17 Oct PRELIMS BITs: Countries in the news
This article covers “ prelims related topic Countries in the news
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
GS: CA: Current events of national and international importance
FOR PRELIMS:
Countries: Algeria, Malawi, Mauritania, their geographical and political features.
WHY IN THE NEWS:
President Droupadi Murmu embarks on a 3-nation visit to Algeria, Mauritania, and Malawi.

ALGERIA:
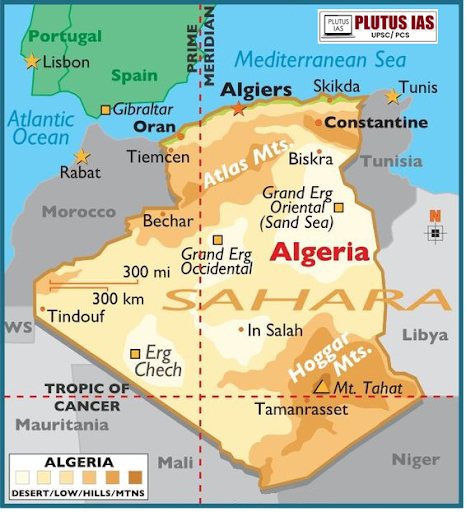
Geography
Location: North Africa, bordered by Tunisia, Libya, Niger, Mali, Mauritania, Western Sahara, Morocco, and the Mediterranean Sea.
Area: 2,381,741 square kilometers (919,595 sq mi) — the largest country in Africa and the tenth-largest in the world.
Topography: Dominated by the Sahara Desert, with the Tell Atlas and Saharan Atlas in the north and various mountain ranges, including the Hoggar Mountains.
Climate: Semi-arid, with a more fertile climate in the northern regions.
History
Colonial Era: Invaded by France in 1830; gained independence in 1962 after a brutal war.
Civil War: Experienced a civil war from 1992 to 2002.
Government and Politics
Political System: Semi-presidential republic consisting of 58 provinces (wilayas) and 1,541 communes.
Regional Influence: A regional power in North Africa and a member of multiple international organizations including the African Union and OPEC.
Economy
Economic Profile: One of Africa’s largest economies, heavily reliant on petroleum and natural gas reserves.
Major Company: Sonatrach, the national oil company, is the largest company in Africa.
Human Development: Second-highest Human Development Index in continental Africa.
Major Cities
Capital: Algiers.
Other Major Cities: Oran, Constantine, and Annaba.
Malawi:
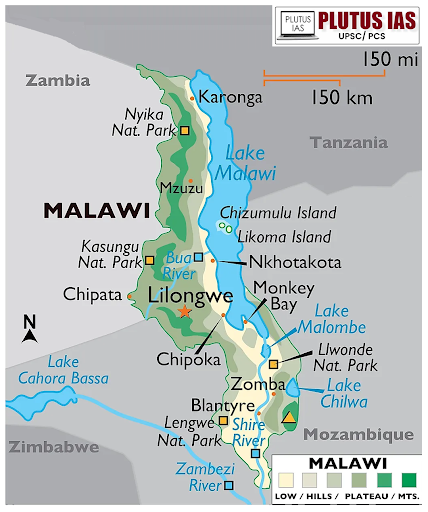
General Information
Official Name: Republic of Malawi
Former Name: Nyasaland
Location: Southeastern Africa, landlocked
Borders: Zambia (west), Tanzania (north/northeast), Mozambique (east/south/southwest)
Capital: Lilongwe
Major Cities: Blantyre, Mzuzu, Zomba
History: Colonial Rule: Became a British protectorate in 1891, renamed Nyasaland in 1907.
Independence: Gained independence in 1964 and renamed Malawi; Hastings Banda became the first Prime Minister.
Dictatorship: Banda established a one-party state, and declared himself President for life in 1971.
Political System
Government Type: Unitary presidential republic.
Current President: Lazarus Chakwera (elected in 2020).
Constitution: Established in 1995, promoting a multiparty system.
Political History: Transitioned to democracy in 1993; the first multiparty elections were held in 1994.
Economy
Economic Structure: Primarily agrarian, with agriculture employing the majority of the population.
Key Exports: Tobacco, tea, and sugar.
Development Needs: Heavily reliant on foreign aid; significant challenges in poverty, education, and healthcare.
Geography
Location: Landlocked country in southeastern Africa.
Borders:
Zambia: Northwest
Tanzania: Northeast
Mozambique: South, southwest, and southeast
Topography:
Great Rift Valley runs north to south through the country.
Lake Malawi: Forms over three-quarters of the eastern boundary, approximately 587 km (365 miles) long and 84 km (52 miles) wide.
Shire River: Flows from Lake Malawi and joins the Zambezi River in Mozambique.
Mountainous areas rise to altitudes of 914 to 2,438 meters (3,000 to 8,000 ft).
Notable peaks: Zomba (2,134 meters) and Mulanje (3,048 meters).
