19 Jul Soft Power in International Relations
Soft Power in International Relations – UPSC CSE GS Paper 2
Soft Power is a vital component of International Relations (IR) and a key part of the UPSC CSE GS Paper 2 syllabus. Coined by political scientist Joseph Nye, the term refers to a country’s ability to shape the preferences of others through appeal and attraction rather than coercion (hard power).
What is Soft Power?
Soft power is the capacity of a state to influence the actions and behavior of other nations through intangible assets like culture, political values, foreign policy, and moral leadership. Unlike hard power, which uses force or payments, soft power works by building long-term credibility, legitimacy, and influence.
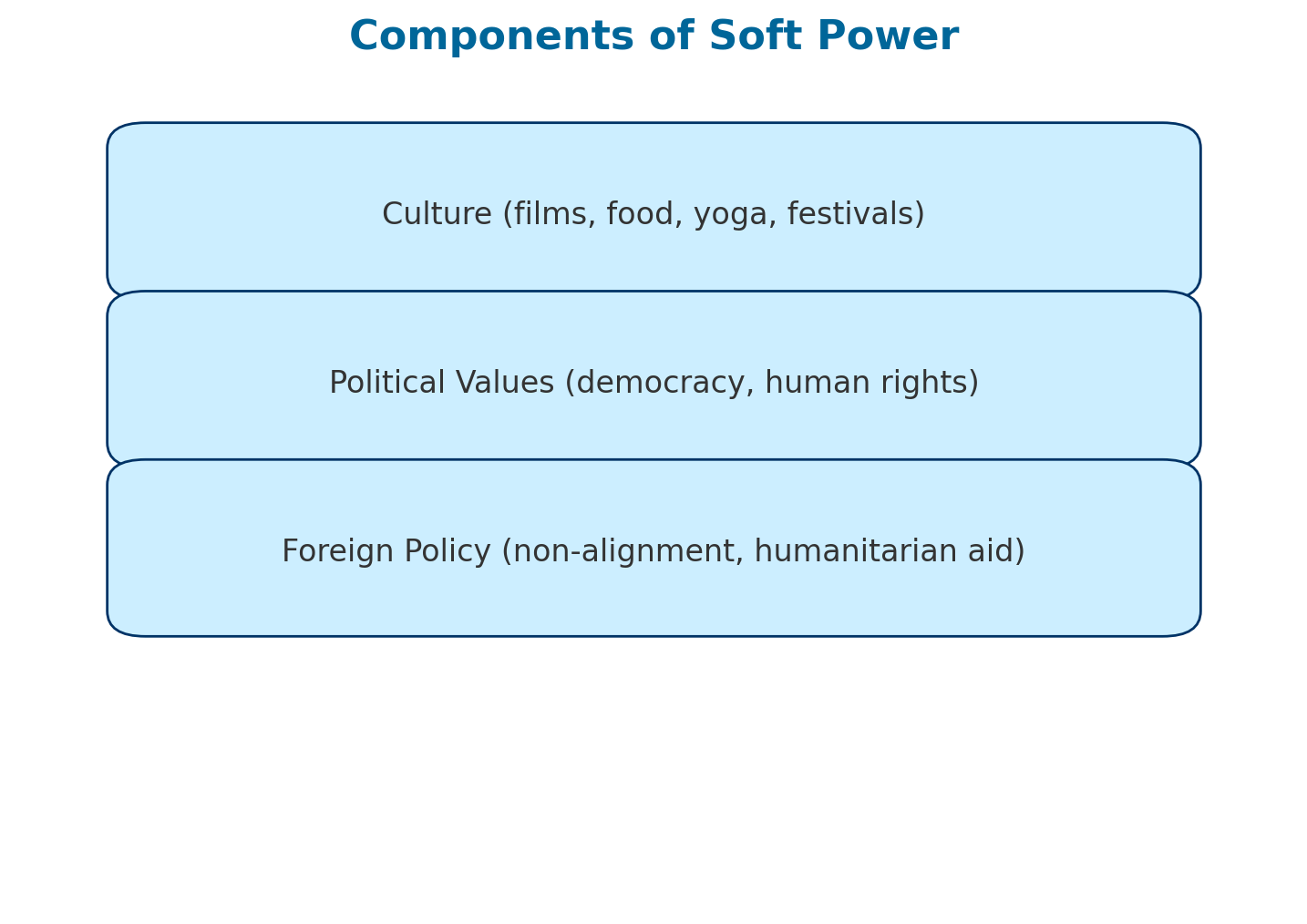
Key Components of Soft Power:
- Culture: Cuisine, films, literature, music, and traditions.
