06 Apr Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) – A digital intervention in Health Sector
This article covers “ Daily Current Affairs for UPSC” and the topic details how five lakh patients used QR codes for faster Outpatient Department (OPD) registration. The topic mentions the Health Ministry’s Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission which introduced the “scan and share” service in October 2022. The topic is important how digital interventions in the health sector are revolutionizing healthcare.
Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
For Prelims:
- About National Health Authority – Composition, functions, and issues
- About Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission – Components, performance, and issues.
- About QR code technology
For Mains: GS 2, Welfare Schemes for Vulnerable Sections of the Population by the Centre and States and the Performance of these Schemes; Mechanisms, Laws, Institutions and Bodies constituted for the Protection and Betterment of these Vulnerable Sections.
- Impact of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission on the health sector
- Various digital interventions by the government in the health sector
Performance of Ayushman Digital Bharat Mission: Features, Challenges, Status, and Way Ahead.
Content of the Article:
- Why in news
- Background
- About Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
- Digital Interventions in Health Care
- Benefits of Digitization of Health Care
- Issues Related to Digital Interventions in India
- Government Interventions in Health Care
- Way Forward
Why in news:
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare announced that QR code-enabled OPD registration at hospital counters has been successful in reducing long queues. It has benefited up to five lakh patients by streamlining the registration process, reducing waiting times, and providing better healthcare experiences for patients

Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission Ecosystem
Background of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
Indian hospitals, specifically government ones suffer from long queues which cause inconvenience and delays for patients. The patients have to wait long hours to see a doctor or to get admitted to the hospital.
To address this issue, the National Health Authority under Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission launched QR code-enabled registration and online appointment booking systems. These initiatives have helped to streamline the patient registration process, reduce waiting times, and improve the overall patient experience.
About Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission is a healthcare initiative launched by the Government of India in 2021.
Aim: To create a digital infrastructure for the Indian healthcare system, with the goal of improving the efficiency, affordability, accessibility, and quality of healthcare services in the country.
Salient Features Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
- To create a seamless online platform offering a wide range of data, information, and infrastructural services,
- To enable the exchange of longitudinal health records with citizen consent
- To ensure the security, confidentiality, and privacy of health-related personal information.
Components Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
- Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) Number for every citizen: A Health ID is a unique code that encapsulates personal health records, which can be linked to the government digital system.
- ABHA Application: It is an electronic application through which patients can maintain and manage and update their health information in a safe, secure, and confidential environment.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry: It is a comprehensive repository that includes all healthcare professionals involved in delivering healthcare across modern and traditional medicine systems.
- Healthcare facilities Registries: It is a comprehensive repository that includes all health facilities across different systems of medicine, including public and private hospitals, clinics, diagnostic laboratories, imaging centers, and pharmacies, among others, in the country.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): It is an open protocol for digital health services, connecting End User Applications (EUAs) and participating Health Service Provider (HSP) applications. It enables a range of digital health services between patients and HSPs, such as appointment booking, teleconsultation, and service discovery.