Climate:
Hot in the low-lying areas, and temperate in the northern highlands.
Wet season: November to April, with peak rains in late March.
Dry season: May to September, characterized by mist and little rainfall.
Lake Malawi/Calender lake
Geographical Location:
Situated between Malawi, Mozambique, and Tanzania.
It is the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system.
Size and Volume:
1. Fourth largest freshwater lake in the world by volume.
2. Ninth largest lake in the world by surface area. Contains a major depression in the north-central region, with another depression reaching 528 m (1,732 ft) in the far north.
Biodiversity:
Home to over 700 species of fish, primarily cichlids, making it the lake with the highest fish species diversity in the world.
The lake is crucial for local fisheries and biodiversity.
Water Characteristics:
Classified as a meromictic lake, meaning its water layers do not mix.
Maintains a permanent stratification with oxic-anoxic boundaries.
Hydrology:
The largest inflow: the Ruhuhu River.
Main outflow: Shire River, which feeds into the Zambezi River in Mozambique.
Over 80% of water loss is due to evaporation.
Economic Importance:
The outflows support hydropower, irrigation, and biodiversity downstream.
Vital for local economies dependent on fishing and agriculture.
Mauritania:
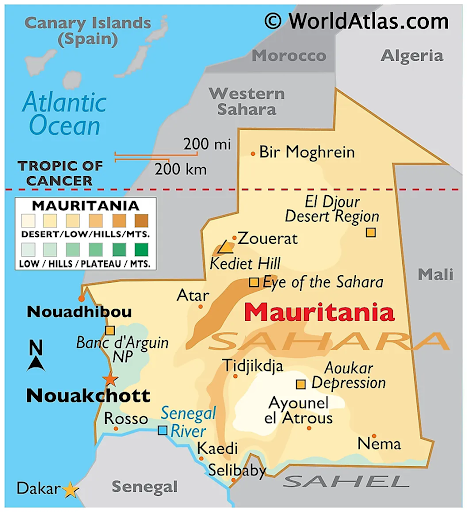
General Information
Official Name: Islamic Republic of Mauritania
Location: Northwest Africa
Borders:
Atlantic Ocean: West
Western Sahara: North and northwest
Algeria: Northeast
Mali: East and southeast
Senegal: Southwest
Capital: Nouakchott (largest city)
History
Ancient Background: The name is derived from the ancient Berber kingdom of Mauretania.
Colonial Era: Colonized by France in the early 20th century as part of French West Africa.
Independence: Achieved in 1960; has experienced recurrent coups and military rule.
Recent Political Transition: In 2019, General Mohamed Ould Ghazouani succeeded General Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz, marking the first peaceful transition of power since independence.
Ethnic Composition:
Bidhan (White Moors): ~30% of the population
Haratin (Black Moors): ~40%
Sub-Saharan ethnic groups: ~30%
Government Structure
Type: Unitary presidential republic.
Parliament:
National Assembly: A single chamber with 176 members elected for five-year terms in single-seat constituencies.
Political Leadership
President: Elected by an absolute majority in a two-round system if necessary.
Prime Minister: Appointed by the President.
Economy
Natural Resources: Abundant resources, including iron ore and petroleum.
Economic Activities: Primarily based on agriculture, livestock, and fishing.
Challenges: Despite resources, Mauritania remains poor and faces human rights issues.
Geography
Terrain: Generally flat, characterized by vast arid plains interspersed with occasional ridges and cliffs.
Desert Regions: Approximately three-quarters of the country consists of desert or semidesert, with desertification increasing since the mid-1960s.
Topography
Scarps: A series of scarps bisect the plains, separating sandstone plateaus.
Adrar Plateau: The highest plateau, reaching about 500 meters (1,600 feet).
Isolated Peaks:
Guelbs: Smaller peaks rich in minerals.
Kedias: Larger peaks, with Kediet ej Jill being the highest at 915 meters (3,000 feet).
Guelb er Richat: A prominent geological feature known as the “Eye of the Sahara,” located in the north-central region.
Vegetation and Ecoregions
Natural Vegetation: Varies with rainfall; includes traces of tropical forest along the Sénégal River, and savanna in the southeast.
Desert: Sandy desert dominates the center and north.
Climate
Rainfall Pattern: Influences the distribution of natural vegetation, with vegetation belts extending from east to west.
Unique Features
El Djouf (Empty Quarter): A vast region of large dunes merging into the Sahara.
Coastal Areas: Along the coast, alternating clayey plains (regs) and shifting dunes (ergs), influenced by high winds, are found.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 17th Oct 2024
PRELIMS QUESTION
Q.Consider the following pairs:
| Country | Features | |
| 1 | Algeria | OPEC member |
| 2 | Mauritania | Part of the Maghreb region |
| 3 | Malawi | Only Landlocked country in Africa |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. All three
D. None
ANSWER: B



No Comments