01 Sep Rozgar Mela and Unemployment in India
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “Rozgar Mela and Unemployment in India”. The topic “Rozgar Mela and Unemployment in India” has relevance in the “Economy” section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
What is Rozgar Mela?
What are Unemployment Types?
For Mains:
GS3: Economy
Why in the news?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi issued appointment letters through video conferencing on Monday to new recruits joining as a result of the Rozgar Mela (Employment Fair).
Rozgar Mela
- The Rozgar Mela serves as an expedited approach to connect job seekers with employers. This event brings together multiple employers and job seekers to apply and interview for positions.
- The aim of the Rozgar Mela is to accelerate employment growth, offer significant opportunities for youth empowerment, and encourage their active engagement in national development.
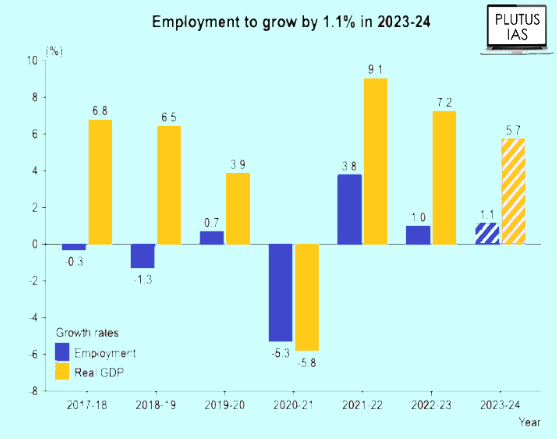
Defining Unemployment
- The unemployment rate is the proportion of individuals without jobs within the labor force.
- The labor force encompasses those who provide or express willingness to provide labor for economic activities, covering both employed and unemployed individuals.
- As per the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PFLS) 2017-18, India’s labor force exhibited a 6.1% unemployment rate, with 17.8% of youth aged 15-29 facing unemployment.
Reasons of Unemployment
- Jobless Growth: A country’s GDP can increase without significant job creation or even with job losses. While GDP growth is necessary for job creation, it’s not enough.
- Slow Manufacturing sector growth: India’s growth relies on the service sector, which is less labor-intensive than manufacturing. The manufacturing phase has provided limited well-paid jobs, especially for those with lower education and skills.
- Skill Mismatch: There’s often a mismatch between the skills possessed by job seekers and the skills demanded by available job opportunities. This discrepancy results in unemployment even when there are vacancies.
- Informal Sector Dominance: A significant portion of India’s economy operates in the informal sector, which often lacks stable jobs and social security benefits, leading to underemployment and insecurity.
| Types of Unemployment | |
| Frictional Unemployment |
|
| Structural Unemployment |
|
| Cyclical Unemployment |
|
| Seasonal Unemployment |
|
| Natural Unemployment |
|
Way Forward
- Shift to Enabling Environment: The demand for a substantial number of jobs surpasses the capacity of any government to provide direct employment. Instead, the government’s role lies in fostering conditions that empower the economy to generate jobs organically.
- Elevate Manufacturing Sector: Prioritize the composition of GDP growth by bolstering the manufacturing sector. A strategic emphasis on labor-intensive manufacturing and support for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) is essential.
- Revise Industrial Policy: Rethink the existing industrial policy framework that leans towards capital-intensive industries. A holistic approach involving cluster development can enhance the efficiency of SMEs collectively.
- Human Capital Investment: Acknowledge labor as more than a production factor with cost considerations. It’s essential to invest in human capital, recognizing the value it adds to the workforce.
Sources:
Will Rozgar Mela solve India’s unemployment crisis? | Explained News – The Indian Express
Q1. With reference to Unemployment, consider the following statements:
- A significant portion of India’s economy operates in the formal sector.
- A mismatch between the skills possessed by job seekers and the skills demanded by available job opportunities.
- Uneven distribution of economic opportunities and development across regions.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct reasons for Unemployment in India?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) None
Answer: (a)
Q2. Consider the following pairs:
| Natural Unemployment | A combination of frictional and structural unemployment. |
| Long-Term Unemployment | Involves individuals without jobs for an extended period, typically six months or more. |
| Hidden Unemployment | More people working in an activity or industry than necessary for efficient performance |
| Disguised Unemployment | Occurs when individuals work part-time or in jobs below their skill level. |
How many of the abovementioned pairs are correctly matched ?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All Four
Answer: (b)
Q3. Discuss the major types of unemployment prevalent in India. How does each type impact the country’s workforce and economy?



No Comments