10 Feb Daily Current Affairs 10 February 2021
India must return to traditional diplomacy
Context:
Rihana’s and other celebrities’ tweets and after a backlash in Indian society.
Earlier India’s policy was to absorb or provide a cushion and to promote India’s interest.
What Now:
India is pursuing the pushback strategy which needs recalibration as India started a campaign against foreign celebrities or other’s who are doing a campaign to malign India’s image.
Why India needs to reconsider:
- It is not the foreign celebrities but the liberal media or the world who poses more challenges in the upcoming time.
- Wolf warrior-like strategy may not work for India as it worked for china.
Swarn Rajput
Fine-tuning the State-of-the-app technology
Why State apps are necessary:
- Recently many mobile apps have been launched by the central government and state government. This gave a light on duplicating the efforts and wastage of resources.
- Collection, ownership of data, protection of privacy.
Issues:
Data privacy, state and central coordination, centralised approach
How to solve:
- Adoption of an API-based microservices architecture and federated database structure.
- An appropriate governance framework.
- Countries in Europe such as U.KGermany have considered transcending from an centralised information flow to a decentralised information flow for contact-tracing applications.
- scrutiny to technology platforms developed by the States brings the opportunity of improved public services overall and more spillover effects.
Swarn Rajput
Trans fat
What is Trans Fat:
Trans-fatty acids are the form of unsaturated fat that comes in both natural and artificial form.
Natural-> occur in the meat and dairy from ruminant animals, such as cattle, sheep, and goats.
- They are formed in the stomach during digestion of grass.
Artificial trans fats are an outcome of hydrogenation
- Hydrogenation-> turn vegetable oils into solids or semisolid to improve the shelf life of the product.
Why they are a concern :
- Bad cholesterol will result in the blocking of veins, leading to a heart attack.
- More fat reduces efficiency and increases obesity.
- Stomach problems.
What the Government is doing.
- By January 1, 2022, industrial trans fat will limit to 2% by mass of the total oils/fats present in the product.
->Saturated trans fat can also be transformed into unsaturated by repeated use at high temperatures.’
Denmark-> first country to limit industrially produced trans fat content in all foods to 2% of fats and oils.
- Denmark will eliminate industrially-produced trans fat in all products by 2023.
Swarn Rajput
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR ):-
->It was Set up in 2007 under CPCR Act, 2005
->A statutory body under the Ministry of Women & Child Development
->The Commission’s Mandate is to ensure
- That all Laws
- Policies
- Programs
- Administrative Mechanisms are in consonance with the Child Right In accordance with the Constitution of India and also the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
->The person in the age group 0 to 18 years is known as a child.
->commission-> chairperson + six members (at least two should be women(
->All of them are appointed by the Central Government for three years.
->The maximum age
- 65 years for Chairman
- 60 years for members.
->The Central Government can remove the Chairperson from his office on the basis of proved misbehavior or incapacity to act.
Swarn Rajput
Road Accidents are a bigger threat than pandemic
Statistics:
- 70% of the accident deaths are in the bracket of 14-45 yr.
- 415 deaths per day
- India holds position 1 in terms of death due to accidents
- India loses 3.14 % of GDP due to road accidents.
Why more accidents in India
- Faulty detailed project report.
- 70% of accidents are due to over speeding.
- Flouting of security norms
- Aging of vehicles.
Tamilnadu case study about road safety: T.N. has decreased 38% of their road accidents.
Recent proposed national road safety council
->is an advisory body.
->Under Motor Vehicles Act, 1988
->chaired by the Minister of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MORTH).
->The official members of NRSC include
- Ministers of State for MORTH
- Minister-in-charge of Road Transport in States/UTs
- representatives from the Ministry of Home Affairs,
- Human Resource Development,
- Railways
- Department of Heavy Industry
- Ministry of Environment and Forests etc.
- Some Nonofficial members are also included.
Swarn Rajput
Citizen Vs Citizen
Context:
MHA plans to make a volunteer corp to flag anti-national content online
Issues:
- No definition of anti-national activity, very subjective in nature.
- Giving the power to the ordinary people without locus standi.
- No statutory backing exists for volunteer corp
- The state is going away from the fundamental responsibility to provide protection to people in crime whether it is cyber crime.
- Free speech, privacy, unofficial surveillance.
- Citizen against citizen will polarise the society, will increase the conflicts in society.
- Ignores the guidelines of Supreme court in Shreya Singhal case where court quashed 66A of IT act 2005.
Recent state government approach
- The government of Bihar gave a blanket gag on online criticism.
- Uttarakhand Police decision to scan social media for anti-national content.
- Kerala government made defamatory post punishable.
