27 Jul Ethanol Blending
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “Ethanol Blending”. The topic “Ethanol Blending” has relevance in the Energy Security section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
About Ethanol?
Applications of Ethanol as Fuel?
For Mains:
GS 3: Energy Security
Benefits of blending ethanol in fuel?
Feedstock Diversification in India?
Government Initiatives to Promote Ethanol Blending in India?
Why in the news?
The Prime Minister announced that India has commenced the rollout of 20% ethanol-blended petrol this year and the country’s aim is to cover the entire nation by 2025.
About Ethanol:
- Ethanol, also referred to as ethyl alcohol, is a renewable biofuel derived from diverse sources such as sugarcane, corn, rice, wheat, and biomass.
- It is 99.9% pure alcohol and can be blended with petrol to create a cleaner fuel alternative.
- Byproducts of ethanol production include Distillers’ Dried Grain with Solubles (DDGS), used as animal feed, and Potash from Incineration Boiler Ash, used as fertilizer.
Applications of Ethanol as Fuel:
- Ethanol is used as a renewable biofuel alternative to gasoline in the transportation sector.
- It can be blended with petrol in various proportions, such as E10 and E20, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants.
- India has implemented the Ethanol Blending Programme to promote the use of ethanol and reduce dependence on imported crude oil.
Benefits of blending ethanol in fuel?
- Renewable Energy Source: Ethanol is produced from renewable plant-based sources, such as sugarcane and corn, making it a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Ethanol has a lower carbon footprint compared to conventional gasoline. When blended with petrol, it helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating the impact of climate change.
- Improved Air Quality: Ethanol-blended fuels produce fewer harmful pollutants, such as carbon monoxide and volatile organic compounds, which contribute to air pollution and smog.
- Energy Security: Ethanol production reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing a country’s energy security and reducing exposure to volatile global oil prices.
- Economic Benefits: Ethanol production supports rural economies by creating jobs in agriculture and biofuel industries. It also helps diversify income streams for farmers.
- Engine Performance and Octane Rating: Ethanol has a high octane rating, which improves engine performance and efficiency. It can help reduce engine knocking and prolong the life of engines.
- Cleaner Fuel: Ethanol-blended fuels burn more cleanly, leading to less engine deposits and maintenance requirements, contributing to cleaner engines and reduced maintenance costs.
- Encouraging Agriculture: Ethanol production promotes the growth of crops used for feedstock, stimulating agricultural activities and providing additional income for farmers.
- Utilization of Byproducts: Ethanol production generates valuable byproducts like Distillers’ Dried Grain with Solubles (DDGS), which is used as animal feed, and potash, which serves as a fertilizer.
- Energy Independence: By utilizing domestic feedstocks for ethanol production, countries can reduce their reliance on foreign oil and achieve greater energy independence.
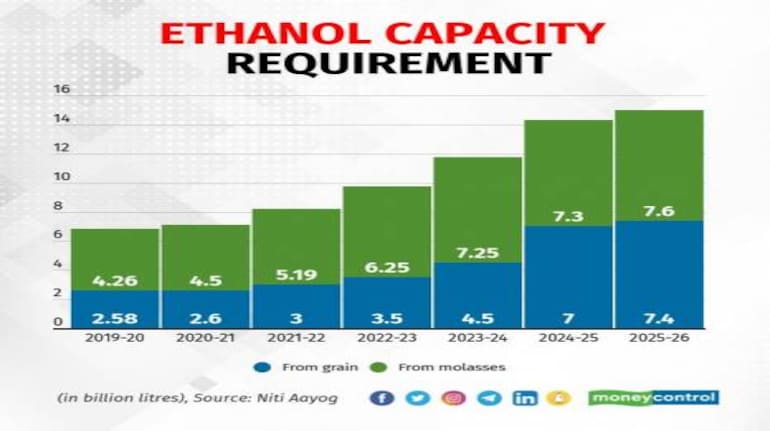
Feedstock Diversification in India:
- India diversified its ethanol feedstocks by including rice, damaged grains, maize, jowar, bajra, and millets.
- The government’s differential pricing policy incentivized the use of alternative feedstocks by fixing higher prices for ethanol produced from certain sources.
- Sugar mills installed distilleries that can operate on multiple feedstocks throughout the year.
Challenges in Feedstock Diversification:
- Processing grains for ethanol production is time-consuming compared to molasses.
- Quality variability of feedstocks can affect production.
- Environmental concerns may arise with the use of non-traditional feedstocks.
Benefits of Feedstock Diversification:
- Diversification of feedstocks minimizes supply fluctuations and price volatility.
- New demand for grains is created with the incorporation of new feedstocks.
Government Initiatives to Promote Ethanol Blending in India:
- National Policy on Biofuels 2018: Provides a framework for the promotion of biofuels, including ethanol, to enhance energy security and sustainability.
- E100 Pilot Project: A pilot project to test the use of 100% ethanol as a fuel in selected regions.
- Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN Yojana 2019: A scheme aimed at boosting the availability of ethanol and biofuels from various feedstocks.
- Repurpose Used Cooking Oil (RUCO): An initiative to collect used cooking oil to convert it into biodiesel and promote its blending with diesel.
SOURCE:https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/the-ethanol-impetus-8856449/
Q.1 According to India’s National Policy on Biofuels, which of the following can be used as raw materials for the production of biofuels?
- Cassava
- Damaged wheat grains
- Groundnut seeds
- Horse gram
- Rotten potatoes
- Sugar beet
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 5 and 6 only
(b) 1, 3, 4 and 6 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Answer: (a)
Q.2 Which of the following are benefits of using ethanol blending in fuel?
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
- Lower engine performance and efficiency
- Promotion of rural economies through job creation
Select the correct option(s) from the choices given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (d)
Q.3 Discuss the challenges faced in promoting ethanol blending in fuel and suggest strategies to overcome these obstacles. Evaluate the potential impact of increased ethanol blending on energy security, environment, and rural economies in India.



No Comments