27 Apr New guidelines for Asset Reconstruction Companies
THIS ARTICLE COVERS ‘DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS’ AND THE TOPIC DETAILS OF “New guidelines for Asset Reconstruction Companies”. THIS TOPIC IS RELEVANT IN THE “ECONOMY” SECTION OF THE UPSC CSE EXAM.
Why in the News?
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released directives detailing revised instructions for Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs). These guidelines are applicable to all Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) under section 3 of the SARFAESI Act, 2002. They encompass regulations concerning ARC registration, the necessity of maintaining a minimum net-owned fund, the operational scope of ARCs, and the prescribed guidelines for their activities.
More About the recent Guidelines
Increase in Minimum Net owned Fund requirements:
- The minimum capital requirement for ARCs has been raised to Rs 300 crore, marking a notable increase from the previous threshold of Rs 100 crore.
- Existing ARCs are given a transition period to meet the new minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF) requirement of Rs 300 crore by 31st March 2026.
- As part of the transition process toward the heightened capital requirement, ARCs must ensure a minimum capital of Rs 200 crore by 31st March 2024.
Corporate governance regulations:
- It mandates that ARCs maintain a board comprising a minimum of 50% independent directors, with the chairman being an independent director as well.
- Additionally, ARCs are obligated to establish audit, nomination, and remuneration committees.
Investment Opportunities:
- ARCs are permitted to allocate funds into government securities and deposits within scheduled commercial banks, as well as institutions such as the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI), National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD), or other entities designated by the central bank periodically.
- Furthermore, ARCs have the option to invest in short-term instruments like money market mutual funds, certificates of deposit, and corporate bonds/commercial papers rated AA- or higher by a recognized credit rating agency. However, there exists a restriction wherein the maximum investment in such short-term instruments is limited to 10% of the Net Owned Fund (NOF).
Enhanced Disclosure Requirements:
- ARCs are obligated to provide financial data covering the previous 5 years and a track record detailing returns and recoveries for all security receipt schemes over the past 8 years.
- Additionally, they must disclose their interactions with rating agencies.
Limitations on Management Fees:
- ARCs are now prohibited from levying management fees that are not tied to the asset recovery process.
What are Asset Reconstruction Companies?
- Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) are entities that specialize in acquiring non-performing assets (NPAs) or distressed assets from banks and financial institutions. These companies work to resolve these assets by either restructuring them, recovering dues through various means, or selling them to other investors.
- Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) are entities established under the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act in India.
How do ARCs function in India?
- Acquisition of Distressed Assets: ARCs acquire distressed assets from banks and financial institutions, primarily non-performing loans (NPLs). These assets are purchased at discounted prices, allowing the selling institutions to offload non-performing or stressed assets from their balance sheets.
- Resolution and Recovery: ARCs undertake various strategies to resolve and recover the distressed assets once acquired. This may include debt restructuring, where the terms of the loan are renegotiated to make it easier for the borrower to repay, or asset sales, where the underlying collateral securing the loan is sold to recover funds.
- Legal Proceedings: In cases where debt restructuring or asset sales are not feasible, ARCs may resort to legal action to recover dues from defaulting borrowers. This could involve initiating recovery proceedings through the Debt Recovery Tribunal (DRT) or filing cases in civil courts.
- Debt Restructuring and Rehabilitation: ARCs may work with borrowers to restructure their debt obligations, providing them with more manageable repayment terms to facilitate the revival of their businesses. This may involve extending the repayment period, reducing the interest rate, or converting debt into equity.
- Asset Management: ARCs actively manage the acquired assets to maximize their value. This includes monitoring the performance of the underlying assets, identifying opportunities for value enhancement, and implementing strategies to optimize returns.
- Securitization and Reconstruction: ARCs may securitize the acquired assets by bundling them together and issuing security receipts (SRs) to investors. These SRs represent an undivided interest in the underlying pool of assets and provide investors with a share in the proceeds recovered from the assets.
