01 Mar Action on Volkswagen for violating UFLPA
This article covers ‘Daily Current Affairs’ and the topic details of ”Action on Volkswagen for violating UFLPA”. This topic is relevant in the “International Relations” section of the UPSC CSE exam.
Why in the News?
Recently, vehicles from brands owned by Volkswagen (VW) have been seized in the United States due to violations of the Uyghur Forced Labour Prevention Act (UFLPA). Thousands of high-end European vehicles from names like Porsche, Bentley, and Audi have been seized by US officials, and they are currently conducting investigations into them due to claims that they broke the rules prohibiting the importation of goods produced in China using forced labour.
Background
- Concurrently, BASF, another German company, is expediting the sale of its petrochemical plant in Xinjiang amid allegations that employees from a government-owned joint venture have provided evidence to Chinese authorities regarding the Uyghur communities.
- Similar concerns arose in 2020 regarding Lens Technology, a supplier for Apple, accusing the company of employing forced labour. In that same year, the Australian Strategic Policy Institute released a report alleging four instances of Apple’s connections to forced labour within supply chains based in Xinjiang.
- Reports from the U.S. State Department and the UN Human Rights Commissioner characterize the repression of Uyghurs as genocide and potential crimes against humanity.
Who are the Uyghurs?
- The Uyghurs, numbering around 12 million and predominantly adhering to Islam, reside in Xinjiang, officially designated as the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (XUAR). They possess a distinct language akin to Turkish and identify themselves as culturally and ethnically linked to Central Asian nations. Despite their significant presence, Uyghurs constitute less than half of Xinjiang’s overall population.
- In recent years, there has been a substantial influx of Han Chinese, the ethnic majority in China, into Xinjiang. This demographic shift has been purportedly organised by the state to diminish the minority population in the region. China has faced accusations of specifically targeting Muslim religious figures, imposing restrictions on religious practices, and engaging in the demolition of mosques and tombs.
- Uyghur activists express concerns about the potential erosion of their group’s culture, citing fears of cultural assimilation. They contend that the state’s policies, including the orchestrated migration and alleged suppression of religious and cultural practices, contribute to the perceived threat to the preservation of Uyghur heritage.
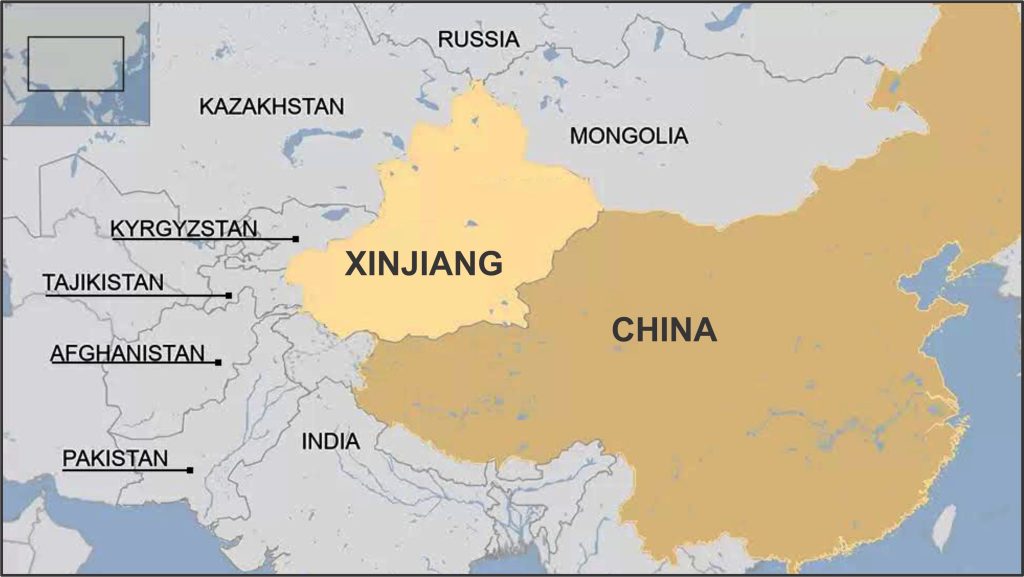
Xinjiang region of China
- Situated in the northwest of China, Xinjiang holds the distinction of being the country’s largest region. Similar to Tibet, Xinjiang operates as an autonomous region in principle, implying a certain degree of self-governance. However, both regions face substantial constraints imposed by the central government in practice.
