22 Feb Annual Report 2022-23 of National Commission of Schedule Castes (NCSC)
This article covers ‘Daily Current Affairs’ and the topic details of ”National Commission of Schedule Castes (NCSC) Annual Report 2022-23″.This topic is relevant in the “Polity” section of the UPSC CSE exam.
Why in the News?
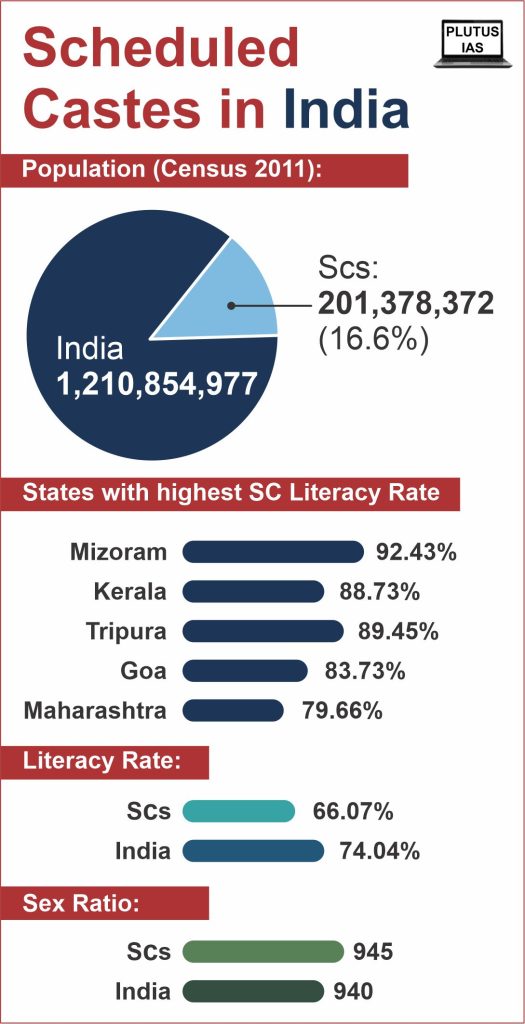
The President of India recently received the National Commission of Schedule Castes’ (NCSC) Annual Report 2022-23 from the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment. The findings provide numerous suggestions on the topics entrusted to the Commission regarding the protection of Constitutional Safeguards for Scheduled Castes (SCs) as stipulated in India’s Constitution.
About the National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC)
- The National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC) is a constitutional authority that works to protect the rights of scheduled castes (SC) in India. Article 338 of India’s constitution addresses this commission.
- It establishes a National Commission for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, tasked with investigating and monitoring all matters relating to the safeguards provided for them, investigating specific complaints, and participating in and advising on the socioeconomic development planning process, among other things.
- Composition:
- Chairperson.
- Vice-chairperson.
- Three other members.
They are appointed by the President of India through a warrant bearing his hand and seal.
Functions of the National Commission for Scheduled Castes
Safeguarding Rights:
One of the core functions of the NCSC is to work towards the effective implementation of constitutional safeguards and protections provided for Scheduled Castes. This includes overseeing the reservation policies, ensuring equal opportunities, and preventing discrimination.
Inquiring into Complaints:
The Commission has the jurisdiction to investigate particular complaints and concerns concerning the Scheduled Castes’ denial of rights and safeguards. It can investigate cases of discrimination, atrocities, or denial of benefits and recommend necessary actions to the concerned authorities.
Monitoring and Evaluating Safeguard Implementation:
NCSC is tasked with monitoring and evaluating the implementation of various safeguards and programs intended for the welfare of Scheduled Castes. This involves reviewing the progress of initiatives aimed at their educational, economic, and social advancement.
Advisory Role:
The Commission provides advice to the President of India on matters related to the welfare and development of Scheduled Castes. It can offer recommendations for policy formulation, legislative measures, and executive actions to improve the conditions of the Scheduled Castes.
Inquiring into Specific Cases of Atrocities:
NCSC investigates and inquires into specific cases of atrocities committed against Scheduled Castes. This includes offences such as untouchability, harassment, violence, or any form of discrimination based on caste, and the Commission recommends actions against the perpetrators.
