12 Aug Ayushman Bharat- Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (PMJAY)
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (PMJAY)”. The topic “Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (PMJAY)” has relevance in the “Governance” section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
What are Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (PMJAY)?
What is its implementing structure?
For Mains:
GS2: Welfare Schemes for vulnerable populations
Why in the news?
A recent report by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) revealed irregularities in the registration and validation of Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana beneficiaries (PMJAY).
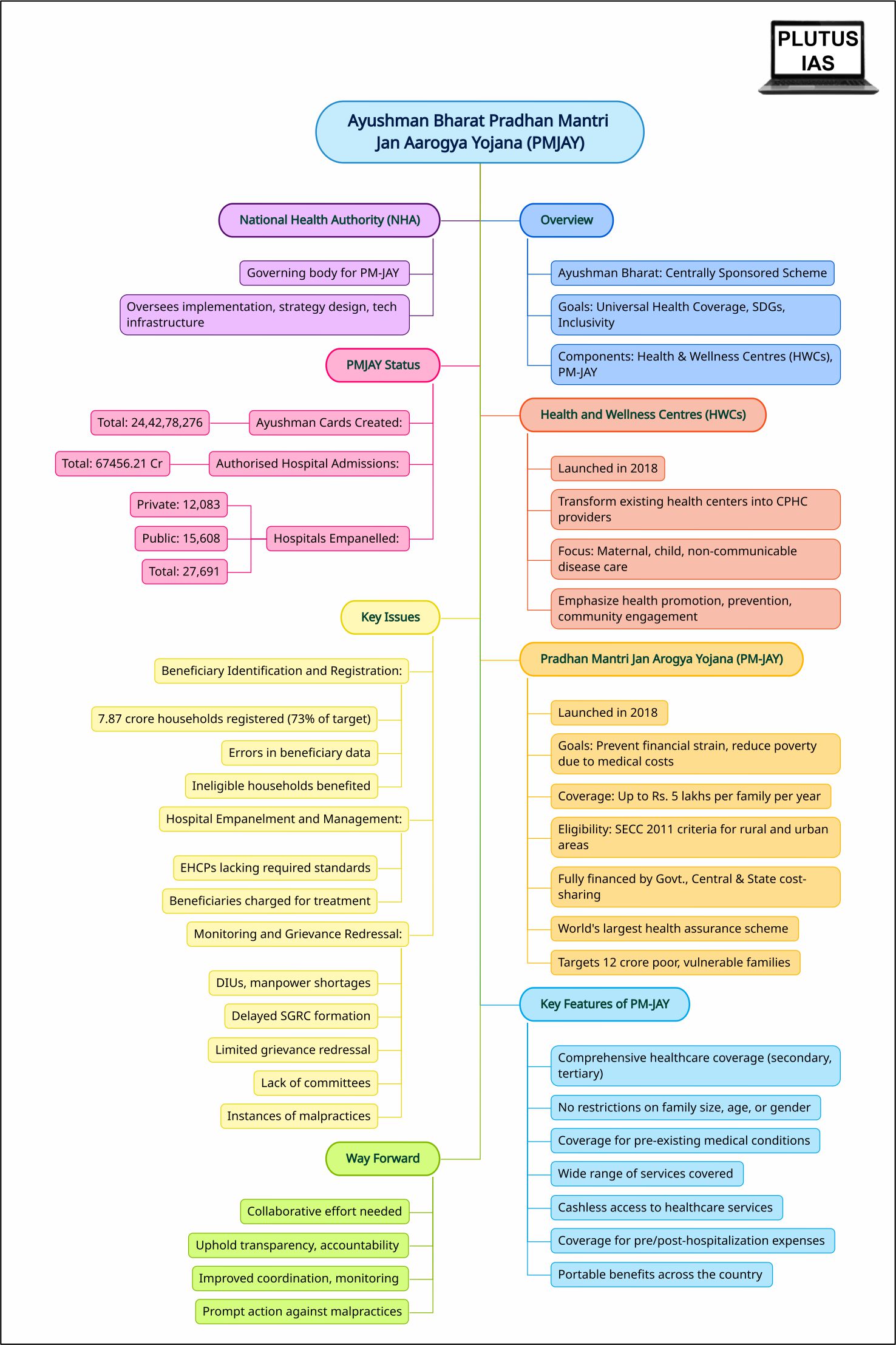
Ayushman Bharat
- Ayushman Bharat is a flagship Centrally Sponsored Scheme of the Indian government designed to achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and align with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) while ensuring inclusivity.
- It replaces the segmented approach to healthcare with a comprehensive, need-based system that addresses health needs from primary to tertiary levels.
- The scheme consists of two main components: Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) and Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY).
Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs)
- Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) were launched in 2018 to transform existing health centers into Comprehensive Primary Health Care (CPHC) providers, focusing on maternal, child, and non-communicable disease care.
- HWCs emphasize health promotion, prevention, and community engagement to reduce chronic diseases and improve overall health.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY)
- PM-JAY, which was launched in 2018, is the world’s largest health assurance scheme, offering up to Rs. 5,00,000 per family per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
- PM-JAY targets over 12 crore poor and vulnerable families (around 55 crore beneficiaries), primarily from the bottom 40% of India’s population.