Way Forward
- Governments should pursue policies that are in sync with the constitution.
Following the guidelines of S.C. is the way forward.
Swarn Rajput
Issue of Parliamentary committee
Context:
Farm bills were not scrutinized by the parliamentary committee and other constitutional bills also didn’t go to committees directly.
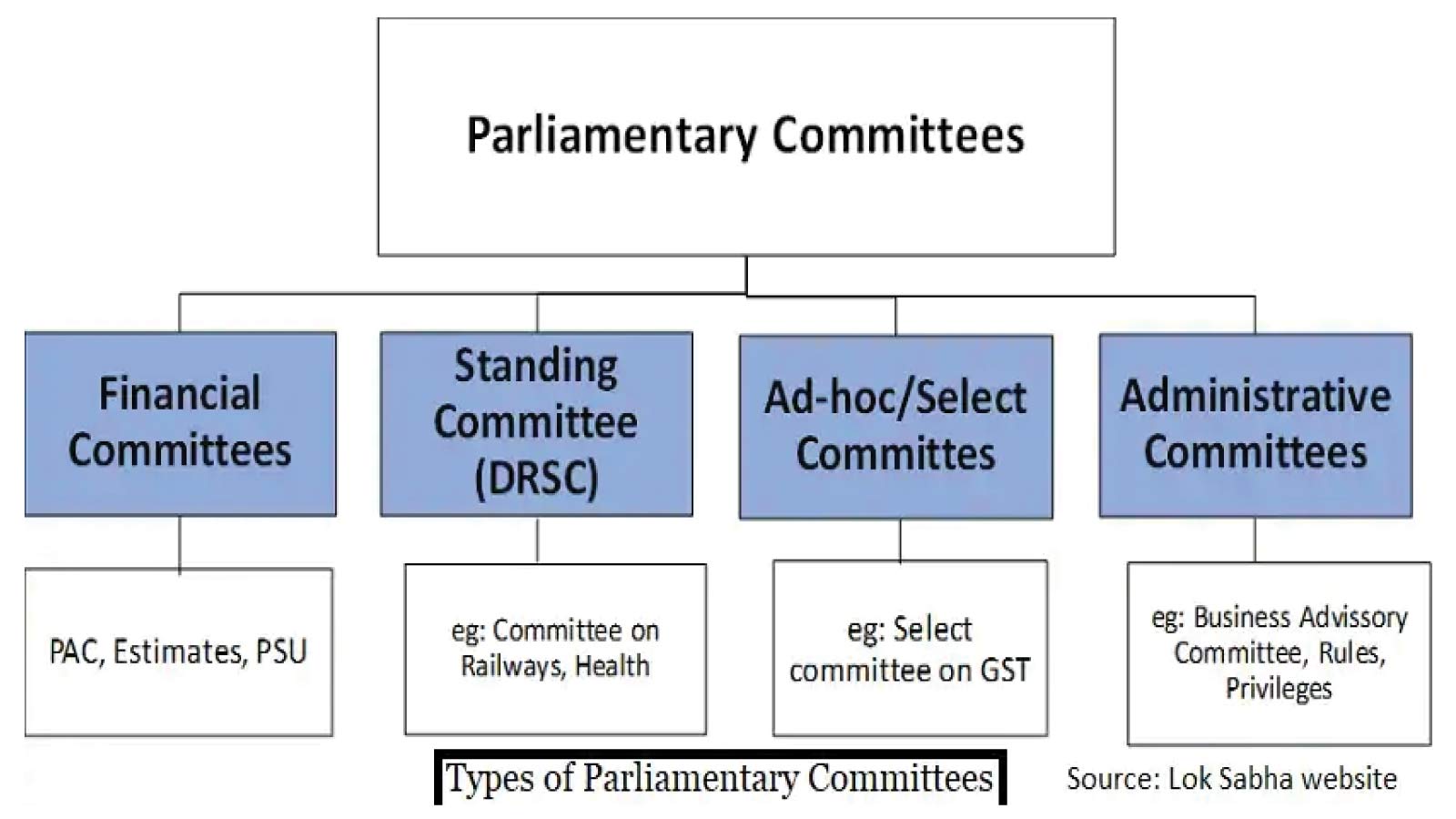
- Due to capacity and time constraints, it is not possible for M.Ps to scrutinise all bills and policies in the house. To counter this issue a committee system came into existence.
