25 Jul Arrows Impossibility Theorem
Arrow’s Impossibility Theorem – UPSC Economics Optional Notes
Introduction
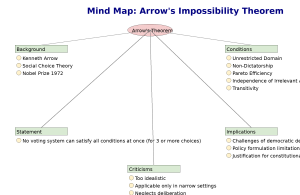
Arrow’s Impossibility Theorem is one of the most profound results in the field of social choice theory and welfare economics. It was proposed by economist Kenneth J. Arrow in his groundbreaking 1951 work “Social Choice and Individual Values”. The theorem explores the difficulty of converting individual preferences into a collective or social preference in a consistent and fair way.
This concept is pivotal in understanding the limitations of democratic decision-making and the theoretical foundations of welfare economics. Arrow was awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics in 1972 for this contribution.
Best ias coaching in hindi medium
What is Arrow’s Impossibility Theorem?
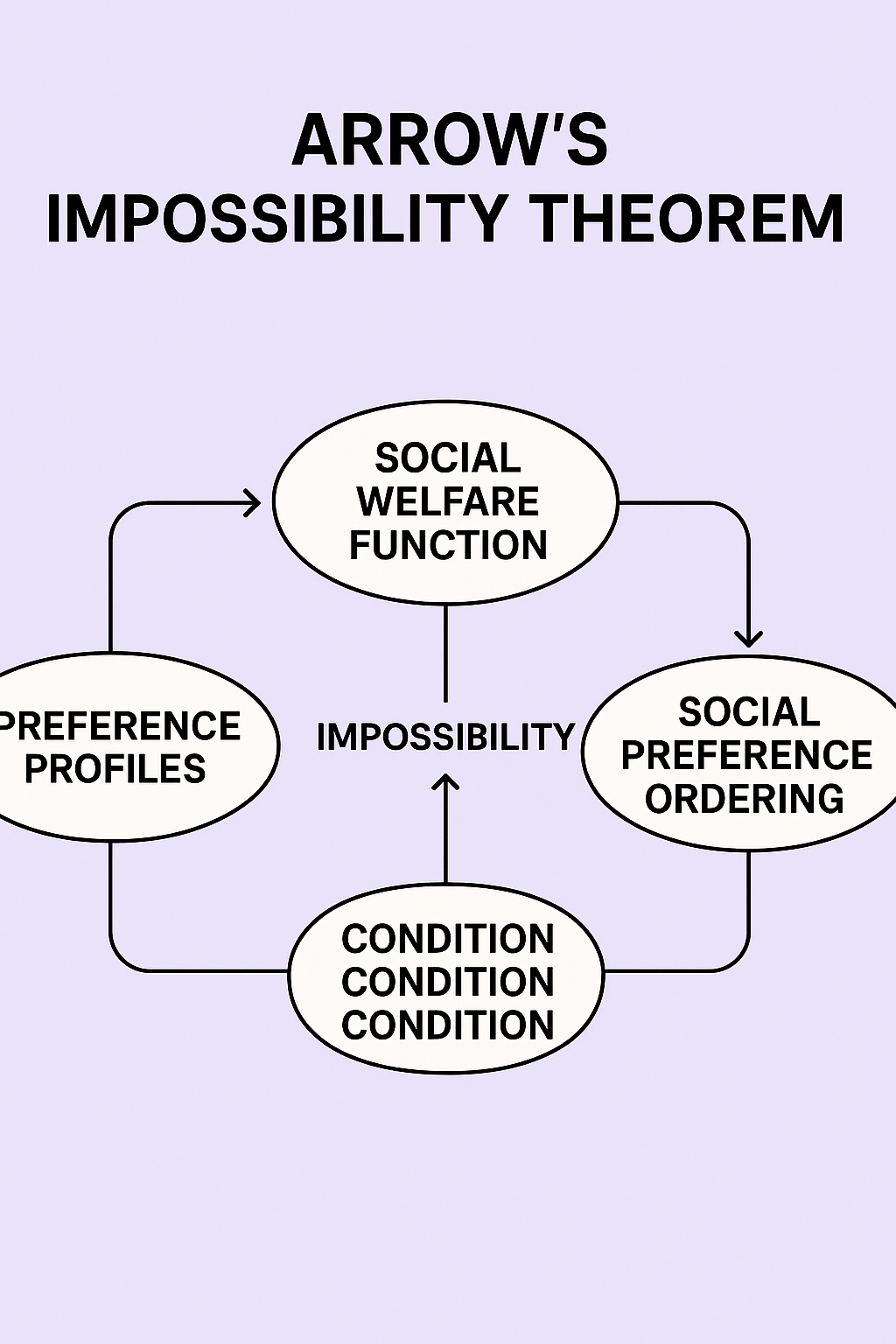
The theorem asserts that no voting or social welfare function can simultaneously satisfy a set of desirable conditions if there are three or more alternatives to choose from. This makes it “impossible” to construct a fair social choice rule under these criteria.
