19 Jul Realism in International Relations
Realism in International Relations – A Key IR Theory for UPSC CSE
Realism is one of the oldest and most dominant theories in International Relations (IR), widely studied by students preparing for UPSC Civil Services Examination. Rooted in classical political philosophy and refined through modern strategic thought, Realism provides a pragmatic framework to understand how states behave in the anarchic global system. It is particularly relevant for GS Paper 2 of the UPSC Mains syllabus under the topic of International Relations.
Core Assumptions of Realism
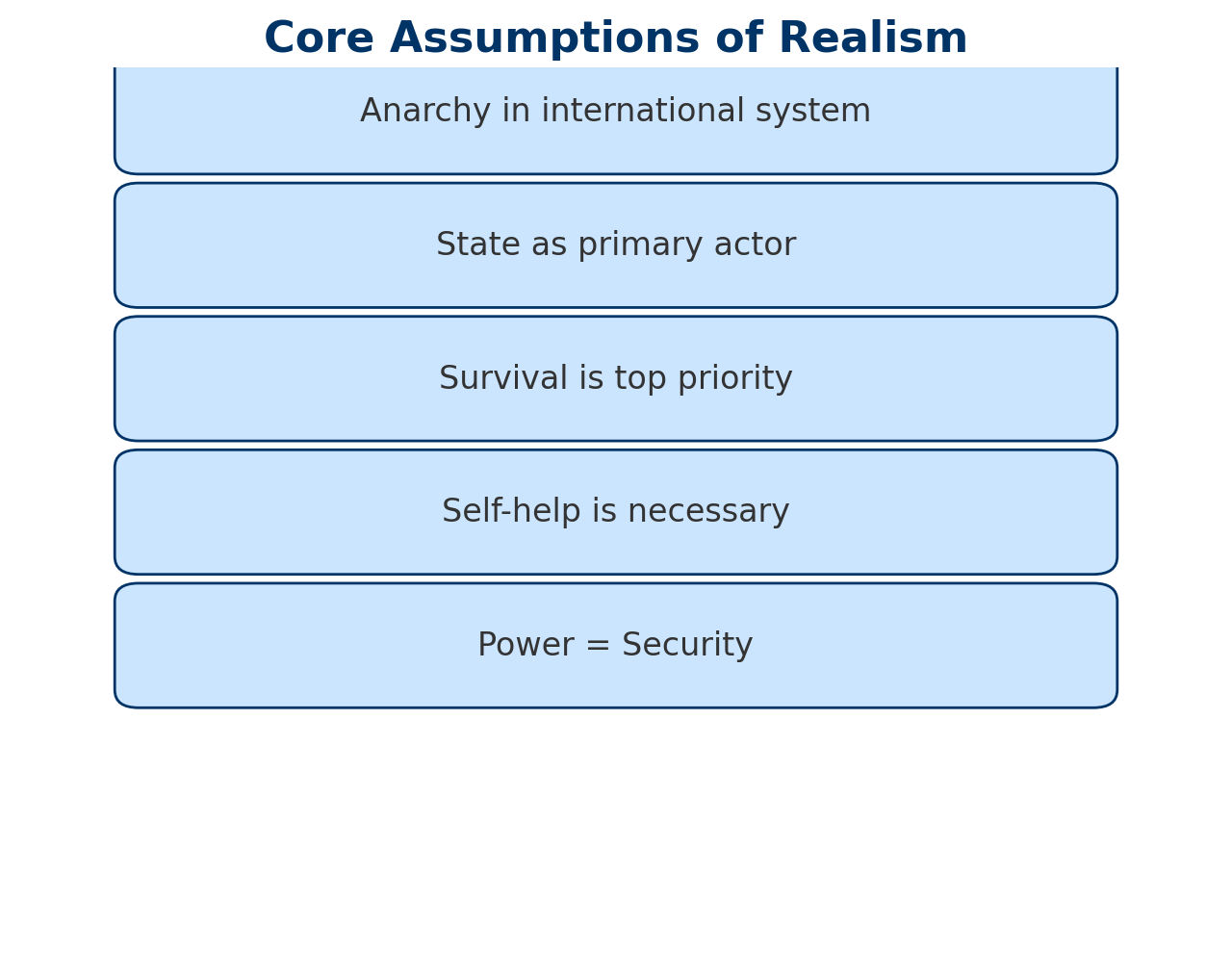
Realism assumes that the international system is anarchic — meaning there is no overarching authority above sovereign states. In such a system, each state acts as a rational, unitary actor primarily concerned with its own survival and national interest.
