18 Sep “Capital Expenditure: The Catalyst for Economic Growth”
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details of “Capital Expenditure: The Catalyst for Economic Growth”
Syllabus mapping:
GS-3: Economy- Government Budgeting.
For Prelims:
What is the Capex, its types, and recent trends in Capex?
For Mains:
What is the significance of the Capex in overall economic development what are the reasons for the decline/ increase in Capex and how India can manage the CapEX with revenue expenditure?
Why in the News?
Union Finance Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman recently chaired the second meeting to review Capital Expenditure (CapEx) for the Ministry of Railways in New Delhi.

What is the CapEx?
Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital Expenditure (CapEx) refers to government spending focused on acquiring, upgrading, or maintaining physical assets and infrastructure that benefit society. This includes investments in roads, schools, hospitals, public transport, and other essential facilities aimed at enhancing public services and long-term economic growth.
Effective capital expenditure (Capex): Effective capital expenditure (Capex) in India is the total government spending on investments that create long-term assets and infrastructure, plus grants given to the states, for creating capital assets. It’s a measure of the true extent of public investment by the central government.
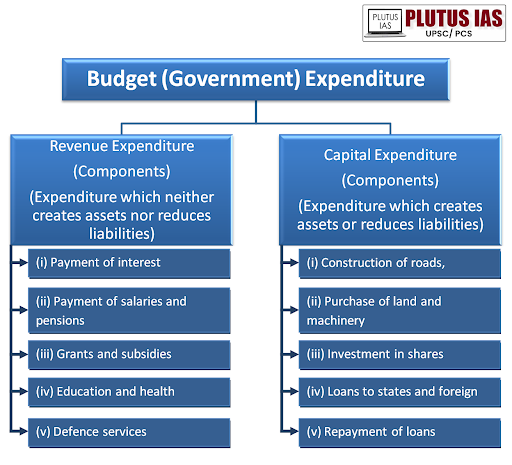
Types of Government CapEx:
Infrastructure Projects: Roads, bridges, and public transportation systems.
Public Facilities: Schools, hospitals, and community centers.
Equipment and Technology: Purchase of machinery for public services, such as waste management or emergency response.
Land Acquisitions: Buying land for future development or conservation.

