
05 Feb Daily Current Affairs 5 FEB 2021
Challenges and Opportunities to the democracies in Modern times
Context:
Foreign celebrities used Twitter to raise their voice against farm laws on the pretext of farmer protest. Contrary to this indian government initiated a campaign against them and others by saying defamation of India.
Big Picture:
What is democracy and sovereignty?
Democracy is a political system where everyone has a say in the state’s affairs and has equal rights about the social, economic and political arena.
Sovereignty is defined as the power of the state to take decisions by itself freely.
Is the Sovereignty of India in danger?
The answer lies in the preamble of our constitution, which states India is a sovereign, socialist and democratic republic. But the same constitution (DPSP Article 50) also asks the government to follow a global order i.e. respect the international laws and treaty.
Here Lies the fundamental question of endangering democracy.
- Answer to this question is though india is a sovereign country but international order created by the countries that are rich and strong. So these global order favors them more than India or the other 3rd world countries e.g. UNSC resolutions about Libya, and some other african countries.
- Many critics argue that W.T.O. and other institutions have also somewhere diluted the sovereignty of nations where state has to abide by the global order.
Challenges to Democracy:
- Recent issues of Big Tech Firm intervention in the election e.g. Cambridge Analytical scandal in USA election.
- Big tech firms are dictating the way people think e.g. #Tag on Twitter, suspension of D.J.Trumph account from Twitter.
- In India communalism, regionalism, terrorism, and manipulation based on Big Data.
- Big economies twist the hands of small one e.g. Chinese high-interest loans to economies.
- Poverty (India’s rank in the global hunger index is 94/107)
- inequality is also a bigger threat where the Gini coefficient has risen from .43 in 1990 to .45 in 2005, India’s rank in the Human development index is 131 in 2020.
- Russian and Chinese hackers intervene in the development of India and other economies e.g. the recent kudankulam virus attack and Stuxnet attack in Iran.
- Placing the economic sanctions by one country on another e.g. USA sanction on North Korea and Iran
- India’s rank in the human freedom index in 2020 is 111.
What are the Opportunities
- Democracy provides the way forward when other systems are failing.
- It has the way to raise the voice of people through protest, dissent, etc.
- Though the Chinese development model has described its own merit, suppression of people’s voices remains a concern that is widely accepted by the world community.
- It provides engendering development.
- Engaging with the outside world to provide the success story and to learn from other’s success.
- Check over human right violations and check the government.
What India can learn from recent protests.
- The antidote to the dissent voice or protest is giving them more freedom to express and if they are threatened then counter them ideologically. The beauty of democracy is that it provides an equal voice to raise the issue.
Additional Information:
- Recent amendment in FCRA
- suspension of Greenpeace license
- suspension of Amnesty international’s license
Swarn Rajput
Lok Sabha’s Continuous disruptions
Context: repeated disruptions in the parliament as a united Opposition insisted on having a separate discussion on the farm laws.
Having a Big Picture about Parliament’s functioning, issues, way forward.
- Parliament consists of Rajya sabha (Under article 80), Lok sabha (Under Article 81), and President (Under article 52).
Rajya Sabha:
- Maximum strength is 250, the election of M.P. by MLA of states and UT of pondicherry and Delhi.
- Election through proportional representation system by single transferable vote.
Lok Sabha:
- Maximum strength is 550 ( Earlier it was 552 but CA.A 104 has done away with the reservation to the anglo Indian.)
- Election mode is a direct election based on the constituency.
Features of Parliamentary Government.
- Nominal and Real executive.
- Majority Party rule.
- Collective responsibility-> They act as a team i.e. swim and sink together.
- Political Homogeneity.
- Double membership.
- The leadership of the Prime Minister.
- Dissolution of the Lower House.
- Secrecy-> principle of secrecy of procedure should be upheld by ministers, they cannot divulge information about their proceedings, policies, and decisions.
Parliamentary Powers.
- The Parliament enact legislation for the country.
