19 Sep Genetically modified plants
Genetically Modified Plants
What are genetically modified plants and how are they modified?
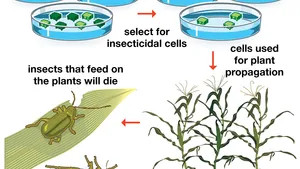
Pic: Genetically modified plants
- These are kinds of living organisms, whose genetic material has been artificially changed in a laboratory through genetic engineering, in a way to favor the expression of desired physiological traits or the creation of wished biological products.
- This is created by the combinations of plants, animals, bacteria, and virus genes that generally do not occur in nature or by traditional cross-breeding methods.
- Most GMOs are designed to withstand the direct application of herbicide or to produce an insecticide.
- Nevertheless, some new technologies are now used to create artificial traits in plants, for example, to resist the browning in apples, and to make new organisms using biology.
- These are a kind of plant, in which the DNAs are modified by genetic engineering for embedding a new trait in the plants which does not happen naturally in the species.
- The purpose of genetic engineering is to transcend the genus barriers by inserting an alien gene in the seed to achieve the desired effect and the alien gene could be from a plant, animal, or even a soil bacterium.
- A few genetically modified variants of maize, canola, soybean, etc are available.
Genetically modified plants in India
- The only GM plant that is allowed in India since 2002, is BT cotton, which has two foreign genes from the soil, Bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), that allow the crop to build a protein toxic to the common pest pink bollworm and another one is Ht Bt which is obtained by the insertion of an additional gene, from another soil bacterium, it permits the plants to resist the common herbicide glyphosate.
- In Bt Brinjal, a gene allows the plant to withstand the attacks of fruit and shoot borers.
- Earlier this, the government of India restricted the commercial release of genetically modified mustard due to very strong opposition from anti-GMO activists and NGOs.
The legal status of GM crops in India
- The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC), is the supreme body in India, that checks the commercial release of GM crops under the aegis of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- This committee is responsible for the growing activities which involve the use of large-scale involvement of hazardous microorganisms and recombinants in research and from the environmental perspective.
- It is also responsible for increasing proposals for releasing genetically engineered (GE) organisms and products into the environment, including experimental field trials.
- It also takes care of the increase in uses of the unapproved GM variant, which can lead to an imprisonment of 5 years and a fine of 1 lakh fine under the Environment Protection Act, 1989
Issue related to the Genetically Modified Crops
Agriculture Genetic Modification conflict: there are possibilities of getting some undesired consequential effect like the resulting food can have an allergic reaction.
- A study by Karolinska Institute Sweden and another study by Biopharmaceutical Company Novartis, have pointed out that CRISPR-Cas9-modified cells can trigger cancer.
The Germline Modification: in this modification process, the gene which is too passed on to the children and future generations is intentionally changed- in a way to create genetically modified people.
- It is the most correct righteous debate related to genome editing centers about human germline modification. This is so because it made the germline can transfer to the future generation also.
- For both safety and social reasons, Human germline modifications have not been considered appropriate for many years.
Genetic Inequality:
- Wealthy families of society will be able to buy the latest upgraded offspring for their children. Consequently, it will bring genetic inequality, and even it will be a greater inequality than the present world already has.
- Many key scientists in this field, have arisen concerns about the misuse of possible misuse of the technology, which can be used for eugenics, to build genetic discrimination.
Regulation of Imported Crops:
- Initially, the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) was responsible for regulating the GMO levels in imported consumables, under the Union environment ministry.
- Later, the role of the committee was mitigated with the enactment of the Food Safety and Standard Act, 2006, and the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) were allotted to check imported goods.
Sources :
- NIH (The national human genome research institute)
- Indian Express (CRISPR: beginning to deliver)
- Yourgenome.org (What is CRISPR-Cas9?)
- Britannica.com
Plutus IAS Current affairs eng med 19th Sep 2022
IAS Current affairs
Nowadays, Current affairs are very important for passing the UPSC exam process like Prelims, Means, and Interviews. If you want to pass the IAS examination, you should read daily current affairs. You get all the best and latest articles on daily current affairs for the UPSC examination from PlutusIAS.
Also, go through the weekly and monthly current affairs from our site.



No Comments