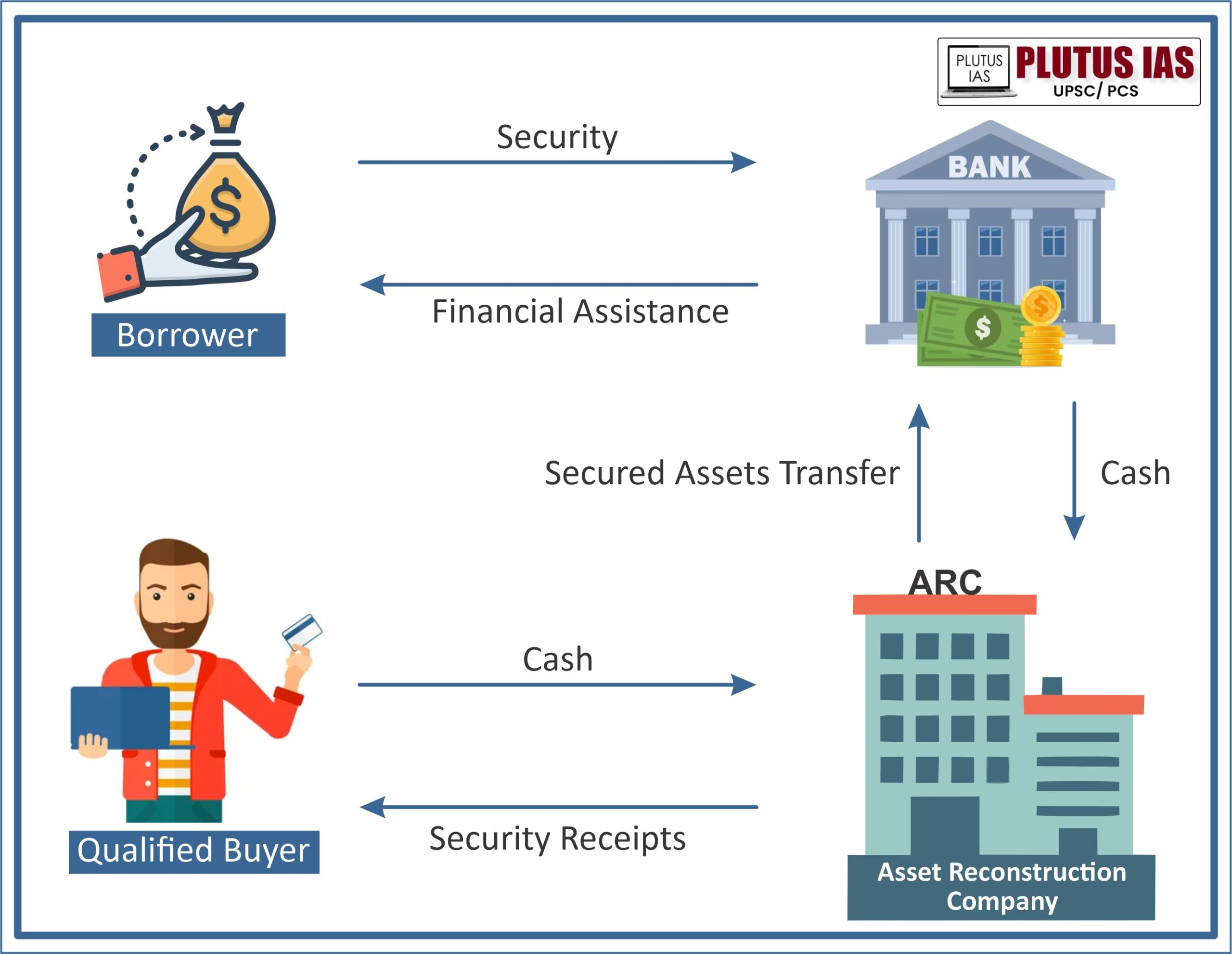
How ARCs Helped India in Controlling NPAs?
- Acquisition of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs): ARCs procure NPAs from banks and financial institutions through bilateral agreements or auctions. This process aids banks in cleansing their balance sheets, enabling them to concentrate on their primary lending functions.
- Resolution of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs): Upon acquiring NPAs, ARCs develop resolution strategies within a six-month timeframe to recover outstanding dues. They employ various approaches such as debt restructuring, enforcement of security interests, settlement of liabilities, asset possession, and business divestment.
- Enhanced Recovery Rates: ARCs have exhibited higher recovery rates compared to banks. As per Reserve Bank of India (RBI) statistics, ARCs acquired 9.7% of the previous fiscal year’s gross NPAs in FY2023, a significant increase from 3.2% in FY2022. This trend underscores the escalating significance of ARCs in NPA resolution efforts.
- Liberating Bank Capital: Through NPA acquisition, ARCs release capital for banks, allowing them to channel resources towards new lending activities and bolstering their financial stability.
- Securitization and Fundraising: ARCs raise capital by issuing security receipts (SRs) to accredited institutional investors. This mechanism furnishes them with financial means to procure and resolve distressed assets effectively.
What more can be done by RBI to strengthen ARCs?
-
- Implement stricter regulatory framework: The RBI should implement stronger regulation and compliance measures for ARCs to ensure transparency and accountability. This includes regular audits, increased disclosure requirements, and enforcing strict adherence to capital adequacy rules.
- Diversify Funding Channels for ARCs: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) might consider permitting ARCs to tap into alternative funding streams like external commercial borrowings or bond issuance to complement their capital needs. This measure would furnish ARCs with additional financial resources, enabling them to acquire and address distressed assets more effectively.
- Encourage collaboration between banks and ARCs: Banks must collaborate closely with ARCs to facilitate faster resolution of NPAs. Standardized processes for data sharing, joint assessment of stressed assets, and coordinated decision-making will enhance efficiency and speed up resolution timelines.
- Promote Consolidation and Expertise: The RBI could encourage the merging of smaller ARCs to form larger, specialized entities adept at handling and resolving intricate distressed assets more effectively. This initiative might entail easing specific regulatory conditions governing mergers and acquisitions involving ARCs.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 27th April 2024
Prelims based Question
Q1. Consider the following statements:
- The functioning of ARCs is governed by the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code of 2016.
- RBI oversees the functioning of ARCs.
Choose the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a). 1 Only
(b). 2 Only
(c). Both 1 and 2
(d). Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER: B
Mains based Question
Q1.Analyze the role of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in strengthening Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs). Discuss potential measures that the RBI could implement to enhance the regulatory framework for ARCs.



No Comments