- ensure that the executive does not overstep its authority and remains responsible i.e. responsible government.
- The financial powers -> grant of resources to the government + ensure the government does not misspend or overspend. This functioned through annual financial statements under article 112.
- Highest forum of debate in the country.
- Parliament considers and represents the divergent views of members from different groups of different parts of the country.
- Parliament also performs some electoral functions. Election of president and vice president, speaker, vice speaker, etc.
- Judicial functions-> Parliament decides about the removal of President, vice-President, and judges of High Courts and Supreme Court.
Shortfalls in our Parliamentary system
- Anti-defection law -> restrains MPs from voting according to their conscience but allows according to political parties’ dictation.
- Lack of recorded voting -> reduces the accountability of the MP ie. voters don’t know about M.P. stand.
- Party affiliation of the Speaker
- Frequent bypassing of committees (just 25% of Bills have been referred to committees in this Lok Sabha).
- Insufficient time and research support to examine Bills.
- Parliament doesn’t have a calendar. (Parliament is held at the convenience of the executive).
What are the issues in our Parliament?
- Criminalization of parliament. According to A.D.R, 43 % of M.P.s are criminals.
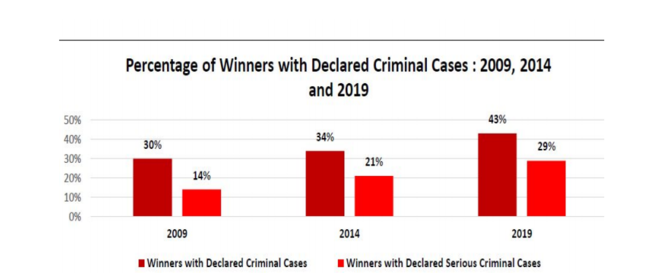
- Women’s representation is 14 %.
Delay in policymaking:
- Several critical issues raised in the Parliament have seen a slow movement. Example: Passing of Triple Talaq Bill, judicial accountability bill, delay in GST bill, judicial accountability bill etc.
Protests and walkouts:
- The recent walkouts and protests for farm laws and in the past also show a waste of precious time of parliament.
Lack of debate and discussion over key issues:
- The recent 124th constitutional amendment bill which provided 10% reservation to EWS was passed after just a single day of discussion.
Duration for which Parliament meets:
- Average number of days parliament met in the past came down to 70 in 2017 from 120 in the 1950s.
Un-parliamentary behaviour:
- Instances of disruptions + physical violence e.g. slogans and shouting,watching movies in parliament,using pepper sprays, etc.
Absence of MPs
Waste of taxpayers’ money:
- The budget session washout of 2018 is estimated to have cost the nation almost 200 Crore based on loss of productivity and expenses of running both houses of Parliament.
Poor image in world media
- It shows India is not a substantive democracy.
Way Forward: Measures to improve its efficiency.
- Training for parliamentary members about the business of the house.
- A minimum 120 days of meeting of both the houses must be mandated through legislation as suggested by 2nd ARC and NCRWC.
- Salaries + privileges of legislators should be linked to the performance. Penalty by speaker and chairmen including imposition of fines, suspension from session etc. for unruly members.
- Presiding Officers should be given more power to control unruly behaviour of members.
- a code of conduct and code of ethics for members of the house to make them ethical.
- Political parties should be made more responsible for their conduct inside the Parliament.
- coordination committees to include members of the ruling party and opposition for smooth conduct of the House.
- Introduction of reforms in Parliament
- Reforms in political parties and government should also be the focus.
Swarn Rajput
Bill To Define Delhi Govt. And L-G Powers
Context:
- The Home Ministry is all set to introduce a legislation in the Budget session of the Parliament to amend the Government Of National Capital Territory Of Delhi Act, 1991 pertaining to the powers and functions of the Delhi government and the Lieutenant Governor.
- The legislation aims to provide greater details of the roles and power of the LG in addition to define the powers of the Delhi government on the lines of the Supreme Court judgment of February 2019.
