18 Nov Voice of Global South Summit (VoGS)
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “ Voice of Global South Summit (VoGS)”. This topic has relevance in the International Relations section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
About Voice of Global South Summit (VoGS)?
About the Global South?
For Mains:
GS 2: International Relations
Significance of Global South?
Challenges for Consolidation?
Way Forward?
Why in the news?
The follow-up edition of the Voice of the Global South Summit, hosted by India was held recently. It expands upon the inaugural summit conducted in January, which convened delegates from 125 nations in the Global South.
About Voice of Global South Summit (VoGS)
The Voice of Global South (VoGS) Summit, an Indian initiative, serves as a unified platform for countries in Asia, Africa, and South America to articulate their viewpoints and priorities on pressing global issues. It seeks to find collaborative solutions to challenges faced by developing nations through constructive dialogue.
Foundation and Objectives:
The genesis of this initiative lies in recent global events, including the COVID-19 pandemic, escalating debt, the Ukraine conflict, and issues related to food and energy security. These challenges often do not receive adequate attention on existing global platforms. The summit is inspired by India’s Prime Minister vision of inclusive development, encapsulated in the philosophy of ‘Sabka Saath Sabka Vikas Sabka Vishwas aur Sabka Prayas.’
Global South:
The term ‘Global South’ refers to countries in Asia, Africa, and South America, distinguishing them based on economic development and historical factors. India, along with major nations like Brazil, China, Indonesia, and Mexico, aims to represent the underrepresented Global South in international forums.
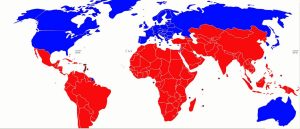
Features of Global South:
- Primarily lower-income countries, often with colonial histories.
- Not strictly confined to the Southern Hemisphere, with some nations located in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Employed as a neutral substitute for the term “Third World.”
- Recognizes shared history and challenges the dominance of the Global North in international affairs.
Indian Context:
- India advocates for the reform of multilateral institutions such as the UNSC, UN, and IMF.
- Aims to unite Global South nations for collective representation and collaboration.
- Seeks cooperation with other Global South countries while challenging global capitalist structures.
Significance of Global South:
- Aims to address shared concerns like energy security and sustainable development.
- Creates potential for technical and idea exchanges among Global South nations.
- Provides a platform for highlighting concerns often overlooked on the global stage.
Challenges for Consolidation:
- Ongoing debates over climate reparations and the exclusion of India and China.
- Ramifications of the Russia-Ukraine Conflict on the Least Developed Nations.
- The Growing Ascendancy of China in the Global South through Programs Such as the Belt and Road Initiative.
Way Forward:
- India should actively engage in regional politics within the Global South.
- Recognition of differentiation within the Global South in terms of wealth, needs, and capabilities.
Below is a table differentiating the First, Second, and Third World classifications:
| Criteria | First World | Second World | Third World |
| Economic Development | Developed and Industrialized Nations | Industrializing or Socialist Nations | Developing and Less-Developed Nations |
| Geopolitical Influence | High | Moderate to High | Low |
| Historical Context | Capitalist Democracies (during Cold War) | Socialist Bloc (during Cold War) | Non-Aligned or Unaligned Nations (Cold War) |
| Examples | USA, Canada, Western European Countries | Former USSR, China, Eastern Europe | India, Brazil, African and Asian Countries |
| Development Indicators | High GDP, HDI, Industrialization, Advanced Technology | Moderate GDP, Industrialization Progress | Lower GDP, Limited Industrialization |
It’s essential to note that the terms “First,” “Second,” and “Third World” have evolved and are now considered outdated. The classifications were originally based on Cold War-era geopolitical alliances and economic structures, and they don’t accurately represent the current global geopolitical landscape. The preferred terminology today is “Developed,” “Developing,” and “Least Developed” nations or Global South and North nations.
Q.1 Regarding the “Global South” recently seen in the news, consider the following statements:
- Primarily lower-income countries, often with colonial histories.
- These countries are strictly confined to the Southern Hemisphere.
- ‘Global South’ is Used as an alternative to “Third World.”
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
ANSWER: B
Q.2 Regarding the “Voice of Global South Summit (VoGS)” recently seen in the news, consider the following statements:
- It is a joint initiative of India, China and Brazil.
- This initiative is primarily aimed at reforming the IMF.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER: D
Q.3 Analyze the challenges faced by developing countries in the current global scenario and assess how platforms like Voice of Global South Summit VoGS can contribute to addressing these challenges.



No Comments