19 Jul UNAIDS Report
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “UNAIDS Report”. The topic “UNAIDS Report” has relevance in the Public Health section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
About AIDS Disease?
For Mains:
GS 2: Public Health
India’s Initiatives to Curb AIDS Disease?
Key Highlights of the UNAIDS Report?
Why in the news?
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) claimed a life every minute in 2022, according to a new report by UNAIDS.
About AIDS Disease:
- AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) is a chronic and potentially life-threatening health condition caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
- HIV primarily targets CD4, a type of white blood cell (T cells), in the body’s immune system.
- T cells play a crucial role in detecting anomalies and infections in the body.
- Once HIV enters the body, it multiplies and destroys CD4 cells, leading to severe damage to the immune system. Once infected, the virus remains in the body permanently.
- The CD4 count of an HIV-infected person significantly reduces. In a healthy body, the CD4 count is between 500-1600, but in an infected body, it can drop as low as 200.
Transmission:
- HIV spreads through contact with certain body fluids, such as blood and semen, from an infected person.
- Transmission routes include unprotected sex, sharing contaminated needles, and mother-to-child transmission during childbirth or breastfeeding.
Symptoms:
- Initial symptoms of HIV infection include fatigue, fever, and sores.
- Over time, if HIV is not treated, it can progress to AIDS, leading to severe symptoms like pneumonia and certain cancers.
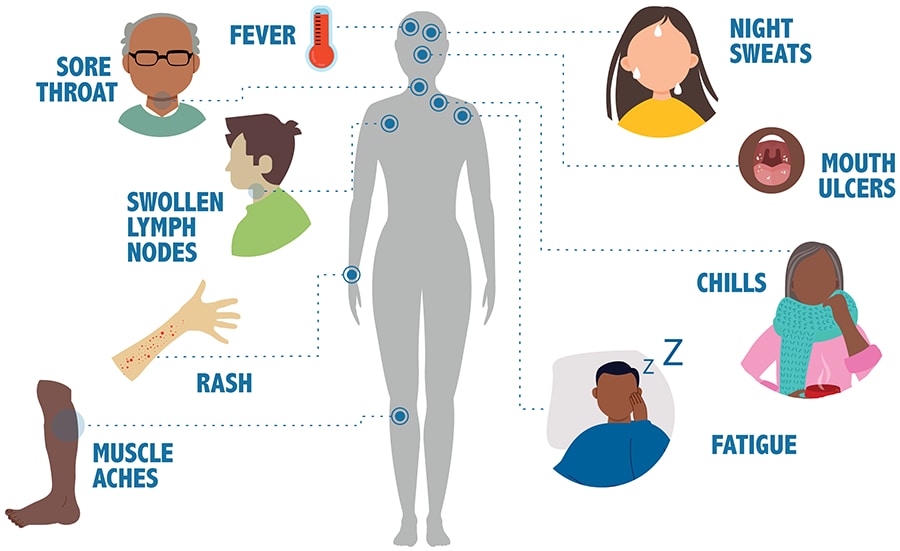
Prevention:
- Precautions can be taken to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing the disease effectively.
- Pre-marital testing, including an HIV test, can ensure overall safety.
- Protective techniques should be used to prevent transmission of HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases.
India’s Initiatives to Curb AIDS Disease:
- HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act, 2017:
- The Act mandates both central and state governments to take measures to prevent the spread of HIV or AIDS.
Access to ART:
- India has made Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) affordable and accessible to over 90% of people living with HIV in the world.
Memorandum of Understanding (MoU):
- In 2019, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare signed a MoU with the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment to enhance HIV/AIDS outreach.
- The MoU aims to reduce the incidence of social stigma and discrimination against victims of drug abuse, children, and people living with HIV/AIDS.
Project Sunrise:
- Launched in 2016 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Project Sunrise aims to tackle the rising HIV prevalence in north-eastern states of India, particularly among people injecting drugs.
Key Highlights of the UNAIDS Report:
AIDS-Related Deaths and Access to Treatment:
- AIDS claimed a life every minute in 2022.
- Approximately 9.2 million people living with HIV worldwide lacked access to treatment in 2022.
- Out of the 2.1 million people receiving treatment, many were not virally suppressed.
Treatment Progress and Global Targets:
- 29.8 million out of 39 million people living with HIV globally are receiving life-saving treatment.
- Between 2020 and 2022, 1.6 million additional people received HIV treatment each year.
- The global target of 35 million people receiving HIV treatment by 2025 is within reach if the progress is sustained.
Slow Treatment Progress in Certain Regions:
- Eastern Europe, Central Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa exhibited slower treatment progress.
- Only around half of the over two million people living with HIV in these regions received antiretroviral therapy in 2022.
Gender Discrimination and Treatment Rates:
- Men living with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa, the Caribbean, Eastern Europe, and Central Asia are less likely to receive treatment compared to women.
- Gender discrimination needs to be addressed to ensure equal access to treatment.
Impact on Children:
- AIDS-related deaths among children reduced by 64% from 2010 to 2022.
- However, approximately 84,000 children lost their lives to HIV in 2022.
- Around 43% of the 1.5 million children living with HIV did not receive treatment in 2022.
Challenges in HIV Prevention:
- Women and girls accounted for 63% of all new HIV infections in sub-Saharan Africa.
- Only about 42% of districts with high HIV incidence in the region have dedicated prevention programs.
- Enhanced prevention efforts are needed to address this gap.
Funding Gaps:
- HIV incidence has declined in regions with increased prevention funding.
- Eastern Europe, Central Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa face challenges in their HIV epidemics due to a lack of funding.
- In 2022, only USD 20.8 billion was available for HIV programs in low- and middle-income countries, falling short of the USD 29.3 billion required by 2025.
Fluctuating Funding Levels:
- In the early 2010s, funding substantially increased, but it has since fallen back to 2013 levels.
- In 2022, there was a 2.6% drop in funding compared to the previous year, with only USD 20.8 billion available for HIV programs in low- and middle-income countries.
- The funding gap remains significant, as the required amount by 2025 is USD 29.3 billion.
Q.1 Which ministry in India launched Project Sunrise to address the rising HIV prevalence?
(A) Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
(B) Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
(C) Ministry of Home Affairs
(D) Ministry of Women and Child Development
ANSWER: A
Q.2 Which of the following statements is/are true according to the UNAIDS Report?
- The global target of 35 million people receiving HIV treatment by 2025 is achievable based on current progress.
- Eastern Europe, Central Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa exhibited significant progress in HIV treatment rates in 2022.
- AIDS-related deaths among children reduced by 64% from 2010 to 2022.
- The HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act, 2017, mandates state governments to take measures to prevent the spread of HIV.
- India has made Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) accessible to over 90% of people living with HIV in the world.
Select the correct option(s):
(A) 1, 2, and 3
(B) 3, 4, and 5
(C) 1 and 5
(D) 2 and 4
ANSWER: C
Q.3 Discuss the prevalence of HIV/AIDS in India and the measures taken by the Indian government to combat the disease. How effective have these initiatives been in reducing the impact of HIV/AIDS on public health and society? Identify the challenges faced by India in its fight against HIV/AIDS and suggest potential strategies to overcome them.



No Comments