21 Sep Five-Country Biosphere Reserve (GS-2: CONSERVATION, GOVERNMENT POLICIES AND ENVIRONMENT.)
Posted at 21 Sep 2021
in Biodiversity, Current Affairs, Environment and climate change, GS Paper III
0 Comments
CONTEXT:- Mura-Drava-Danube (MDD) has been announced as the world’s first ‘five-country biosphere reserve’ by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
About MDD
MDD biosphere reserve covers a total area of 700 km of the Mura, Drava and Danube rivers and stretches covering the regions of Austria, Slovenia, Croatia, Hungary and Serbia. It covers a total area of over a million hectares and known as ‘Amazon of Europe’, makes it the largest riverine protected area on the continent.
The physiography of the forest consists of floodplain forests, gravel and sand banks, river islands, oxbows and meadows. Also, it is home to a variety of rare flora and fauna. Some of the rare species are Europe’s highest density of breeding white-tailed eagle, some endangered species such as the little tern, black stork, otters, beavers and sturgeons. According to WWF it is also an important annual resting and feeding place for more than 250,000 migratory birds and home to 900,000 people who live in the biosphere reserve.
Criteria for Designation of Biosphere Reserve
Biosphere Reserve (BR) is an international designation by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) for regions of natural and cultural landscapes extending over large areas of terrestrial or coastal/marine ecosystems or a combination of both. These Reserves try to balance economic and social development and maintenance of cultural values associated along with the preservation of nature and are thus special environments for both people and nature and are living examples of how human beings and nature can co-exist while respecting each others’ needs.
An area to be designated as Biosphere Reserve, a site must contain a protected and minimally disturbed core area of value of nature conservation. Core area must be a bio-geographical unit and should be large enough to sustain a viable population representing all trophic levels. It must involve all the stakeholders including participation of local communities and use of their knowledge in biodiversity preservation.
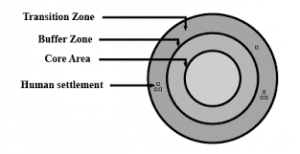
Structure of Biosphere Reserve
Core Areas: It is the maximum protected area of a biosphere reserve. It may contain endemic plants and animals. It conserves the wild relatives of economic species and also represents important genetic reservoirs having exceptional scientific interest. It is a protected region, like a National Park or Sanctuary/protected/regulated mostly under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972. It is kept free from human interference.
Buffer Zone: The core zone is surrounded by Buffer zone and its activities are managed in this area in the ways that help in the protection of the core zone. It includes activities ecological restoration, limited tourism, fishing, grazing, etc; which are permitted to reduce its effect on the core zone. Research and educational activities are to be encouraged.
Transition Zone: It is the outermost zone of the biosphere reserve. It is the zone of the blend of working where human ventures and conservation are done in harmony. It includes settlements, croplands, managed forests and areas for intensive recreation and other economic uses characteristics of the region.
Functions of Biosphere Reserve
Conservation: Managing Biosphere Reserve’s, endemic species, genetic resources, landscapes & ecosystems. It may prevent man-animal conflict along with the wildlife, culture and customs of tribals are also protected.
Development: Promoting economic and human growth that is sustainable on a sociocultural and ecological level. It seeks to strengthen the main three pillars of sustainable development: social, economic and protection of the environment.
Logistic support: Promoting scientific research activities, environmental education, training and monitoring in the context of local, national and international conservation and sustainable development.
Man and Biosphere Programme
It is a programme launched in 1971 under UNESCO. Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB) is an intergovernmental scientific programme that aims to establish a scientific basis for the improvement of cordial relationships between people and their environments.
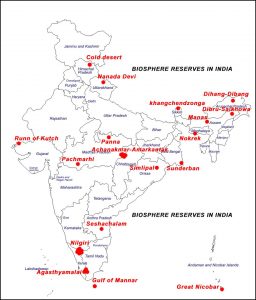
MAB combines natural, social sciences, economics and education to improve human livelihoods and the equitable sharing of benefits, and to safeguard natural and managed ecosystems, thus promoting innovative approaches to economic development that are socially and culturally appropriate, and environmentally sustainable. There are a total of 12 Biosphere reserves in India that find their place in UNESCO’s List of Man & Biosphere Reserves Programme.
By ANSHUM VERMA
Faculty ( Polity , Geography & Environment)
Download plutus IAS 21st SEPTEMBER 2021 Current Affairs
Plutus IAS Current Affair Team Member



No Comments