
04 Feb Daily Current Affairs 4th February 2021
The Urban Vision
Statistics: census office definition:
(a) All administrative units that have been defined under statute (i.e., settlements declared based on state government definition).
(b) Administrative units satisfying the following three criteria:
(i) A minimum population of 5,000 persons;
(ii) 75 percent and above of the male main working population being engaged in non–agricultural pursuits; and
(iii) A density of population of at least 400 persons per sq. km. (1,000 per sq. mile).
Facts for UPSC-> Urban area provide more 80 percent of world GDP and more than 70 percent of Greenhouse gasses according to U.N.
-
-
-
- In India 30 percent of the population resides in urban areas and provides more than 70 percent of G.D.P. according to the U.N. by 2030 50 % population will be in the urban area.
Why Urban areas are important.
-
- They provides
- Agglomerates economy.
- Concentration of resources (Physical +Human)
- Economy in process and production (e.g. in cities you can find a software engineer, a cobbler, technician etc.)
- What more
- Provides Jobs, good living standard.
- Provides good social services e.g. Education, health.
- They are the engines of economies.
- Provides connectivity to various places there by feeling of brotherhood.
- Help to eradicate the caste system.
- Provides women an economic opportunity.
- Labour market pooling( more number of different skills persons are available)
- Knowledge spillover. (i.e. new entrepreneurs, new jobs etc.)
-
- What is the issue in indian urbanisation
- Messy and Hidden
- Issue of migrants such as no home, no jobs, underpaid.
- Issue of high land prices
- Deficit in physical and financial infrastructure.
- Issues in urban governance
- Lack of Fund
- Lack of skilled human resources
- Unnecessary state government control over budget.
- Lack of power devolution from state government.
- Issues such as degraded environment, slums, crime.
- How to tackle
- Use of technology for crime prevention such as A.I, CCTV etc.
- Devolution of fund and power to the Local government
- People participate in governance to mobilise local resources.
- Good Governance.
- Slum rehabilitation and provision of Home to newcomers such as P.M.AAY.
- Water conservation to be made mandatory for the new physical infrastructure.
- To remove the high rent issue, model tenancy act implementation.
- Free the land from the loss making PSU by Privatisation as suggested by 2nd ARC.
- Swarn rajput
Issue Of Biodiversity and Pandemic
Why Biodiversity is important:
- 20% of countries have fragile ecosystems (including India).
- 55% of the global GDP depends on biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Provides different services such as supporting and in figure.
What are the Threat to Biodiversity:
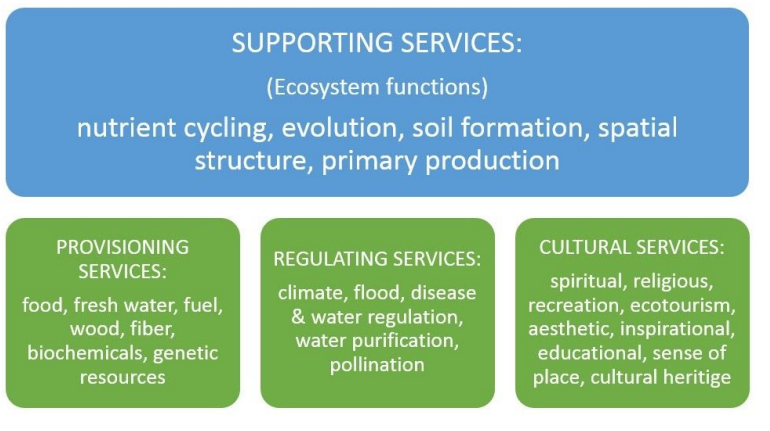
Way Forward:
- Integration of Economies with Biodiversity rather than seeing into silos.
- reduce investments and subsidies in the activities that will degrade our natural habitats
- Global cooperation.
- enhance investment in research and development in sustainability science.
- To restore and enhance biodiversity->, strengthen its sustainable use +generate green jobs + encourage the Indian public to participate and appreciate the natural and associated cultural treasures
- Swarn rajput
DNA Technology (Use and Application) Regulation Bill, 2019
Context:
- The contentious provisions of the DNA Technology (Use and Application) Regulation Bill, 2019 was reviewed by retired Supreme Court judge Justice Madan Lokur.
- In his submission, he feared that such unbridled power could be abused/misused categorically and it can be a threat to the life, dignity, liberty of the private citizens of the country.
- Justice Madan Lokur submitted his report to the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Science and Technology.
History and existence of the bill:
- The bill was passed in 2019 by the Parliament with the hope that the scientific procedures would bring accuracy and swiftness in the justice delivery system.
- The bill was originally introduced in August 2018 in the Lok Sabha but lapsed.
- The utility of DNA(Deoxyribonucleic Acid) based technologies for solving crimes, and to identify missing persons was the driving force in tabling the bill.
- The bill also mandates the establishment of a DNA Regulatory Board; accreditation of DNA laboratories undertaking DNA testing and analysing.
- Collection of DNA would be based on the following categories, which are; the victims, offenders, suspects, undertrials, missing persons and unknown deceased persons.
Key Issues:
- The bill does not define each and every term mentioned from whom the DNA data will be collected from.
- The category ‘suspect’ is a vague one. The fear is that this category will be exploited as much for violating the right to privacy on a mere suspicion.
- Cast and community based profiling remains the biggest worry of all.
- The fear of planting evidence for repeated offenders is a possibility for which there are no safeguards as yet.
Way forward:
- A strong data protection law is the need of the hour to counter the apprehensions on misuse of data.
- Existence of procedural safeguards to prevent the leakage or manipulation of DNA samples and an allocation of time frame in some cases would go hand in hand.
- On the issue of privacy, consent can be sought for crimes that are less heinous.
Q. How does DNA technology work?
|
-Ajit Satapathy
Air pollution: Contribution of Cement
Context:
- Recently, the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has directed the Northern Railway to construct warehouses on platforms for the handling of cement bags in a bid to curb air pollution resulting from loading and unloading of the cement bags.
- The Delhi Pollution Control Committee (DPCC) imposed a fine on the Northern Railway for failing to curb pollution.
History:
- Cement manufacturing, the stone-like building material, is responsible for 7% of global carbon dioxide emissions. That is even higher than the combined emissions of all the trucks in the world.
- The reason why cement’s contribution to emissions is immense because of the chemical process required to produce it.
- India, after China, is the biggest cement producer in the world and it contributes to 8% of the global capacity as of 2019.
Key Issues:
- 98% of the total cement production in India are privately owned. The demand for the sustainable materials is very low and hence it is a hindrance in regulating production and keeping the economic activity on par with market demands.
- It is estimated that the cement production will rise by 12%-23% by 2050. Hence, the contribution to the air pollution will increase proportionally.
- The cement products which cause lower environmental stress are often expensive than the regular product. Hence, there is no sustainable alternative to meet the market demand.

