30 Mar India’s fiscal deficit target
Source – The Hindu and PIB.
General Studies – Growth of Indian Economy, Fiscal Consolidation, Fiscal Deficit, Gross Domestic Product
Why in the News ?
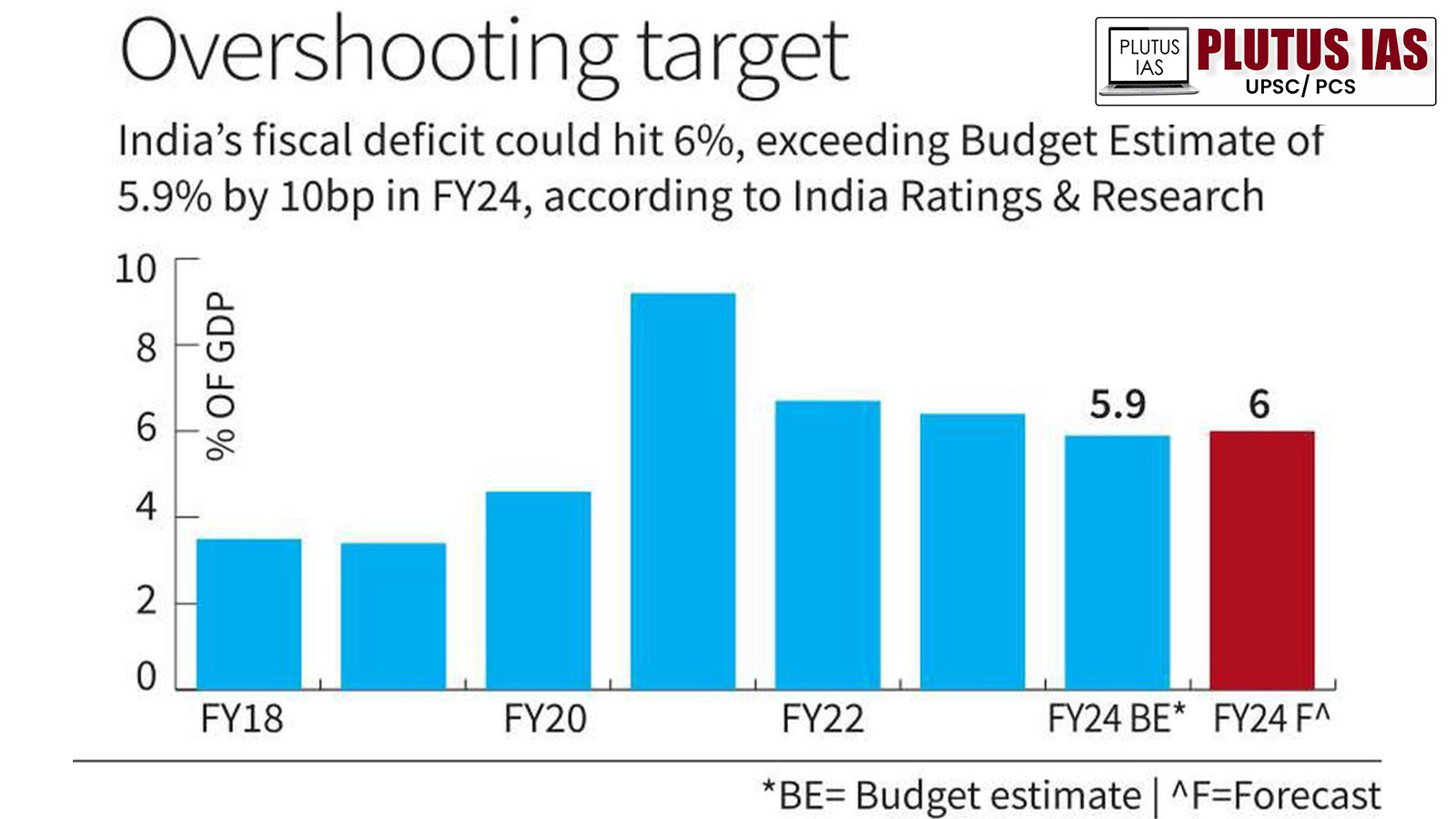
- India’s central government has increased the fiscal deficit to Rs 15 lakh crore by the end of February 2024 from Rs 11 lakh crore in January 2024. This has led to an increase in the fiscal deficit by 86.5%, which has been significantly contributed by the increase in tax devolution and capital expenditure of the states.
- The Finance Ministry has also lowered its target for gross domestic product (GDP), which will be reduced to 5.1% in 2024-25. It is an effort by the central government in India to address financial challenges.
- The central government still has the capacity to spend Rs 6 lakh crore in March, which can help the central government handle the current financial challenges. Because India is facing financial challenges in dealing with national debts.
- Therefore, the Union Finance Ministry in its Interim Budget 2024-25 has projected India’s fiscal deficit as the GDP for the financial year 2024-25.. It has been decided to reduce the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) to 5.1%.
Fiscal deficit and National debt :
- The total amount owed by the government of a country to its creditors at a given time is called national debt.
- Government debt comprises various liabilities including domestic and external debt along with obligations of schemes such as small savings, provident funds and special securities.
- These liabilities include both interest payments and repayment of the principal amount, placing a considerable financial burden on the government’s finances.
- This is the amount of debt that the government has accumulated while borrowing to overcome fiscal deficit over several years.
- The higher the government’s fiscal deficit as a share of GDP, the less likely it is to make payments to its creditors.
- The fiscal deficit of countries with large economies cannot be high.
- By 2022, major deficit countries include Italy -7.8%, Hungary -6.3%, South Africa -4.8%, Spain -4.7%, France -4.7%.
Importance of fiscal consolidation in an emerging economy :
- Ways and means of reducing fiscal deficit is called fiscal consolidation.
- Any government can control its economy in reinforcement Borrows to cover the losses. Due to which he has to allocate a part of his earnings to repay the loan. Therefore as the debt increases, the interest burden will also increase.
Meaning of fiscal deficit :

