24 Oct Lemru Elephant Reserve
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “ Lemru Elephant Reserve”. This topic has relevance in the Environment section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
About Lemru Elephant Reserve?
About Elephants?
Conservation Status of Indian Elephants?
For Mains:
GS 3: Environment
India’s Initiatives for Conservation of Elephants?
Why in the news?
In response to the Chhattisgarh government’s request, the Union coal ministry has decided not to auction the 40 coal blocks belonging to Coal India Limited (CIL) located in and around the Lemru Elephant Corridor (LEC).
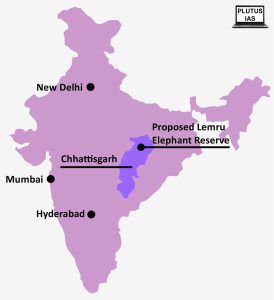
About Lemru Elephant Reserve:
- Location: The Lemru Elephant Reserve is situated in the Korba district of Chhattisgarh, India.
- Objectives: The primary objectives of the Lemru Elephant Reserve are to provide elephants with a permanent habitat, reduce property damage, and mitigate human-elephant conflicts. It is also an integral part of an elephant corridor that connects Lemru (Korba), Badalkhol (Jashpur), and Tamorpingla (Surguja).
- Elephant Reserves in India: In India, there are a total of 33 notified Elephant Reserves (ERs) across 14 states. These reserves play a crucial role in the conservation and protection of elephants and their habitats.
About Elephants:
- Keystone Species: Elephants are considered keystone species because they play a crucial role in their ecosystems. They have a significant impact on the environment by shaping the landscape, dispersing seeds, and creating water holes. Their presence and activities influence the entire ecosystem in which they live.
- Asian Elephant Subspecies: There are three subspecies of Asian elephants, which are as follows:
- Indian Elephant: The Indian elephant (Elephas maximus indicus) has the widest range among the Asian elephant subspecies and accounts for the majority of the remaining elephants on the continent. They are found in various parts of South Asia, including India.
- Sumatran Elephant: The Sumatran elephant (Elephas maximus sumatranus) is native to the Indonesian island of Sumatra. It is the smallest of the Asian elephant subspecies.
- Sri Lankan Elephant: The Sri Lankan elephant (Elephas maximus maximus) is native to Sri Lanka. It is the largest of the Asian elephant subspecies.
Conservation Status of Indian Elephants:
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: In India, the Indian elephant is listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, which provides them with the highest level of legal protection.
- IUCN Red List: Indian elephants are classified as “Endangered” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species.
- CITES: They are listed under CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) Appendix I, which includes species threatened with extinction. This listing restricts international trade in Indian elephants and their parts.
India’s Initiatives for Conservation of Elephants:
- Gaj Yatra: Gaj Yatra is a nationwide campaign launched on World Elephant Day in 2017 to protect elephants and raise awareness about their conservation.
- Project Elephant: Launched in 1992, Project Elephant is a centrally sponsored scheme in India aimed at protecting elephants, their habitats, and addressing human-elephant conflicts.
- Seed Bombs: In an effort to enrich the food stock for wild elephants and prevent man-elephant conflicts, Odisha’s Athagarh Forest Division has started casting seed balls (or seed bombs) inside different reserve forest areas.
- Right of Passage of Animals: The Supreme Court upheld the 2011 order of the Madras High Court regarding the Nilgiris elephant corridor, affirming the right of passage for elephants and the closure of resorts in the area to ensure the safe movement of elephants.
International Initiatives to Conserve Elephants:
- Monitoring the Illegal Killing of Elephants (MIKE) Program: MIKE is an international collaboration launched in 2003 to track trends related to the illegal killing of elephants in Africa and Asia. It helps monitor the effectiveness of field conservation efforts and combat illegal poaching of elephants.
Project Elephant
- Launch Date: Project Elephant was initiated by the Government of India in 1992. It operates as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme with the following key objectives:
- Protection of Elephants, their Habitat, and Corridors: The project aims to safeguard the population of elephants in India by preserving their natural habitats and migratory corridors.
- Addressing Man-Animal Conflict: Project Elephant seeks to address the challenges arising from conflicts between humans and elephants, finding ways to minimize such conflicts and promote coexistence.
- Welfare of Captive Elephants: The project also focuses on the welfare and well-being of elephants held in captivity, ensuring they are treated ethically and in line with established standards.
- Implementation: The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India, primarily administers Project Elephant. It provides financial and technical support to states and union territories that are home to significant elephant populations. This support helps these regions in implementing the objectives of Project Elephant effectively and in collaboration with local stakeholders.
Source: Chhattisgarh: 40 coal blocks in Lemru reserve not to be mined, says Coal ministry
Q.1 Consider the following statements:
- The Lemru Elephant Reserve is located in the state of Jharkhand, India.
- There are 33 notified Elephant Reserves (ERs) in India, spread across 14 states.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER: B
Q.2 Consider the following statements:
- Project Elephant was launched by the Government of India in 1992.
- Project Elephant was initiated as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- The Sri Lankan elephant is the largest of the Asian elephant subspecies.
How many of the above statement/s is/are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
ANSWER: C
Q.3 Project Elephant is a significant conservation initiative in India. Explain the objectives and key strategies of Project Elephant. How do elephants serve as keystone species?



No Comments