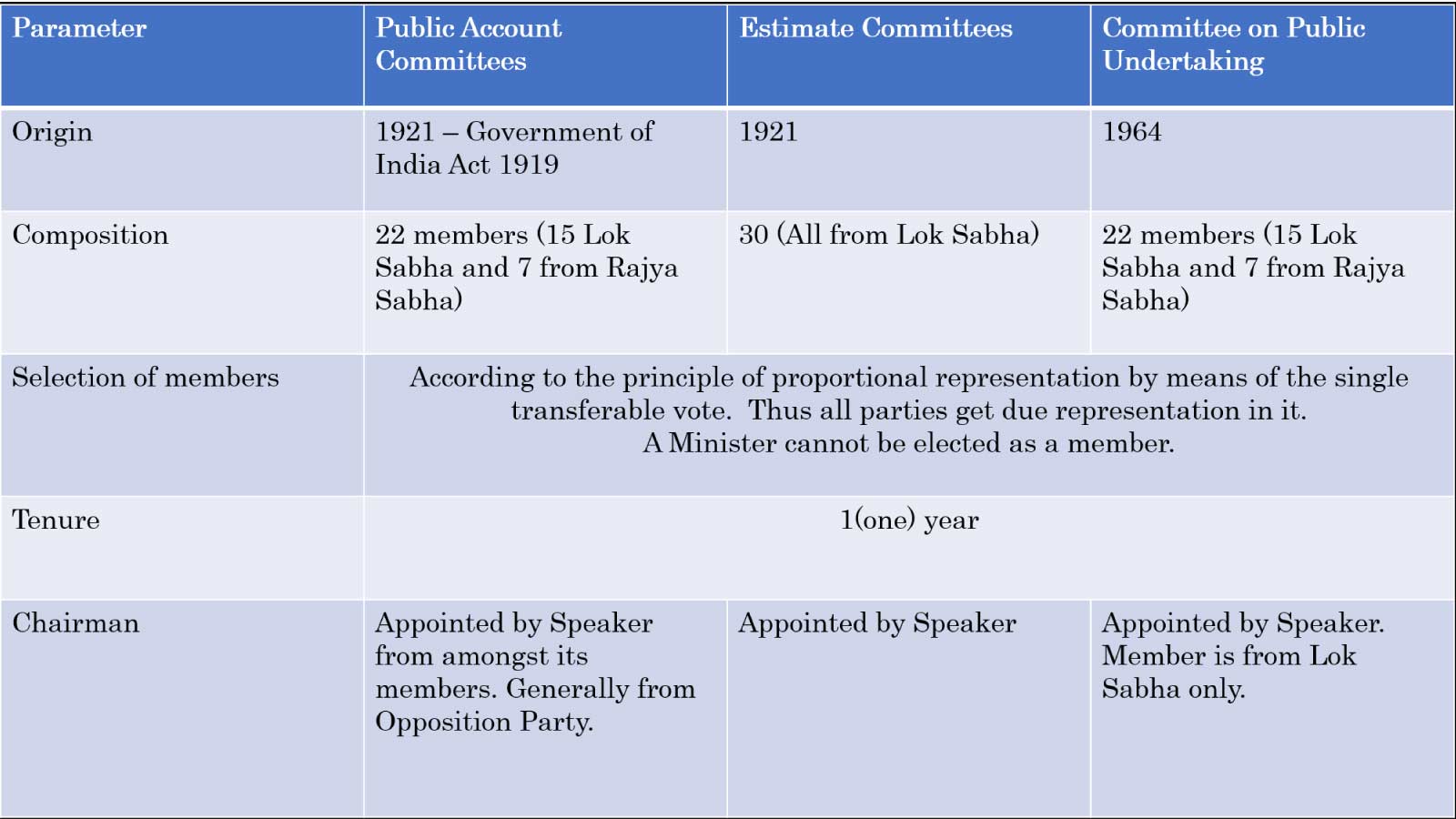
- The earliest Parliamentary Committees-> Public Accounts Committee (1921)
- Estimates Committee (1950).
- 1993->Department Related Standing Committees (DRSC)
Issues in the committee system
Though Standing Committees have improved the capacity and ability of Parliament’s to examine policies better But several challenges are at the forefront.
Fewer bills referred
- Absence of rule to ensure all bills are referred to committees. As per convention, the ministry who is preparing the bill recommends the Speaker to refer a bill to the Standing Committee.