- The difference between the total expenditure of any government and its total revenue (except borrowing)Is called fiscal deficit.
- It is an indicator of the extent to which a government must borrow to finance its operations.
- This country’s Gross domestic product (GDP) is expressed as a percentage.
- from high fiscal deficit inflation , currency devaluation And the debt burden may increase, while the low fiscal deficit is seen as a positive sign of fiscal discipline and a healthy economy.
Positive aspects of fiscal deficit :
Increase in government expenditure: Fiscal deficit enables the government to increase spending on public services, infrastructure and other critical sectors that can stimulate economic growth.
Financing of public investment : The government can finance long-term investments such as infrastructure projects through fiscal deficit.
Employment Creation : Increasing government spending can lead to job creation, which can help reduce unemployment and raise standards of living.
Negative aspects of fiscal deficit :
Balance of Payment Problems : If a country is facing a large fiscal deficit, it may have to borrow from foreign sources, which may lead to a decrease in foreign exchange reserves and put pressure on the balance of payments.
Inflationary Pressure : Large fiscal deficits can lead to increased money supply and high inflation, which reduces the purchasing power of the general public.
Increase in debt burden : Persistently high fiscal deficits lead to increased government debt, putting pressure on future generations to repay the debt.
Flow of private investment : The government may have to borrow heavily to meet the fiscal deficit, causing interest rates to rise, and the private sector may find it difficult to obtain credit, leading to the exit of private investment.
Other types of fiscal deficit in India :
Effective Revenue Deficit :
- The difference between the revenue deficit and the grants given for creation of capital assets is called effective revenue deficit.
- The concept of effective revenue deficit on public expenditure was suggested by the Rangarajan Committee in India.
Revenue loss :
- It tells the excess of revenue expenditure of the government over revenue receipts.
- So Revenue deficit = Revenue expenditure – Revenue receipts.
Primary deficit :
- Primary deficit is equal to fiscal deficit plus interest payments.
- It states the difference between a government’s expenditure requirements and its receipts, not taking into account the expenditure incurred on interest payments on loans taken by a government during previous years to fuel its economy.
- Hence Primary Deficit = Fiscal Deficit – Interest Payments.
Conclusion :

- According to the data of the Central Government in India, despite the increase in fiscal deficit in February, this year’s fiscal deficit target set by the government can be achieved.
- The priority of the Central Government of India is to bring the economy out of imbalance through capital expenditure (capex) in present time
- Increasing government investment in the infrastructure of the Indian economy will also increase private investment, which will boost economic (GDP) growth and result in reducing the fiscal deficit to GDP ratio.
- By implementing a combination of fiscal consolidation measures, India can effectively manage its national debt and fiscal deficit while ensuring fiscal stability, economic growth and long-term prosperity.
- Achieving fiscal sustainability in India requires a balance between short-term stabilization efforts and long-term structural reforms.
- It is quite commendable that some ministries, despite missing their targets, will still deliver positive results in terms of deficit figures for the full year.
- It is good for the government to tighten the reins for better economic outcomes at the macro level, but consistently missing spending targets compromises the desired results and indicates the need for better outlay planning and less borrowing in the coming years. There may be scope for taking.
Practice Questions for Preliminary Exam :
Q.1. Consider the following statements regarding reducing India’s fiscal deficit target.
- The Finance Ministry has decided to reduce India’s fiscal deficit to 5.1% of GDP in the financial year 2024-25 in the interim Budget 2024-25.
- Government debt comprises various liabilities including domestic and external debt along with obligations of schemes such as small savings, provident funds and special securities.
- The Finance Ministry has set a target of reducing GDP growth to 5.1% in the financial year 2024-25.
- The higher the fiscal deficit of the government, the less likely it is to make payments to its creditors.
Which of the above statement / statements is/ are correct?
(A). Only 1, 2 and 3.
(B). Only 2, 3 and 4
(C). None of these
(D). All of these
Answer – (D)
Practice Questions for Main Exam :
Q.1. Highlight the various aspects of the fiscal deficit in India and discuss in detail the importance of fiscal consolidation in an emerging economy and the important factors in meeting the fiscal deficit target set by the government.
Qualified Preliminary and Main Examination ( Written ) and Shortlisted for Personality Test (INTERVIEW) three times Of UPSC CIVIL SERVICES EXAMINATION in the year of 2017, 2018 and 2020. Shortlisted for Personality Test (INTERVIEW) of 64th and 67th BPSC CIVIL SERVICES.
M. A M. Phil and Ph. D From (SLL & CS) JAWAHARLAL NEHRU UNIVERSITY, NEW DELHI.



No Comments