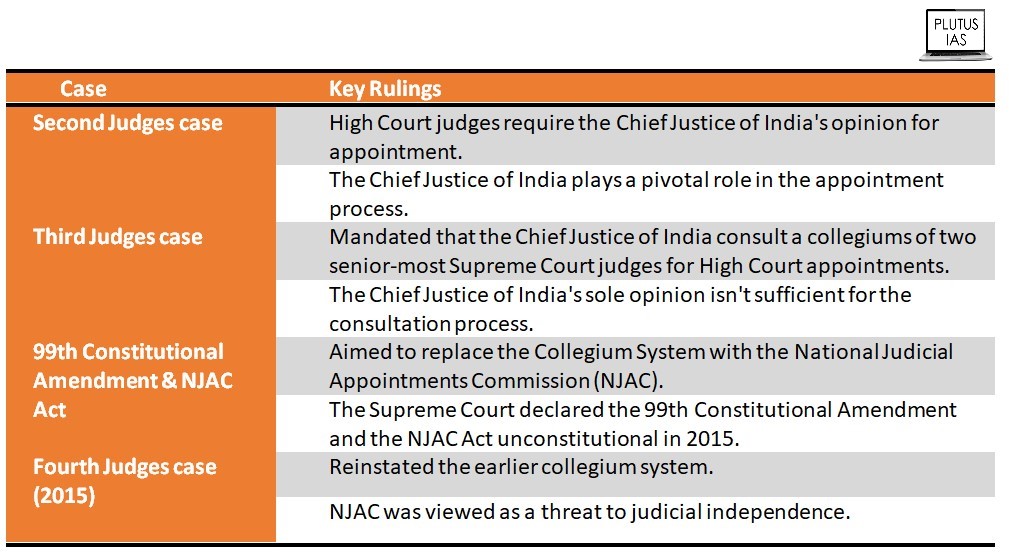
- Independence: The independence of the judiciary is under threat from the government. The government has been trying to interfere in appointing judges and undermining the Collegium system.
Sources: Govt notifies 16 transfers, 17 new appointments of judges across HCs | Latest News India
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 20th Oct 2023
Q1. With reference to Judges of High Courts, consider the following statements:
- The President of India appoints the Judge of a High Court.
- The judge of the High Court resigns by writing to the Chief Justice of India.
- High court judges serve until the age of 62.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) None
Q2. Consider the following:
- The candidate must be a citizen of India.
- The candidate must have attained the age of 35 years.
- The candidate must have been a judge of a subordinate court in India for at least 10 years or an advocate of a High Court for at least 10 years.
- The candidate must be a distinguished jurist.
How many of the above are eligibility criteria for the Judge of the High Court?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All Four
Q3. What is the procedure for the Appointment of Judges of High Courts? Analyse the challenges faced by the High Courts of India.



No Comments