Promoting Socio-Economic Development:
NCSC works towards the socio-economic development of Scheduled Castes by advocating for their rights in various sectors, such as education, employment, and healthcare. The Commission strives to bridge the gaps in development indicators between Scheduled Castes and other communities.
Reviewing Constitutional and Legal Safeguards:
The Commission reviews the safeguards provided in the Constitution and other laws for the Scheduled Castes and recommends amendments or modifications as deemed necessary to ensure their effective implementation.
Raising Awareness and Sensitization:
NCSC undertakes initiatives to raise awareness and sensitisation about the rights and issues faced by Scheduled Castes. This includes organising campaigns, workshops, and outreach programs to promote social inclusion and eliminate discrimination.
Facilitating Social Justice:
The Commission plays a crucial role in facilitating social justice by ensuring that Scheduled Castes have equal access to opportunities, resources, and benefits. It aims to create an environment where individuals from Scheduled Castes can lead dignified lives without facing discrimination.
Issues related to the National Commission for Scheduled Castes
Implementation Gap:
Despite the constitutional mandate, there is often a significant gap between the policies formulated for the welfare of Scheduled Castes and their effective implementation. The NCSC faces challenges in ensuring that the intended benefits reach the targeted population due to bureaucratic hurdles and lack of accountability.
Delayed Redressal:
One major issue is the delay in addressing complaints and grievances filed by members of Scheduled Castes. The lengthy bureaucratic processes and procedural complexities often result in delayed justice, undermining the purpose of the Commission’s existence.
Limited Enforcement Powers:
The NCSC lacks enforcement powers, limiting its ability to ensure the implementation of its recommendations. While it can make recommendations and report on violations, the Commission relies on other authorities to enforce its directives, which may not always be effective.
Inadequate Representation:
Some critics argue that the composition of the NCSC does not always adequately represent the diversity within Scheduled Castes. Issues related to gender, regional disparities, and sub-caste variations may not receive sufficient attention, affecting the Commission’s ability to address the nuanced challenges faced by different sections.
Political Interference:
There have been instances where the NCSC has faced allegations of political interference, impacting its independence. Political considerations in appointments and decision-making processes may compromise the Commission’s ability to function impartially.
Limited Awareness:
Lack of awareness among Scheduled Castes about their rights and the role of the NCSC remains a challenge. This hinders the Commission’s outreach efforts and its ability to address issues at the grassroots level.
Insufficient Resources:
The NCSC often faces challenges due to inadequate financial and human resources. Insufficient staff and budget constraints limit the Commission’s capacity to handle the increasing volume of complaints and conduct comprehensive reviews of welfare programs.
Need for Judicial Powers:
Critics argue that providing the NCSC with judicial powers would enhance its effectiveness. Currently, the Commission relies on other institutions for legal action, and empowering it with direct judicial authority could expedite the resolution of cases.
Monitoring Private Sector:
The NCSC faces challenges in monitoring and addressing discrimination against Scheduled Castes in the private sector. While it can intervene in public sector cases, its jurisdiction over private enterprises is limited, creating a gap in safeguarding the rights of Scheduled Castes in various employment sectors.
Coordination with States:
The effectiveness of the NCSC depends on effective coordination with state governments. Issues arise when there is a lack of cooperation or differing priorities between the national and state authorities, hindering the seamless implementation of welfare measures.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 22th Feb 2024
Prelims practice question
Q1. What is the NCSC’s primary role in terms of advising the President of India
A. Legislative drafting
B.Constitutional amendments
C.Advisory on matters related to Scheduled Castes
D.International diplomacy
ANSWER: C
Mains practice question
Q1. Evaluate the role of the NCSC in addressing complaints and grievances filed by Scheduled Castes. How effective has the Commission been in providing redressal and ensuring justice for instances of discrimination or atrocities?
I am a content developer and have done my Post Graduation in Political Science. I have given 2 UPSC mains, 1 IB ACIO interview and have cleared UGC NET JRF too.



No Comments