- Xinjiang, primarily a desert region, plays a significant role in global cotton production, contributing about a fifth of the world’s supply. Concerns raised by human rights organisations centre around the alleged use of forced labour in the harvesting of this cotton. In 2021, several Western brands responded to these concerns by removing Xinjiang cotton from their supply chains. This decision, however, triggered a backlash from Chinese celebrities and the online community.
- Beyond its cotton production, Xinjiang is endowed with abundant reserves of oil and natural gas. Given its strategic proximity to Central Asia and Europe, Beijing considers Xinjiang a crucial trade link. This geographical positioning enhances its importance in the eyes of the Chinese government, contributing to the region’s economic and strategic significance.
Accusations Against China
- Chinese authorities face allegations of enforcing forced labour, systematic implementation of forced birth control, torture, and the separation of children from incarcerated parents. Multiple nations, including the United States, Canada, and the Netherlands, have accused China of committing genocide, as per the international convention’s definition of intending to destroy, either wholly or partially, a national, ethnic, racial, or religious group.
- China stands accused of engaging in the forced mass sterilisation of Uyghur women to control population growth, forcibly separating children from their families, and actively working to erode the cultural traditions of the Uyghur group. In 2018, a UN human rights committee reported credible evidence indicating that China was detaining up to a million people in “counter-extremism centres” in Xinjiang.
- A study conducted by the Australian Strategic Policy Institute in 2020 revealed evidence of over 380 of these “re-education camps” in Xinjiang, representing a 40% increase from previous estimates. The findings further contribute to the mounting international concerns and scrutiny surrounding China’s actions in the region.
The Uyghur Forced Labour Prevention Act (UFLPA): Addressing Concerns of Forced Labour in Xinjiang
The Uyghur Forced Labour Prevention Act (UFLPA) is a United States law enacted in December 2021 aimed at preventing goods produced through forced labour in China’s Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (XUAR) from entering the US market. This act emerged from concerns about the treatment of Uyghur and other minority groups in XUAR.
Key provisions of the UFLPA:
- Presumption of forced labour: The law establishes a presumption that goods manufactured wholly or partly in XUAR, or by entities on a designated list are made with forced labour. This means importers will need to provide “clear and convincing evidence” that their goods were not produced using forced labour to gain entry into the US.
- UFLPA Entity List: The act authorises the creation of a list of entities reasonably believed to be involved in forced labour in XUAR. This list is maintained by the US Department of Homeland Security and currently includes companies involved in various sectors like cotton production, solar panel manufacturing, and technology.
- Forced Labour Enforcement Task Force (FLETF): The UFLPA strengthens the existing FLETF, a government body responsible for coordinating efforts to combat forced labour across the globe. The act mandates the FLETF to develop a strategy for implementing the UFLPA’s provisions and supporting its enforcement.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 1st March 2024
Prelims practise question
Q1. Consider the following pairs: (UPSC Prelims-2016)
Community sometimes in the affairs mentioned in the news
- Kurd — Bangladesh
- Madhesi — Nepal
- Rohingya — Myanmar
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
Answer: (c)
Mains practise question
Q1. What role does the United Nations play in preventing and responding to instances of discrimination and persecution based on race, ethnicity, or religion?
I am a content developer and have done my Post Graduation in Political Science. I have given 2 UPSC mains, 1 IB ACIO interview and have cleared UGC NET JRF too.



No Comments