09 Sep Flash flood and its risk in coming years (9th Sept 2022)
Why in the news?
Death toll in Himachal downpour rises to 21, railway bridge collapses
What are they, and how are they different?
- Flash Floods:- Flash Floods refer to such environmental situations where outrageous or continuous rainfall over a period of days, or during particular seasons can lead to stagnation of water and cause flooding in a much shorter span of time.
- A study by the US’s meteorological agency, the National Weather Service, says flash floods are caused when rainfall creates flooding in less than 6 hours.
- It adds that flash floods can also be caused by factors apart from rainfall, like when water goes beyond the levels of a dam.
- In the Indian climate, flash floods are often associated with cloudbursts – sudden, intense rainfall in a short period of time.
- Himalayan states further face the challenge of overflowing glacial lakes, formed due to the melting of glaciers, and their numbers have been increasing in the last few years.
- Flash flooding generally occurs more where rivers are narrow and steep, so they flow more quickly,
- They can also occur in urban areas located near small rivers since hard surfaces such as roads and concrete do not allow the water to absorb into the ground.
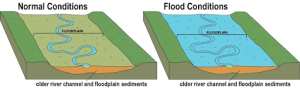
How common are these floods and normal floods?
- Flash floods have been frequently witnessed in cities like Chennai and Mumbai.
- India is the worst flood-affected country in the world after Bangladesh and accounts for one-fifth of the global death count due to floods, as per government data issued from a project by the Assam State Disaster Management Authority.
- Depression and cyclonic storms in the coastal areas of Orissa, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, and others also cause flash floods.
- Also, the data from the National Disaster Management Authority, stated that one of the primary reasons for flood situations occurring so commonly is that nearly 75 percent of the total Indian rainfall is concentrated over a short monsoon season of four months (June to September).which results, the rivers witness a heavy discharge during these months.
Consequences of Flash Flood

- Loss of the natural environment (including vegetation, agriculture, geomorphology, and pollution)
- Loss of the human population (entrapments, injuries, fatalities).
- Loss of infrastructure in the particular area.
Way forward.
As stated by the Indian geologist there is one way of dealing with the current situation is a comprehensive strategy of monitoring the ground in hilly areas, planning development works in a way that is sensitive to the region’s ecology, and mitigation to reduce the extent of damages.
Sources
https://bit.ly/3B3odwT( The Indian Express)
Plutus IAS current affairs eng med 9th Sep 2022



No Comments