- State-Centrism: The state is the primary and most important actor in international relations.
- Self-Help: In the absence of a global government, states must rely on their own resources to ensure security.
- Power and Security: States compete for power to secure their existence, often leading to conflict and alliances.
- National Interest: States are motivated by national interest, especially in terms of security and strategic autonomy.
Historical Development
Realism draws from ancient thinkers like Thucydides, who documented the Peloponnesian War, and Machiavelli, who emphasized power and pragmatism in politics. In modern times, Hans Morgenthau laid the foundation of Classical Realism through his work “Politics Among Nations,” asserting that political behavior is governed by objective laws rooted in human nature.
Neorealism (Structural Realism)
Kenneth Waltz, the father of Neorealism, shifted the focus from human nature to the structure of the international system. He argued that the absence of a central authority (anarchy) compels states to compete for power, often resulting in arms races and balance-of-power politics.
Applications of Realism in Indian Foreign Policy
India’s strategic behavior often reflects realist principles. Some key examples include:
- India-Pakistan Relations: Deterrence through nuclear capability and military preparedness.
- India-China Border Management: Realpolitik in handling Galwan and Doklam standoffs.
- QUAD and Indo-Pacific Strategy: Forming coalitions to counterbalance China’s rise.
- Defense Modernization: Strengthening indigenous capabilities under ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ for national security.

Realism in Indian Foreign Policy a Look
Strengths and Criticism
Strengths
- Explains conflict, war, and power politics effectively.
- Focuses on real-world dynamics and strategic interests.
- Useful in analyzing India’s external defense and diplomacy.
Criticism
- Overemphasis on conflict; underplays cooperation and diplomacy.
- Neglects the role of international organizations and global norms.
- Fails to explain growing importance of non-state actors and globalization.
Previous Year UPSC Questions Related to Realism
- 2020: Do you think that India’s foreign policy is increasingly being shaped by realism rather than idealism? Discuss.
- 2018: What do you understand by the term ‘strategic autonomy’? Do you think it is a realist foreign policy approach?
- 2016: ‘India’s foreign policy has witnessed a transformation from non-alignment to multi-alignment’. Analyze in the context of realist thinking.
- 2013: Discuss the evolution of India’s strategic doctrine in the light of contemporary challenges.
Probable Questions on Realism for UPSC Mains
- Examine the key principles of Realism in International Relations. How do they manifest in India’s foreign policy today?
- Critically analyze the relevance of Neorealism in a multipolar world order.
- How does Realism help in understanding conflicts and alliances in South Asia?
- Compare and contrast Realism and Liberalism in the context of India’s foreign policy decisions.
- Is Realism still a valid framework to understand global power dynamics in the 21st century? Discuss with examples.
Why UPSC Aspirants Should Study Realism
Understanding Realism is essential for UPSC Mains GS Paper 2 and essay writing. It helps aspirants critically evaluate India’s foreign policy decisions and strategic partnerships. When integrated into answers, realism adds analytical depth, particularly in bilateral relations, security issues, and diplomacy-based questions.
Conclusion
Realism offers a powerful lens to examine the complexities of international relations. Though often challenged by liberal and constructivist perspectives, it remains foundational in understanding global power structures and India’s foreign policy in an increasingly multipolar world.
Keywords: Realism in IR, IR theories for UPSC, Realism UPSC notes, International Relations UPSC GS2




No Comments