Digital Interventions in Health Care – Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
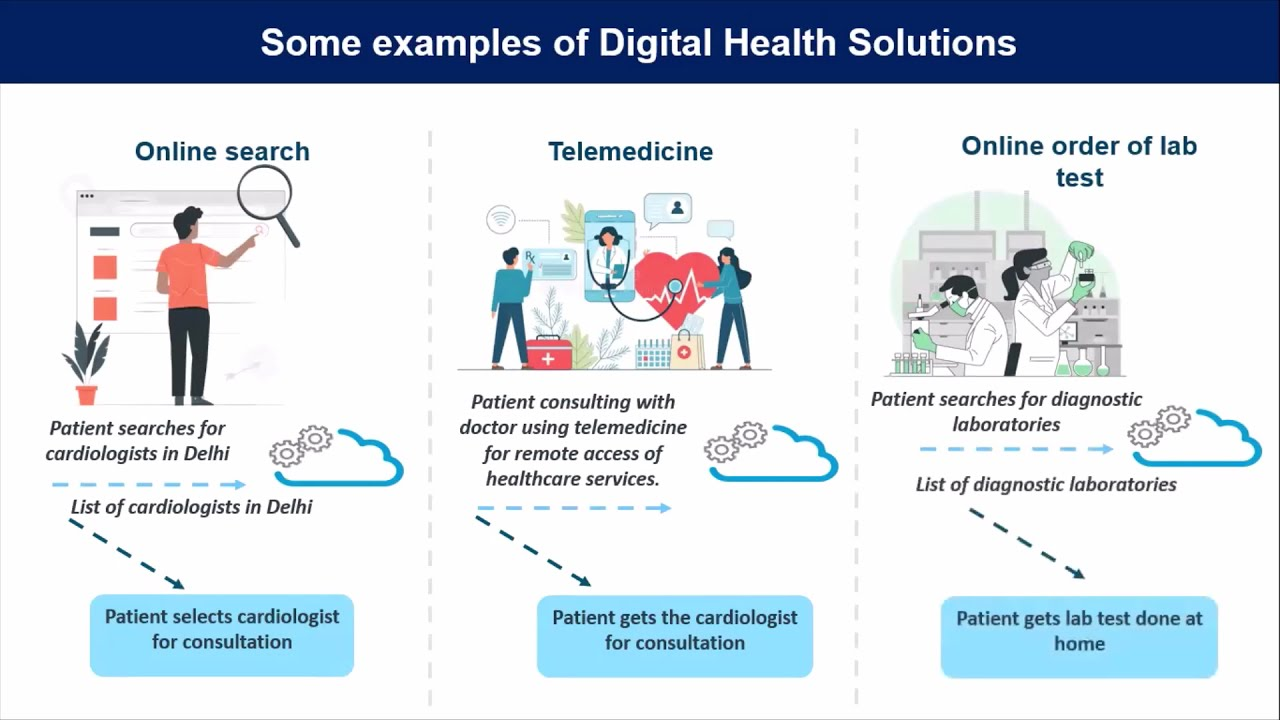
Digital Interventions in Health Care – Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
Digital interventions in healthcare have gained significant traction in India in recent years, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. The following are some examples of digital interventions in healthcare in India:
- Telemedicine: Telemedicine refers to the delivery of healthcare services through telecommunication and digital communication technologies. It has gained significant popularity in India, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. Several platforms, including Practo, mFine, etc offer telemedicine services in India.
- Health information systems: Digital Health information systems, including electronic health records (EHRs), have become increasingly popular in India. The government has launched several initiatives to promote the adoption of EHRs, including the National Health Stack (NHS) and the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM).
- Mobile health (mHealth): mHealth refers to the use of mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to provide healthcare services. Several mHealth apps, including 1mg, Medlife, and Netmeds, offer digital healthcare services in India.
- Electronic prescribing (e-prescribing): E-prescribing refers to the process of electronically transmitting prescriptions from digital healthcare providers to pharmacies. The government of India has launched the National Electronic Health Authority (NEHA) initiative to promote the adoption of e-prescribing.
- Digital health platforms: Several digital health platforms, including Practo, 1mg, and CureFit, offer a wide range of healthcare services, including telemedicine, laboratory tests, and home healthcare services.