Examples of Government CapEx
Infrastructure Development: A government might invest Rs 500 crore in building a new highway, improving connectivity, and promoting economic activities in the region.
Public Health Facilities: Allocating funds to upgrade hospitals can improve healthcare services and enhance community well-being.
Education Infrastructure: Investing in new school buildings or renovating existing ones can lead to better educational environments for students.
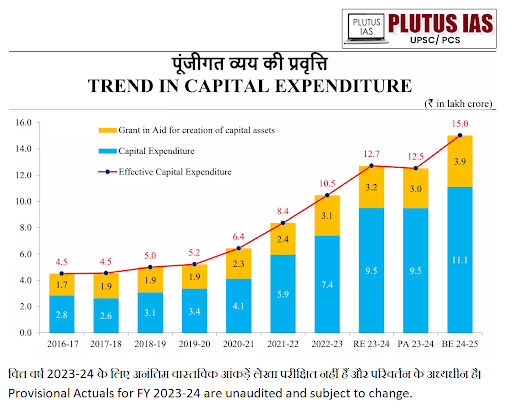
Reasons for the increased CapEx in recent years:
Government Initiatives and Policies: The National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), Make in India, and production-linked Incentive Scheme are the vehicles for increasing the CapEx in the recent period.
Focus on Economic Recovery: Following the economic disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, the government has prioritized CapEx to stimulate growth and job creation.
Public Sector Investment: Increased spending by public sector enterprises, specifically railways and roads to bolster economic activity.
Increased Budget Allocations: Recent budgets have allocated a higher percentage to CapEx, reflecting a commitment to long-term development.
Financing and Investment: Low interest rates and favorable lending conditions have made it easier for both the government and private sectors to finance capital projects.
Emphasis on Infrastructure Development: Recognition of the need for improved infrastructure in transportation, energy, and urban development has driven up CapEx.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Growth in PPP models has led to increased investment from the private sector in infrastructure projects, complementing government spending.
Technological Advancements: Investments in digital infrastructure like Digital India Mission, and technology-driven projects have also seen a rise, aligning with global trends.
Environmental Sustainability: Growing emphasis on sustainable development has led to investments in green infrastructure, such as renewable energy projects.
Features of the CapEx:
Long-term Investments: CapEx represents long-term investments, meaning the assets purchased or upgraded typically have a useful life of one year or more. For example, constructing a bridge or a school has benefits that extend for decades.
Budgeting and Planning: Effective CapEx requires careful budgeting to ensure that funds are allocated efficiently. Governments need to assess the potential economic impact of their investments and ensure they align with long-term goals.
Impact on the Economy: Properly executed CapEx can lead to job creation, improved infrastructure, and enhanced quality of life for citizens. For example, investing in public transport can reduce congestion and pollution, while building schools can improve educational outcomes.
Monitoring and Accountability: Government CapEx is closely monitored by taxpayers, analysts, and policymakers to ensure that funds are spent wisely. Regular reviews and audits help in assessing the effectiveness and efficiency of capital projects.
Depreciation Considerations: Just like in the private sector, the value of capital assets owned by the government can depreciate over time. This impacts future budgeting and funding requirements for maintenance or replacements.
Importance of Capital Expenditure (CapEx)
Creation of Long-Term Assets: CapEx leads to the development of physical assets, such as infrastructure and facilities, which can generate revenue over many years.
Boosting Economic Capacity: By adding or improving production facilities, CapEx enhances operational efficiency and increases the economy’s ability to produce goods and services.
Labor Participation: Investments in infrastructure and development projects can create jobs, increase labor participation, and drive economic growth.
Repayment of Loans: CapEx also includes the repayment of loans, which reduces liabilities and strengthens the financial position of the government.
Future Revenue Generation: Well-planned capital investments can yield significant returns in the future, supporting ongoing public services and economic stability.
Fiscal Discipline: While essential, governments must exercise caution with CapEx to avoid overspending. For instance, in the financial year 2019-20, capital expenditure was 14.2% of the Budget Estimates, leading to necessary cuts in public spending to meet deficit targets.
Challenges that limit the CapEx Impacts:
1. Rapid Rise in Interest Rates: the global scenario is impacting the real potential of government expenditure.
2. Inflation Impact on Capital Allocation: In the last few years the RBI has not been able to limit inflation to the prescribed upper limit this erodes the value of rupees and limits the Capital expenditure’s impact on the economy.
3. Impact of Increased Energy Prices: Due to Global uncertainty India which is the second largest importer of crude oil diverted the funds from the capital accounts.
4. CapEx Challenges in a Recession: India’s ICOR is still high compared to the other developed countries which reflects the capital expenditure is not contributing to sustainable growth.
5. Capital and Human Resource Constraints: Due to the NPA and Crowding out effects banks are averting the loans to the private sector and this is limiting the public-private partnership.
6. Impact of Extreme Weather: In recent times this has the one of the major challenges which limit government expenditure, in fact, extreme weather like Lnaslide floods in some states are consuming the government budget.
7. Unequal developments: The infrastructure projects and developmental projects are contracted in the particular states. For example, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamilnadu, etc.
Ways to boost the CapEX impacts on the economy:
1. Increase Public Investment: The government can allocate more funds to the healthcare education, and infrastructure sectors to boost the CapEx impact on the economic development.
2. Leverage Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Attract Private Investment: Encourage collaboration with private firms for infrastructure projects, sharing risks and rewards.
3. Streamline Regulatory Processes: The simplification of the approvals and enhancing transparency can increase investments. The use of the MCA portal can help in this.
4. Focus on Emerging Sectors: The government now can focus on green energy and other innovative technologies that will help to boost the economy.
5. Improve Financial Access: Provide favorable financing options for capital projects, especially for small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
6. Regional Development Initiatives: the direct CapEx towards emerging regions like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and eastern India will address the regional disparities.
7. Promote Skill Development: The Skill India program and other programs have the potential to provide skills to many youths. Hence government can directly invest in such reward-giving programs.
8. Utilize Technology for Efficiency: Implement advanced project management and monitoring tools to optimize CapEx deployment.
Conclusion:
Capital Expenditure is a critical tool for governments aiming to enhance public services, stimulate economic growth, and improve the overall quality of life for their citizens. Effective planning, execution, and monitoring of CapEx projects ensure that these investments yield long-term benefits and sustainability.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 18th Sep 2024
Prelims Question:
Q. Consider the following expenditures:
1. Payment of Officials in the defense ministry.
2. Purchases of a new machine in ministry
3. Repairing the existing government vehicle
4. Construction of the road in a remote area
5. Transferring the ownership of the Air India
6. Pying debt of the World Bank.
7. Investment in the Government Securities.
How many mentioned above are classified as part of the capital expenditure (CapEx) of the Government of India?
A. Only two
B. Only three
C. Only Four
D. Only five.
ANSWER: B
Mains Question:
Q. Account for the recent increase in the capital expenditure of the government of India and mention the significance of the CapEX for the economic development in India.
(150 words 10 marks)




No Comments