Supreme Court Verdict in 2019:
- The Court confirmed the Delhi High Court’s decision that the Anti-Corruption Branch’s jurisdiction is confined to Delhi officials and statutory bodies. It does not extend to Central government officials.
History of Conflict:
- The Delhi Govt. and the Central Govt have been at loggerheads with respect to jurisdiction over various matters, allocation of funds and matters to do with legal proceedings as well.
- In 2016, the LG was often accused of snooping on Delhi CM and other ministers, acting on the behest of the Prime Minister office’s discretion.
- In 2015, suspension of two all India Service officers were suspended by the Delhi Govt., which brought the debate of jurisdiction even further.
Latest Court Verdict related to this matter:
- In 2016, the court declared the L-G the boss of Delhi.
- In 2017, a five-judge Constitution Bench reserved its judgment reversed the decision and proclaimed that the LG can not stultify daily governance by sitting over files.
- In 2019, the top Court observed that the National Capital Territory of Delhi does not have either legislative or executive power over the police.
Way Forward:
- Keeping in mind that the Delhi NCR is a region with special features having the state assembly and the Central Govt influence, conflicts are bound to happen.
- Keeping this in mind the SC has already laid down the foundation and the role and powers of each organ of the state has been defined.
- The said legislation is said to bring more parity and clarity in roles of both LG and the elected legislatures of the Delhi assembly.
-Ajit Satapathy
PRELIMS FACTS
1. According to.the report published by PHDCCI for resilient economy in 2021 India stands second in the world
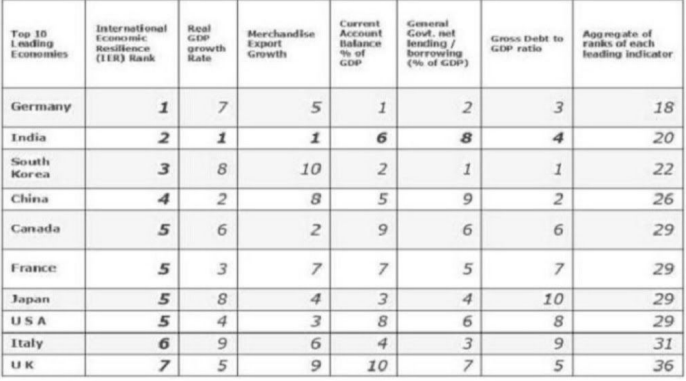
PhD Chamber of Commerce and Industry released a report as per the International Economic resilience 2021 in which India ranked second.The first rank secured by Germany.It reflects India’s strong “economic resurgence” to the global economic turmoil caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The ranking is based on analysis of five indicators
Real GDP growth rate,Merchandise export growth rate, Current account balance (as a percentage of GDP), General government net lending/borrowing (as a percentage of GDP) and Gross debt-to-GDP ratio
2.HAR GHAR PANI,HAR GHAR SAFAI MISSION LAUNCHED BY PUNJAB CM

Jal Jeevan mission of GoI, NABARD, World Bank and the State Budget funded for this scheme to provide 100% potable piped supply in all rural households
3 . Unified web portal for monitoring progress of GOBARDHAN activities launched by Government of India

Various ministry participate in this unified web portal Agriculture Minister Narendra Singh Tomar, Petroleum Minister Dharmendra Pradhan, Animal Husbandry Minister Giriraj Singh, Jal Shakti Minister
Gajendra Singh Shekhawat and Minister of State forJal Shakti Rattan Lal Kataria to monitor the GOBARDHAN activities across the natioN.
GOBARDHAN
- It is beneficial for the rural people by sanitizing andcleaning the villages and increasing farm yields.
- Consider dung not to be used as a waste but also usedas a source of income.
- Gobardhan aims to positively impact village cleanliness and generate wealth and energy from cattle and organic waste.
Alokit Kapoor
[download id=”33557″]




No Comments