23 Jul Continental drift
Continental Drift Theory – UPSC Geography Optional Notes
Introduction
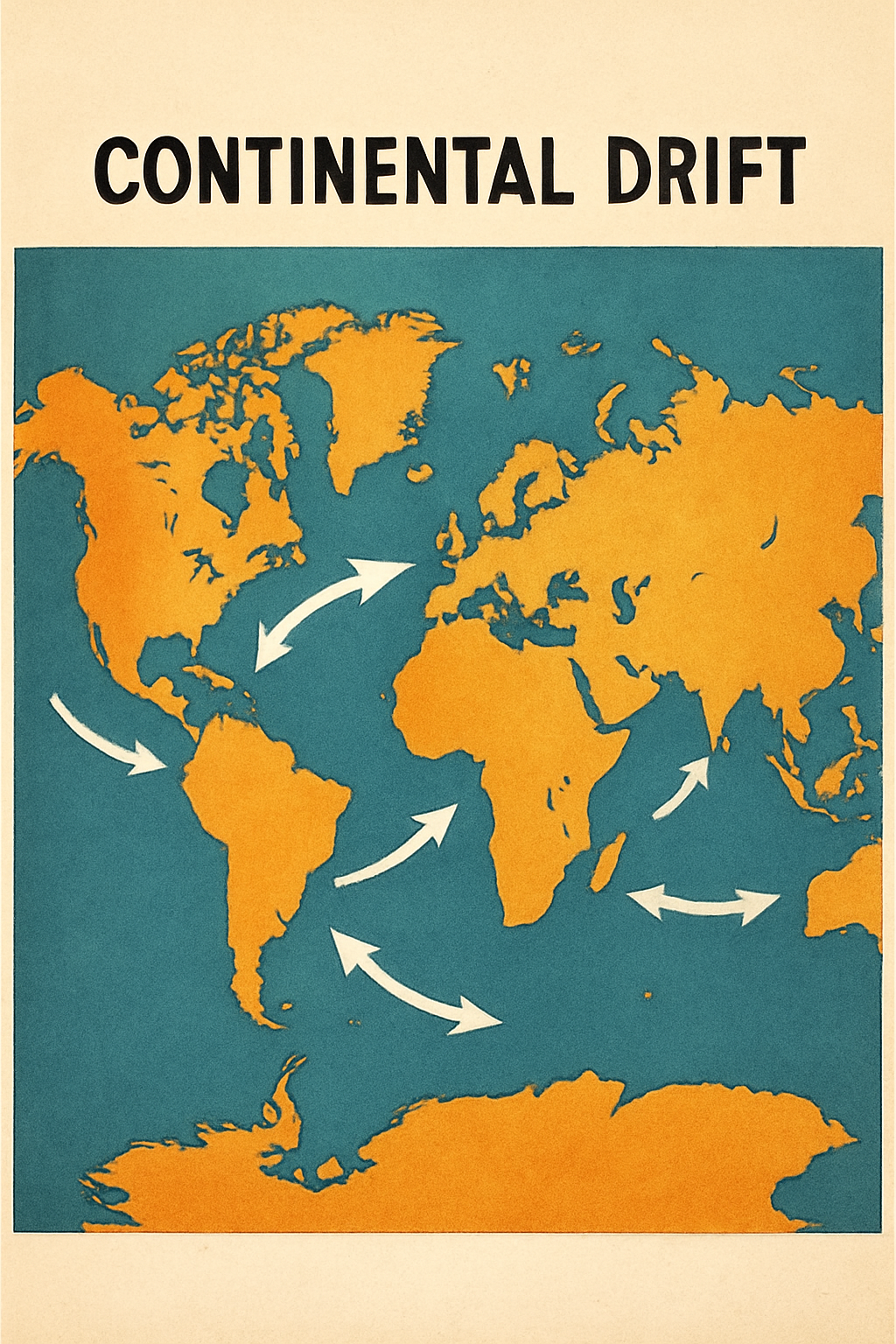
The Continental Drift Theory, proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912, remains a cornerstone in the understanding of Earth’s geological evolution. Although later modified and expanded by Plate Tectonic Theory, Wegener’s idea revolutionized Earth science by suggesting that continents have not always been stationary, but rather drifted across the globe over geological time. This topic holds immense importance for UPSC aspirants taking Geography as their optional subject.
1. Background
- Proponent: Alfred Wegener (German meteorologist and geophysicist)
- Published work: “The Origin of Continents and Oceans” (1915)
- Suggested that all present continents were once part of a single supercontinent named Pangaea.
continental drift Mind Map
2. Key Concepts of Continental Drift
- All continents were once part of a single landmass: Pangaea.
- Pangaea split into two major landmasses: Laurasia (north) and Gondwana (south).
- Over millions of years, these landmasses drifted to their current positions.
- The drift is caused by unknown forces (Wegener couldn’t explain them fully).
3. Evidences Supporting Continental Drift
i. Jigsaw Fit of Continents
The coastlines of Africa and South America fit together like puzzle pieces, indicating they were once joined.
ii. Fossil Evidence
- Mesosaurus: A freshwater reptile found in both South America and Africa.
- Glossopteris: A plant found in continents of the southern hemisphere.
iii. Geological Similarities
- Similar rock formations and mountain ranges in South America and Africa.
- Coal deposits found in now-cold regions like Antarctica indicate a once-tropical climate.
iv. Paleoclimatic Evidence
Glacial deposits found in tropical regions and evidence of tropical flora in now-cold regions support the drift theory.
v. Matching Tectonic Features
Mountain ranges and geological structures on different continents align when the continents are brought together.
Best UPSC coaching for IFOS exam
Best agriculture optional coaching
4. Supercontinent Pangaea
Pangaea began to break apart during the Mesozoic era (~200 million years ago). It split into:
- Laurasia: North America, Europe, and Asia (north).
- Gondwana: South America, Africa, India, Australia, Antarctica.
The Tethys Sea existed between the two blocks.
5. Limitations of Wegener’s Theory
- Lacked a mechanism for the drift – proposed centrifugal force and tidal pull which were rejected.
- Did not consider ocean floor features (like mid-ocean ridges).
- Rejected by many geologists until the 1960s.
6. Legacy and Modern Interpretations
Continental Drift laid the foundation for the development of Plate Tectonic Theory in the 1960s. Plate tectonics offered a comprehensive explanation through the concepts of lithospheric plates, mantle convection currents, and seafloor spreading.
7. Importance in Geography
- Understanding origin of continents and ocean basins
- Helps in reconstructing paleogeography
- Foundation for Plate Tectonics
- Impacts climate, ocean currents, and evolution
8. Previous Year Questions (UPSC Geography Optional)
- 2019: Discuss the evidences supporting Wegener’s theory of Continental Drift.
- 2016: How does Plate Tectonic Theory improve upon Continental Drift Theory?
- 2012: Explain the relevance of Continental Drift Theory in the light of present-day plate tectonics.
9. Probable Questions for Prelims & Mains
- Critically evaluate Alfred Wegener’s Continental Drift Theory.
- List and explain the evidences supporting Continental Drift.
- Differentiate between Continental Drift and Plate Tectonic Theory.
- Explain the concept of Pangaea and its breakup.
Conclusion
Alfred Wegener’s Continental Drift Theory, despite its early criticism, revolutionized Earth sciences and paved the way for Plate Tectonic Theory. It provided an early model to understand the dynamic nature of Earth’s surface, supported by fossil, geological, and paleoclimatic evidence. Understanding this theory is essential for any UPSC Geography Optional student to grasp the evolution of modern geology.




No Comments