Benefits of Digitization of Health Care – Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
Digital healthcare has numerous benefits, including
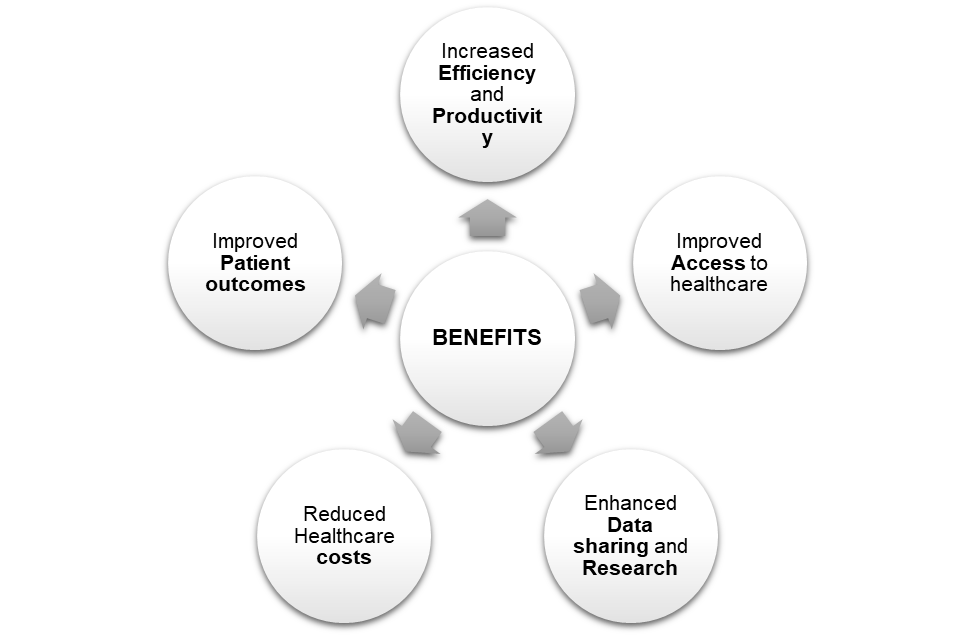
Benefits of Digitization of Health Care – Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
- Improved access to healthcare: Digital interventions, such as telemedicine and mobile health, enable patients to access healthcare services from the comfort of their homes. This is particularly beneficial for those patients living in remote or underserved areas who may not have access to healthcare services.
- Increased efficiency and productivity: Digital interventions, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and electronic prescribing (e-prescribing), can streamline healthcare processes and reduce administrative burdens. This can increase efficiency and productivity, allowing healthcare providers to focus more on patient care.
- Improved patient outcomes: Digital interventions can improve patient outcomes by enabling more accurate and timely diagnoses, providing personalized treatment plans, and enabling patients to better manage their health.
- Reduced healthcare costs: Digital interventions can reduce healthcare costs by eliminating the need for unnecessary in-person visits, reducing administrative costs, and enabling better resource utilization.
Enhanced data sharing and research: Digital interventions enable the sharing of health data across different healthcare providers and organizations, enabling more coordinated care and facilitating research and development of new treatments and therapies.
Issues Related to Digital Interventions in India
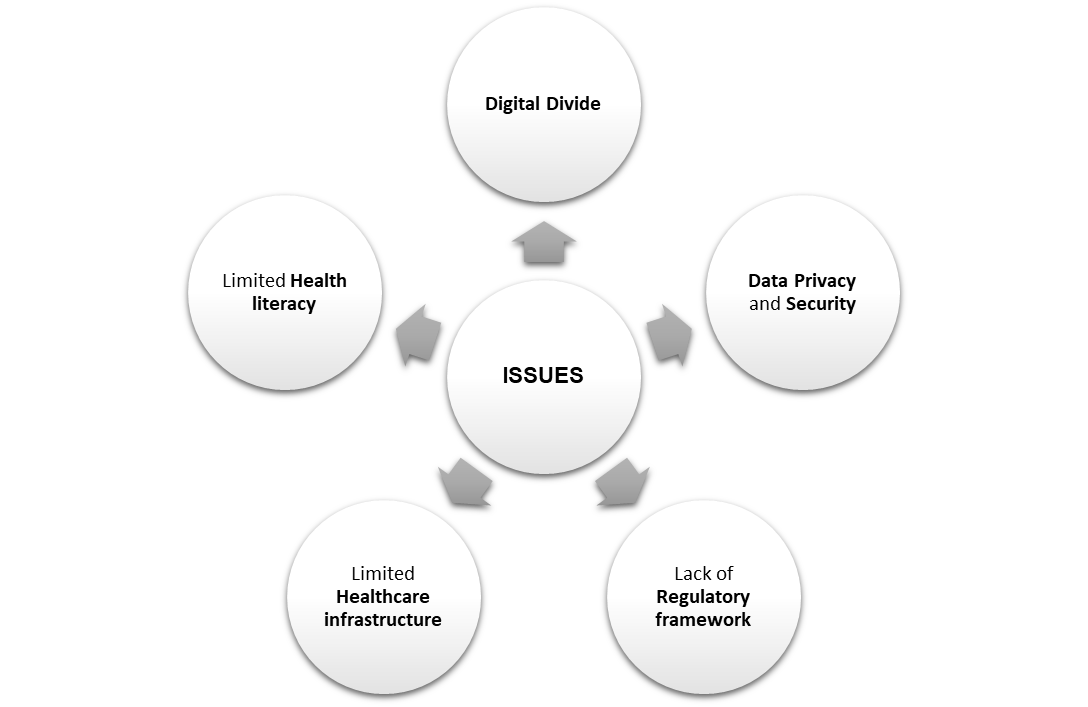
Issues Related to Digital Interventions in India
Despite the potential benefits, there are several issues related to digital interventions in healthcare in India. These include:
- Digital divide: India has a significant digital divide, with many people still lacking access to digital devices and the internet. This limits the potential reach and impact of digital interventions in healthcare.
Data privacy and security: Data privacy and security are significant concerns in India, particularly given the large amount of sensitive health data that is being collected and stored by digital interventions. There is a need to develop robust data protection laws and security protocols to safeguard against data breaches and misuse.
Lack of regulatory framework: There is a lack of a clear regulatory framework governing digital interventions in healthcare in India. This has led to confusion and uncertainty among healthcare providers and patients regarding the legality and safety of these interventions. - Limited healthcare infrastructure: India has a limited healthcare infrastructure, particularly in rural and remote areas. This can limit the potential reach and impact of digital interventions in healthcare, particularly those that require sophisticated technology and infrastructure.