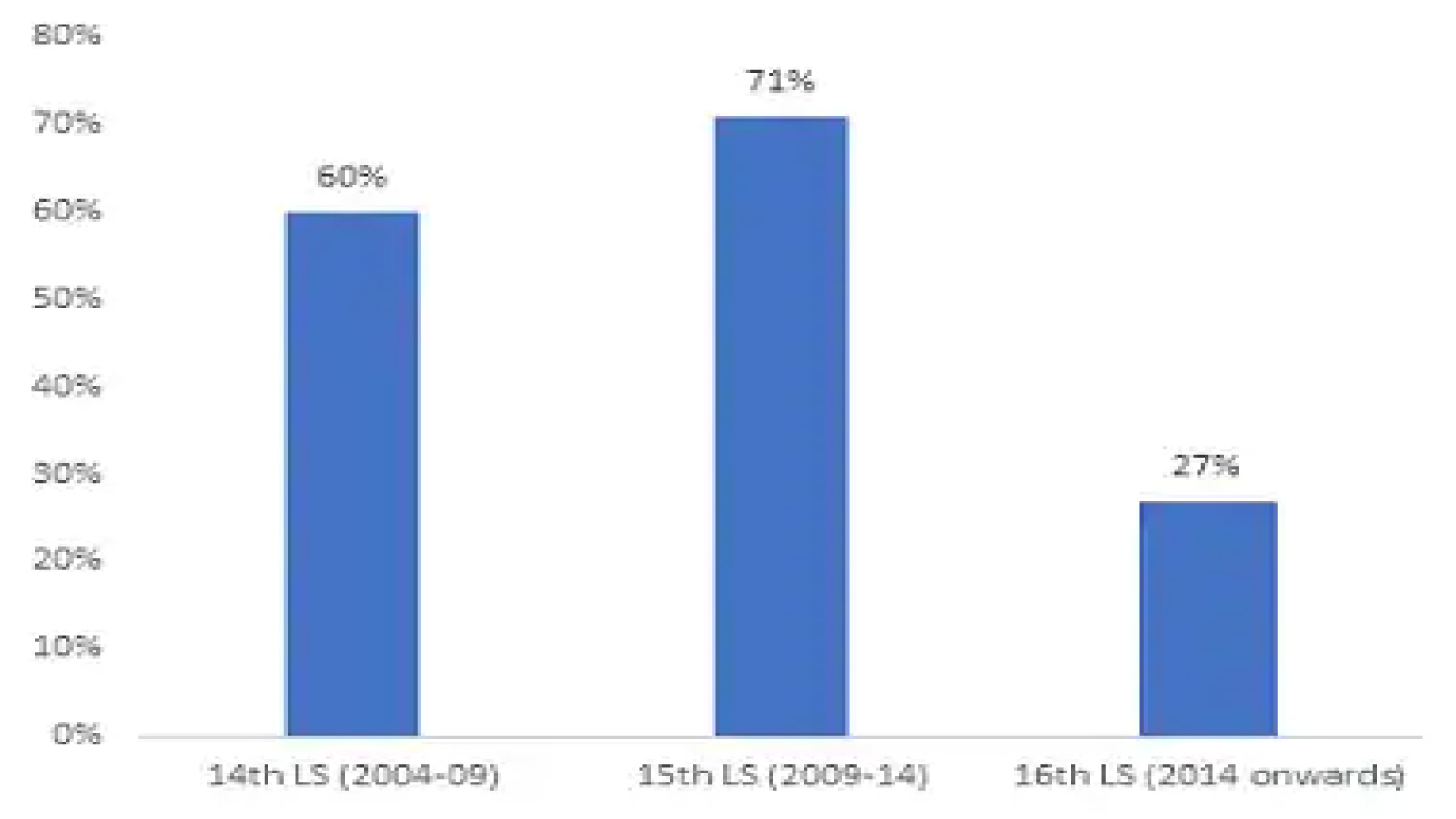
From the graph, it is evident that the 14th and 15th Lok Sabha recommended only 60 percent and 71 percent of bills to be referred to committees.
Longer tenure for members:
->The committee system allows-> legislators to develop technical expertise
But Presently the members are nominated for one year.
->Discussion of committee reports: Recommendations are not binding.
Research Support: examine issues that are technical in nature.
- it is important that quality research is made available to them.
Way forward
- There is a need for referring all bills to committees
- longer tenure for members
- strengthening committees with adequate research support as recommended by (NCRWC).
Swarn Rajput
Martyr Town Dhekiajuli of Assam
Context-
The Prime Minister of India visited two significant historical places in Assam. The first place was Sivasagar’s Jerenga Pothar, where the 17th century Ahom Princess Joymoti sacrificed her life and the second place was Dhekiajuli town which is associated with the quit India movement of 1942.
About the Dhekiajuli-
- As a part of Quit India Movement processions of freedom fighters marched to various police stations across several towns in Assam.
- The squads were recognised as Mrityu Bahini or death squads.
- They had wide participation and set out to unfurl the tricolour atop police stations.
- In Dhekiajuli at least 15 people were shot dead, three of them are women, including 12 year old Tileshwari Barua.