Way forward:
- The Cement Sustainability Initiative(CSI) is a global group of major cement producers who operate in multiple countries who believe there is a strong business case for the pursuit of sustainable development.
- India became an associate member of The International Energy Agency(IEA) in 2018 which works to ensure reliable, affordable and clean energy for its member countries.
- Plants installed before the 1990s are operating at relatively high energy consumption levels and hence need to be modernized.
- Production of blended cements (Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) and Portland Slag Cement (PSC)) in the country in the year 2010-11 was as high as 67%, as against only 36% in 2000-01 reflects that we are using secondary materials.
- Strict regulations must be in place to ensure that the lapses in curbing pollution are penalised and adhering to prescribed norms are incentivised
Ajit Satapathy
Stardust 1.0
Context-
Recently Stardust 1.0 has been launched from Maine. The United States has become the first commercial space launch which is powered by biofuel.
About Stardust 1.0-
- It is a launch Vehicle which is suited for student and budget payload.
- The rocket is manufactured by Blushift which is an aerospace company based in Maine.
- The company is associated in developing rockets that are powered by bio-derived fuels. The Rocket is 20 feet tall and it has a mass of approximately 250 kg
Objective-
Such efforts are part of a growing number of commercial space companies that are working to provide easier and cheaper access to space to laypeople.
What is Biofuels-
- Any Hydro-carbon fuels that are produced from an organic matter in a short period of time.
- The two most common kinds of biofuels used these days are ethanol and biodiesel and they both represent the first generation of Biofuel
– Khyati Khare
PRELIMS FACTS-
ASEAN india Hackathon 2021 launched by Ministry of Education

Ramesh Pokhriyal Nishank addressed the inaugural ceremony of ASEAN India Hackathon 2021 from February 1 to February 3.
Purpose–To build the economic and cultural ties through cooperation in the field of science and technology and education.
2. Union for International Cancer Control celebrated World Cancer Day on 4 February

Theme- I Am And I will.
Purpose- To raise awareness about cancer and presing governments and individuals across the world to take action against the diseases.
Headquarters–International Cancer Control –Geneva , Switzerland
3. First Centre for Wetland Conservation and Management gets by India

The Ministry of Environment,Forest and Climate Change opened the first National centre for Sustainable Coastal Management ,Chennai on an occasion of wetland day.
Announced by- Babul Supriyo Minister of State for Environment ,Forest and Climate Change.
– Alokit Kapoor
[download id=”33242″]



No Comments