- Limited health literacy: Many people in India have limited health literacy, which can make it difficult for them to understand and use digital interventions in healthcare effectively.
Government Interventions in Health Care
The Indian government has launched several digital interventions in healthcare to improve the delivery of healthcare services. Some examples of these interventions include
- National Health Stack (NHS): The NHS is a digital infrastructure that aims to streamline the delivery of healthcare services in India. It includes a digital health ID, a personal health record, and a registry of healthcare providers. The NHS also aims to enable the interoperability of health data across different healthcare providers and organizations.
- National Digital Health Blueprint (NDHB): The NDHB is a policy document that outlines the government’s vision for digital health in India. It includes the creation of a National Digital Health Authority (NDHA) to oversee the implementation of digital health initiatives in the country.
- National Health Stack Sandbox: The National Health Stack Sandbox is a testing environment for digital health applications and services. It enables developers to test their applications in a secure and controlled environment before launching them in the market.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission: The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission aims to digitize the entire healthcare ecosystem in India. It includes the creation of a national health registry, and the establishment of digital health infrastructure, and the development of digital health applications and services.
- Telemedicine: The Indian government has promoted telemedicine as a means of delivering healthcare services to remote and underserved areas. It has launched several initiatives, including the Telemedicine Practice Guidelines and the e-Sanjeevani platform, to promote the adoption of telemedicine in the country.
Way Forward
Overall, the digitization of healthcare has the potential to improve access to healthcare services, increase efficiency and productivity, improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and facilitate research and development in the healthcare sector. But, the underlying issues related to data privacy and security, digital literacy, and the digital divide pose significant challenges to the widespread adoption and implementation of digital interventions in healthcare in India. Addressing these issues will be critical in realizing the full potential of digital interventions in India.
Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
Reading daily current affairs should be the principal duty for the UPSC exam preparation. Every UPSC aspirant should read daily current affairs for enhancing better performance in the UPSC examination. Plutus IAS serves the best and latest daily current affairs for the UPSC examination. Here, You get all the updated news from the national and international world. Also, Get the Weekly and monthly current affairs for IAS exam preparation.




No Comments