Significance of Martyr Town of Dhekiajuli-
- Dhekiajuli is known as a historic land and it is a symbol of valour and pride.
- Dhekiajuli was home to possibly the youngest martyr of the Indian freedom Struggle.
- The Dhekiajuli police station was accorded heritage status and restored by the Assam Government
-Khyati Khare
Safety Standards Of Vehicles and Road Accidents In India!
Context:
- Recently, the government conveyed concerns over reports that manufacturers are selling vehicles with deliberately downgraded safety standards in India.
- The government said that the prescribed safety standards are only met for the high-end products in many of the leading automobile industries in India, in a seminar organized by SIAM( Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers).
What is SIAM:
- It aims to achieve sustainable development of the Indian automobile industry and also to promote the development of alternative energy vehicles.
- It works closely with the Govt. of India and shares the vision to promote safety, address air quality improvement, compliance with standards.
Fact: Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH) is the nodal agency for road safety in India.
Issues with road accidents in India:
- Road accidents are a serious public health problem in India. More than 1.5 lakh people die every year in road accidents.
- The number of deaths per year matches that of the total casualties we had due to COVID in the past year yet there are not enough safety measures and accountability for those responsible as compared to the pandemic.
- The govt. had targeted to reduce the number of road fatalities by 50% by the year 2020, while the lockdown might have helped to bring the total numbers down, the bigger picture still persists that we are no closer to what we had targeted.
- Increased urbanization in India causes grave road congestion in most areas which in turn contributes to accidents.
Previous data suggest that the most number of people who die in road accidents are in the age group of 15-34, the young workforce of the country. - 17 people are killed in an hour every day in India.
- In more than 3/4th of the road accidents occur because of the fault of the drive and the most precarious reason for speeding.
Way ahead:
- India became a signatory to the Brasilia Declaration in 2015. It aims to restructure the transport policies in order to promote more sustainable modes of transport such as walking, cycling, using public transport, and pool traveling.
- The rate with which the number of vehicles is increasing, the same rate is not seen in the development of road networks, this needs to be taken care of.
- Young people, reckless driving are the two biggest concerns in addressing the issue. Awareness, a sense of responsibility, strict measures, and penalties must be enforced for those who do not abide by the regulation.
- A strict regulation while giving license and a periodic check is also warranted for such a grave situation.
How does vehicle safety standards help: A particular study showed that updated safety standards in vehicles accounted for a 27% reduction in bodily injury claim frequency and a 19% reduction in property damage frequency.
What is the Govt. doing in relation to vehicle safety standards:
- Bharat New Vehicle Safety Assessment Program (BNVSAP) is introduced to standardize a safety program that will measure the safety of every car model being sold in India and will rate them according to how they fare against the crash tests.
- This program also provides lists of safety measures that need to be mandated for new cars and ensures that every manufacturer adheres to the same.
- The BNVSAP is the 10th New Car Assessment Program (NCAP) which is recognized globally.
- The Motor Vehicle (Amendment) Act 2019 was a change in the right direction. The act saw a rampant rise in fines and an even greater rise in the fines of repeated offenders.
NCAP:
- The first NCAP was set up in 1979, by the United States National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.
- Later, different regions according to their own safety standards put forward an assessment program of their own for each and every car that goes to the market. Example: EURO NCAP, Latin NCAP, ASEAN NCAP, etc.
Conclusion:
- Looking at the grave situation the development of infrastructure for road networks could go a long way in addressing the issue.
- Regulations to ensure the vehicles meet the standards set by the authority would ensure accountability.
- Programs to raise awareness about the issue among the young demographics of India could lead to better results.
- The promotion of sustainable modes of transportation such as cycling, walking is a holistic approach to address the issue.
-Ajit Satapathy
PRELIMS FACTS-
1. Unique 16-digit Unicode to identify landholdings announced by UP Government

Unique 16-digit Unicode to mark all kinds of landholdings in the state introduced by the UP Government put an end to fake registries of the disputed land and saved people from falling into the trap of fraudsters.
2. International Children’s Film festival concludes in Bangladesh

The 14th edition of the International Children’s Film festival came to an end in Dhaka.
Dutch Film Jackie and Oopjen were awarded the Best International Feature Film Award. Bangladeshi film Maati got The Young Talent Award while Lottery won the Special mention under the Young Talent Award.
3. India’s first geothermal field development project in Ladakh established by ONGC.

At Puga village of eastern Ladakh state-owned Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) implemented the first geothermal power project in india.
The whole project is commissioned to 2022.
-Alokit Kapoor
[download id=”35343″]



No Comments