- For both rural and urban areas, eligibility criteria based on the Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011 (SECC 2011) are used.
- The scheme is fully financed by the Government and involves cost-sharing between the Central and State Governments. Its main goal is to prevent the financial strain of medical costs that often result in almost 6 crore Indians falling into poverty each year.
Key Features of PM-JAY:
- It offers comprehensive healthcare coverage, including secondary and tertiary care, in both public and private hospitals across India.
- PM-JAY provides cashless access to healthcare services at hospitals.
- The scheme covers expenses for up to 3 days before hospitalization and 15 days after, encompassing diagnostics and medicines.
- Beneficiaries face no restrictions related to family size, age, or gender.
- From the first day, all pre-existing medical conditions are covered.
- The benefits are portable throughout the country, allowing beneficiaries to receive cashless treatment at any empanelled hospital.
- A wide array of services, including around 1,929 procedures, are covered, encompassing expenses such as drugs, diagnostics, physician’s fees, room charges, and more.
- Public hospitals receive reimbursement at the same rate as private hospitals, ensuring equitable coverage.
National Health Authority (NHA)
- The National Health Authority (NHA) is the governing body in charge of carrying out the “Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana” (PM-JAY).
- As the apex body, it oversees and executes key aspects of the scheme:
-
- Implementation: The NHA ensures nationwide execution of PM-JAY, making sure benefits reach intended recipients and coverage adheres to the plan.
-
- Strategy Design: NHA develops the strategic framework for effective PM-JAY implementation. It defines coverage, identifies eligible beneficiaries, and establishes operational guidelines.
-
- Tech Infrastructure: NHA spearheads creating essential technological systems for PM-JAY, including beneficiary identification, enrollment, claims processing, and monitoring.
PMJAY Status
Ayushman Cards Created:
- Overall, a total of 24,42,78,276 Ayushman Cards have been generated.
- In the last 30 days, 32,75,246 new Ayushman Cards were created.
Authorised Hospital Admissions:
- The total amount authorised for hospital admissions stands at 67456.21 crore rupees.
- Over the last 30 days, hospital admissions worth 1731.24 crore rupees were authorised.
Hospitals Empanelled:
- The empanelment includes a total of 15,608 public hospitals and 12,083 private hospitals, making a combined total of 27,691 empanelled hospitals.
Key Issues Identified in PM-JAY Implementation in CAG report
Beneficiary Identification and Registration:
- Around 7.87 crore beneficiary households were registered, which is 73% of the target.
- Errors occurred in beneficiary data like invalid names, unrealistic birthdates, duplicate IDs, and inaccurate family member counts.
- Ineligible households received benefits, ranging from ₹0.12 lakh to ₹22.44 crore.
Hospital Empanelment and Management:
- Some Empanelled Healthcare Providers (EHCPs) lacked required infrastructure and quality standards.
- Beneficiaries were charged for treatment at EHCPs, increasing their out-of-pocket expenses.
Monitoring and Grievance Redressal:
- District Implementing Units (DIUs) not formed in some states/UTs.
- Manpower shortages in SHAs and DIUs in several states/UTs.
- Delayed formation of State Grievance Redressal Committees (SGRCs).
- Only a small percentage of grievances redressed within the specified time frame.
- Lack of Anti-Fraud Cell, Claim Review Committees, and Mortality/Morbidity Review Committees in some states/UTs.
- Instances of malpractices in hospitals in Assam and Jharkhand without appropriate actions taken.
To address the issues highlighted in the CAG report and further enhance the effectiveness of Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (PMJAY), a collaborative effort is essential. Improved coordination, rigorous monitoring, and prompt action against malpractices will contribute to ensuring that PMJAY fulfils its mission of providing quality healthcare coverage to the most vulnerable sections of India’s population while upholding transparency and accountability.
About Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG)
- The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) is an independent office established by the Indian Constitution (under Article 148- 151) to oversee financial matters.
- As the head of the Indian Audit and Accounts Department, the CAG is responsible for monitoring the financial systems at both the national and state levels. It is directly responsible to the Parliament of India.
- The CAG is appointed by the President for a non-renewable term of six years to ensure compliance with the Constitution and parliamentary laws in financial administration.
Q1. With reference to Ayushman Bharat, consider the following statements:
- Ayushman Bharat is a flagship Centrally Sponsored Scheme of the Indian government aimed at achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and aligning with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Ayushman Bharat’s Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) focus primarily on curative care and specialised treatments for chronic diseases.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) provides coverage of up to Rs. 5 lakhs per family annually for secondary and tertiary care hospitalisation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (c)
Q2. Consider the following:
- The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) is a statutory body under Comptroller and Auditor-General’s (DPC) Act, 1971.
- CAG is in charge of supervising the financial systems at both the national and state levels.
- The CAG is appointed by the President for a six-year term that is renewable.
- CAG functions under the Ministry of Finance.
How many of the abovementioned statements are correct ?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All Four
Answer: (a)
Q3. Discuss the significance of Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (PMJAY) in achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in India. Highlight its key features, achievements and issues involved.



No Comments