31 Jul Contribution Of Vakil, Gadgil, and V.K.R.V Rao in Pre-Liberalization Era
Contribution of Vakil, Gadgil, and V.K.R.V Rao in Pre-Liberalization Era
India’s economic development after independence until the 1991 liberalization was heavily influenced by its own economists and indigenous models of development. Among the most influential thinkers were Vakil, D.R. Gadgil, and V.K.R.V. Rao. These economists shaped the course of Indian planning, development policies, and growth strategies in the early years of the Indian Republic, based on the specific socio-economic conditions of a newly independent nation.
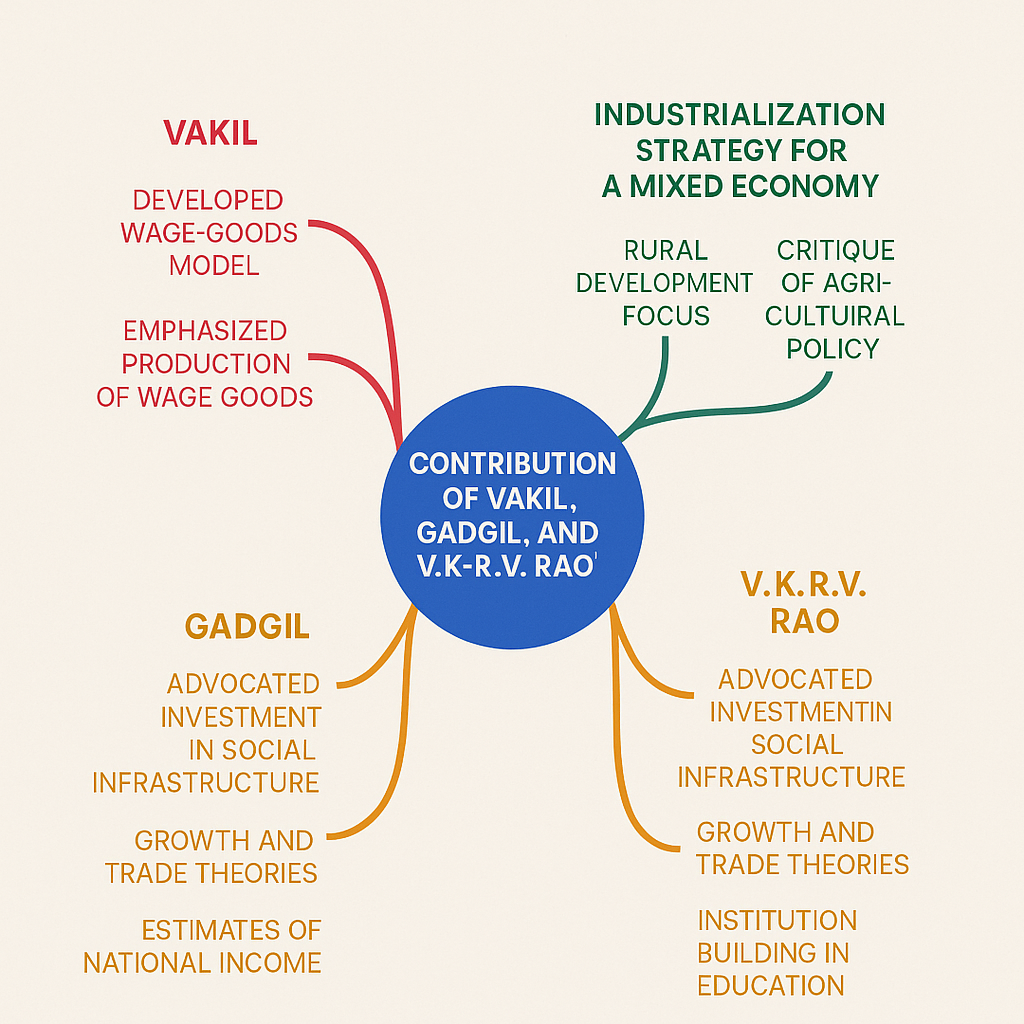
Mind Map: Contributions of Vakil, Gadgil, and V.K.R.V Rao
1. Vakil and Wage-Goods Model
Professor C.N. Vakil, along with P.R. Brahmananda, made a seminal contribution to development economics through the formulation of the Wage-Goods Model.
1.1 Theoretical Foundations
- The model emphasizes the centrality of wage-goods in determining employment and income.