Assumptions / Conditions of the Theorem
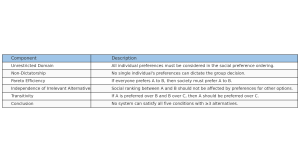
- Unrestricted Domain: The social choice rule must work for any possible set of individual preferences.
- Non-Dictatorship: No single individual’s preferences should always become the social preference regardless of others.
- Pareto Efficiency: If every individual prefers A over B, then society should also prefer A over B.
- Independence of Irrelevant Alternatives (IIA): The choice between two alternatives should depend only on individual preferences between those two.
- Transitivity: If A is socially preferred to B and B to C, then A must be preferred to C.
The Statement of the Theorem
“No social choice function can satisfy all five conditions simultaneously for three or more alternatives.”
This means that every voting system or method of aggregating individual preferences into a collective decision will inevitably violate at least one of these conditions.
High-Resolution Mind Map
Arrows Impossibility Theorem MindMap_HighRes
Infographic – Arrow’s Conditions Explained
Arrows_Impossibility_Theorem_Infographic
Implications for Welfare Economics and Democracy
- Policy Implication: No perfect voting method exists. Policy decisions may always carry some level of unfairness or inconsistency.
- Justification of Constitutional Constraints: Since a perfect aggregation of preferences is impossible, constitutional limits may be necessary to maintain fairness and prevent manipulation.
- Public Choice Theory: Arrow’s theorem forms a foundation for public choice economics which evaluates governmental decision-making structures.
GS paper 4 syllabus and study plan
GS paper 3 syllabus and study plan
Criticisms of Arrow’s Theorem
- Too Idealistic: The assumptions (like unrestricted domain and IIA) are considered unrealistic for practical governance.
- Static Framework: The theorem does not account for deliberative democracy, negotiations, or evolving preferences.
- Applies Only to Formal Systems: Practical decisions are made through broader institutional checks, not just voting rules.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
- Policy making in democratic governments
- Social welfare schemes based on majority voting
- Economics of constitutions and public administration
- Evaluating fairness of taxation or public goods allocation
Arrow’s Theorem in Graphical Illustration
Imagine a voting scenario with 3 candidates – A, B, and C – and 3 voters with the following preferences:
- Voter 1: A > B > C
- Voter 2: B > C > A
- Voter 3: C > A > B
If the society chooses based on majority rule between each pair of candidates, it results in a preference cycle: A > B, B > C, but C > A. This violates transitivity, showing a “voting paradox.”
Previous Year Questions (PYQs) – UPSC Economics Optional
- UPSC 2022: What are the conditions of Arrow’s Impossibility Theorem? Discuss their relevance in modern policy making.
- UPSC 2019: Explain Arrow’s Theorem and its implications for collective decision-making in a democracy.
- UPSC 2016: Why is Arrow’s result called the “Impossibility Theorem”? Explain with suitable examples.
Probable Questions for UPSC 2025
- Mains: Discuss how Arrow’s Impossibility Theorem challenges the assumptions of welfare economics.
- Mains: What role does Arrow’s Theorem play in the formulation of social welfare policies?
- Prelims: Which of the following is NOT a condition in Arrow’s Impossibility Theorem?
a) Pareto Efficiency
b) Unrestricted Domain
c) Market Clearing Condition
d) Non-Dictatorship
Answer: c) Market Clearing Condition
Conclusion
Arrow’s Impossibility Theorem remains a cornerstone in the field of welfare economics and democratic theory. It provides a rigorous proof of the limitations of collective decision-making. For UPSC aspirants, understanding this theorem is essential for mastering concepts in microeconomics, public choice theory, and economic policy formulation. It also helps build critical thinking for General Studies papers and essay writing.




No Comments