10 Oct PRELIMS BITs: Elimination of Trachoma and Micro RNA.
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
General studies: Economic and Social Development-Sustainable Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector Initiatives.
FOR PRELIMS:
What is Trachoma, its nature, etc.?
WHY IN THE NEWS?
The World Health Organization has recognized India for successfully eliminating trachoma as a public health issue. India joins Nepal and Myanmar in the WHO South-East Asia Region, and 19 other countries globally have previously achieved this feat.
Key Facts about Trachoma
Cause: Trachoma is an eye disease caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
Transmission: The infection spreads through contaminated fingers, objects, and flies that contact with discharge from infected individuals’ eyes or noses.
Risk Factors: Environmental factors contributing to trachoma include poor hygiene, overcrowded living conditions, and limited access to water and sanitation facilities.
Complications: Repeated infections can lead to scarring of the eyelids, causing trachomatous trichiasis, where eyelashes turn inward and touch the eyeball. This painful condition can lead to visual impairment and blindness if untreated.
Elimination Strategy: The WHO recommends the SAFE strategy (Surgery, Antibiotics, Facial cleanliness, and Environmental improvement) to eliminate trachoma as a public health problem.
Global Progress: India is one of 20 WHO-validated countries for eliminating trachoma, joining nations such as Benin, Cambodia, China, and others.
Neglected Tropical Diseases Road Map: The 2021–2030 road map aims to prevent, control, eliminate, and eradicate 21 diseases, including trachoma, by 2030.
micro-RNA: The Regulator of Cellular Function
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
General studies: General Science and Recent development in the field of biotechnology.
FOR PRELIMS:
What is RNA its type and what role? What is Mirco RNA?
Why in the news?
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to US scientists Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for their work on the discovery of microRNA.
Key Facts about Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
Definition: RNA is a molecule found in most living organisms and viruses, crucial for various biological functions.
Structure: Composed of nucleotides made of ribose sugars, phosphate groups, and nitrogenous bases.
Typically single-stranded, though some RNA viruses are double-stranded.
Function: Serves primarily as a messenger, transmitting instructions from DNA for protein synthesis.
Regulates gene expression, catalyzes biological reactions, and responds to cellular signals.
Types of RNA:
Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Forms the core of ribosome structure and function.
Transfer RNA (tRNA): Delivers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis.
Relationship to DNA: Structurally similar, with RNA’s backbone made of ribose and DNA’s backbone made of deoxyribose. Both share adenine (A), guanine (G), and cytosine (C), but RNA contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
Therapeutic Potential: Certain RNA molecules may have applications in treating human diseases.
RNA interference (RNAi) screening can analyze entire genomes and pathways on an industrial scale.
Key Facts about micro-RNA (miRNA)
Definition: miRNAs are a class of non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression.
Biogenesis: Transcribed from DNA into primary miRNAs.
Processed into precursor miRNAs and then matured into functional miRNAs.
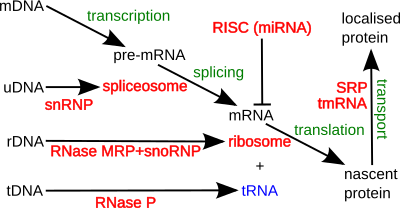
Extracellular Functions: miRNAs can be secreted into extracellular fluids and transported to target cells via vesicles (e.g., exosomes) or by binding to proteins like Argonautes. Function as chemical messengers, facilitating cell-cell communication
Significance of micro-RNA (miRNA) in Human and Animal Diseases
1. Inherited Diseases
Hearing Loss: A mutation in the seed region of miR-96 is linked to hereditary progressive hearing loss.
Keratoconus and Cataracts: A mutation in the seed region of miR-184 is associated with hereditary keratoconus and anterior polar cataracts.
Skeletal Defects: Deletion of the miR-17~92 cluster results in skeletal and growth abnormalities.
2. Cancer
Cell Proliferation Control: Many miRNAs directly target and inhibit cell cycle genes, regulating cell proliferation.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: The first human disease connected to miRNA deregulation; several other miRNAs, termed “oncomirs,” are also linked to cancer.
Role in B Cells: In malignant B cells, miRNAs are involved in critical pathways such as B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling, migration, adhesion, and immunoglobulin production and class-switching. They influence various stages of B cell development, including pre-B, marginal zone, follicular, B1, plasma, and memory B cells.
3. Heart Disease
Developmental Role: Conditional inhibition of miRNA maturation in the murine heart indicates that miRNAs are essential for heart development and function.
4. Nervous System
Neuronal Development: miRNAs play a crucial role in the healthy development and function of the nervous system, regulating neuronal differentiation and maturation at various stages.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 10 Oct 2024
PRELIMS QUESTION?
Q.1, With reference to the trachoma disease, Consider the following statement:
1. Trachoma is a viral disease affecting the lungs and kidneys.
2. India is the first country in South Asia which declared Trachoma free by WHO.
3. Poor hygiene is one of the factors in the spread of trachoma in many parts of the world.
How many of the above-given statements are correct?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. All three
D. None
Q.2. Consider the following diseases:
1. Cancer
2. Hearing Loss
3. Cardiac arrest
4. Skeletal Defects
How many of the above-mentioned diseases are associated with the functioning of the Micro RNA?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. Only three
D. All four
ANSWER:
1. A
2. D



No Comments