- It critiqued the Mahalanobis heavy industry-biased strategy adopted in the Second Five Year Plan.
- Vakil and Brahmananda argued that without adequate production of wage-goods (like food, clothing), increased employment in capital goods sectors would cause inflation and demand bottlenecks.
1.2 Relevance in Indian Context
- India had vast disguised unemployment in agriculture. The model advocated surplus labour be shifted to wage-goods producing sectors.
- Food security, price stability, and rural employment were emphasized.
1.3 Policy Implications
- Recommended prioritizing investment in agriculture and consumer goods sectors.
- Helped initiate debate around balancing capital and consumer goods investment in Indian planning.
Graduation degree with IAS coaching
2. D.R. Gadgil and Decentralized Planning
Dhananjay Ramchandra Gadgil was instrumental in promoting a decentralized, participatory approach to planning that diverged from the highly centralized model of the Planning Commission.
2.1 Gadgil Formula
- Used for resource allocation among Indian states during the Fourth and Fifth Five-Year Plans.
- Focused on objective criteria: population (60%), per capita income (10-20%), tax effort, special problems, and infrastructure.
2.2 Focus on Rural Development
- Emphasized strengthening Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) for grassroots-level economic planning.
- Called for investments in rural infrastructure — roads, irrigation, health, and primary education.
2.3 Social Infrastructure Investment
- Advocated health and education as essential components of economic growth.
- Supported prioritizing the development of small-scale and cottage industries to address rural underemployment.
2.4 National Income Estimation
- Made pioneering attempts to estimate national income with a regional perspective.
- Laid groundwork for state-level economic statistics that informed planning.
3. V.K.R.V. Rao: The Institutional Economist
Dr. V.K.R.V. Rao was a visionary economist and educationist who significantly contributed to the understanding of national income, institutional economics, and the role of social infrastructure in development.
3.1 National Income Estimates
- One of the first Indian economists to provide a scientific estimate of national income in India (1931-32 data).
- Led the establishment of National Income Accounting in post-independence India, contributing to data-led planning.
3.2 Growth and Trade Theories
- Contributed to economic theories on the relationship between trade and development in developing nations.
- Supported a mixed economy model with adequate safeguards for indigenous industry against foreign competition.
3.3 Education and Institution Building
- Founder of Delhi School of Economics, Institute of Economic Growth, and others.
- Believed in education as an essential element of development strategy.
- His institutions became hubs for empirical research guiding India’s early economic policies.
3.4 Policy Engagements
- Member of the Planning Commission, Education Minister, and Vice Chancellor of University of Delhi.
- His integration of economics with public policy set a template for future economists in governance.
Infographic: Key Contributions of Vakil, Gadgil & V.K.R.V. Rao
Best economics optional coaching for upsc
Best economics optional teacher for upsc
best economics optional test series
4. Comparative Perspective
| Economist | Main Contribution | Relevance to Indian Planning |
|---|---|---|
| Vakil | Wage-Goods Model | Rural employment, food security, inflation control |
| Gadgil | Decentralized Planning | State-level resource allocation, rural development |
| V.K.R.V. Rao | National Income, Institution Building | Empirical data for planning, education as economic investment |
5. Legacy and Contemporary Relevance
- Vakil’s focus on wage-goods remains relevant for poverty alleviation policies like MGNREGA and food security.
- Gadgil’s decentralized planning approach laid the foundation for Panchayati Raj and local governance reforms.
- Rao’s emphasis on data-driven policy-making and education retains vital significance in India’s growth strategy.
Previous Year UPSC Questions (Mains)
- Discuss the significance of indigenous economic thinkers in shaping India’s planning approach. (2022)
- What was the contribution of D.R. Gadgil to Indian planning? Explain with examples. (2019)
- Examine the relevance of the Wage-Goods Model for a developing economy like India. (2017)
Probable Questions for UPSC
- Critically examine the role of V.K.R.V Rao in building India’s statistical and educational infrastructure.
- Compare and contrast the approaches of Vakil and Gadgil in tackling poverty and unemployment.
- How did these economists shape the evolution of mixed economy thinking in India?
Probable Prelims Questions
- Who proposed the Wage-Goods Model for employment generation in India?
- Which economist’s formula was used for inter-state resource allocation in Five-Year Plans?
- Who was the founder of the Delhi School of Economics?




No Comments