- Political Values: Democracy, civil liberties, and inclusive governance.
- Foreign Policy: Non-alignment, peace diplomacy, humanitarianism.
Soft Power vs Hard Power vs Smart Power
| Type of Power | Nature | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Soft Power | Influence through attraction | Yoga, Bollywood, democratic ideals |
| Hard Power | Influence through coercion | Military force, sanctions |
| Smart Power | Combination of soft and hard power | India’s cultural diplomacy + defense strategy |
India’s Soft Power: A Strategic Asset
India has a deep reservoir of soft power rooted in its ancient civilization, democratic values, and global humanitarian outlook. It is increasingly using soft power to enhance its global influence, particularly among the Global South.
Major Tools of Indian Soft Power:
- Yoga Diplomacy: International Day of Yoga celebrated globally every year on June 21.
- Bollywood: Popular in Africa, Middle East, Central Asia, and Latin America.
- Indian Diaspora: Over 30 million Indians abroad act as cultural ambassadors.
- AYUSH: Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy promoted worldwide.
- Education & Scholarships: India offers ITEC and ICCR scholarships to developing nations.
- Spiritual Heritage: Buddhism, Sufism, and Vedanta enhance India’s philosophical appeal.
Soft Power in India’s Foreign Policy
India’s foreign policy uses soft power to create goodwill and influence without triggering strategic insecurity.
- Non-Alignment 2.0: India’s strategic autonomy model emphasizes moral high ground.
- South-South Cooperation: Humanitarian aid, vaccines (Vaccine Maitri), and disaster relief missions.
- Digital India Diplomacy: Support for digital governance tools to other nations (e.g., Aadhaar-like models).
Global Examples of Soft Power
- USA: Hollywood, tech innovation, Ivy League universities.
- South Korea: K-pop, Hallyu Wave, Samsung.
- Japan: Anime, pacifist diplomacy, traditional cuisine.
- China: Confucius Institutes, Belt and Road narrative.
Challenges to India’s Soft Power
- Contradictions between domestic policies and global image (e.g., press freedom, religious harmony).
- Lack of institutional infrastructure for promoting soft power systematically.
- Inadequate cultural diplomacy training among Indian diplomats.
- Language barriers and low global penetration of Indian content (compared to English or Spanish content).
Soft Power and UPSC CSE
Soft Power is a high-yield topic in UPSC GS Paper 2 and Essay Paper. Understanding this concept is essential to answer IR and foreign policy-based questions with conceptual clarity.
Relevant UPSC Mains PYQs:
- 2021: “India’s soft power is as important as its hard power in diplomacy.” Elaborate.
- 2019: Discuss India’s cultural and diaspora diplomacy as part of its foreign policy strategy.
- 2015: What do you understand by Smart Power? How has India combined both hard and soft power in its foreign engagements?
Possible UPSC Questions:
- How can India leverage its soft power to improve global standing in a multipolar world?
- Critically assess the limitations of soft power in India’s foreign policy execution.
- Discuss how India’s diaspora contributes to its soft power diplomacy.
Conclusion
In the 21st century, **Soft Power** has become as relevant as military or economic strength. India, with its rich culture and value-driven diplomacy, is uniquely positioned to use soft power for geopolitical advantage. However, to maximize its potential, India needs a coherent cultural diplomacy strategy aligned with its foreign policy goals.
For UPSC aspirants, understanding the nuances of soft power adds depth to IR answers and reflects a balanced understanding of India’s global vision.
Keywords: Soft Power, Joseph Nye, India’s Foreign Policy, Cultural Diplomacy, GS Paper 2, IR syllabus for UPSC CSE




No Comments