03 May Drug Trafficking: A Global Threat to Security and Public Health
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the Topic Drug Trafficking: A Global Threat to Security and Public Health
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
GS-3-Internal Security- Drug Trafficking: A Global Threat to Security and Public Health
FOR PRELIMS
What is drug trafficking? Why is it a serious issue in India?
FOR MAINS
What is the purpose of the Narco Coordination Centre (NCORD)?
Why in the News?
The Amritsar Zonal Unit of the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) has successfully dismantled a major drug diversion cartel through a four-month-long operation spanning four states. The operation resulted in the seizure of drugs worth ₹547 crore and the arrest of 15 individuals. Union Home Minister Amit Shah congratulated the NCB via social media, highlighting the crackdown as a major step towards achieving a drug-free Bharat under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision.

What is drug Trafficking?
Drug Trafficking refers to the illegal trade, cultivation, manufacture, distribution, and sale of substances that are subject to drug prohibition laws. It is a major aspect of organised crime and is considered a serious global issue due to its wide-ranging social, economic, and health impacts.
Key Features of Drug Trafficking:
1. Illicit Production: Growing, producing, or synthesising drugs like heroin, cocaine, cannabis, methamphetamine, etc.
2. Distribution and Transport: Smuggling drugs across borders or within countries via land, sea, or air routes.
3. Sale and Supply Chains: Involves both large criminal networks and street-level dealers.
4. Money Laundering: Proceeds from drug sales are often funnelled into legitimate businesses to conceal the origin of funds.
Drug trafficking scenario in india
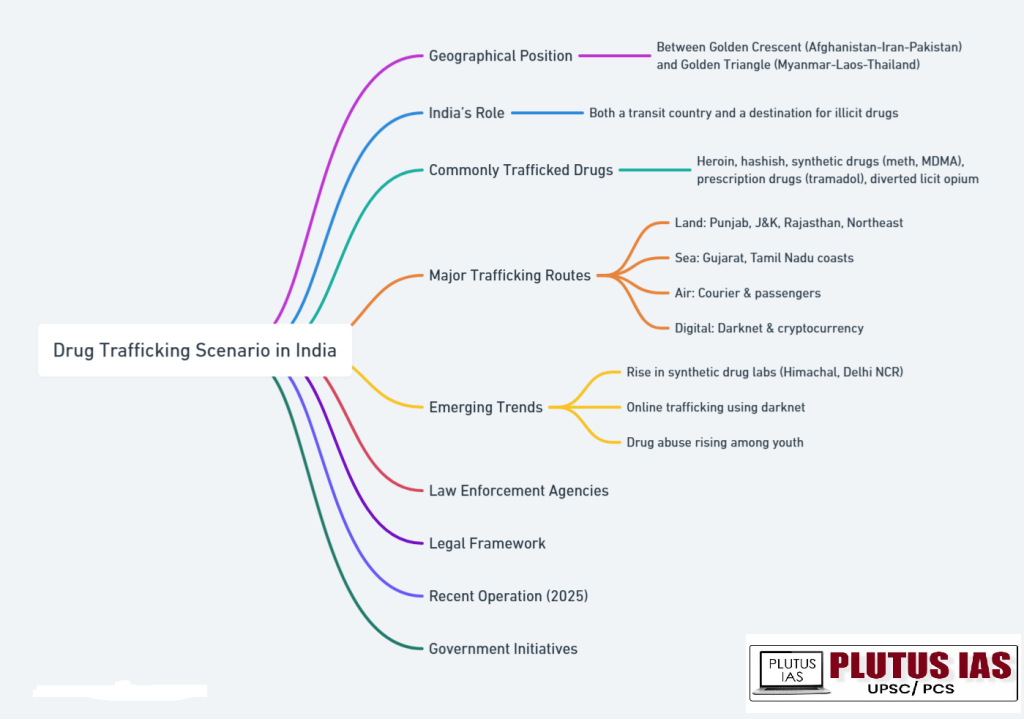
Drug trafficking as a threat to national security
1. Narco-Terrorism: Drug money funds terrorist and insurgent groups, especially in Punjab, J&K, and the Northeast.
2. Cross-border Threat: Smuggling across porous borders (Pakistan, Myanmar) undermines sovereignty and fuels illegal arms trade.
3. Organised Crime Nexus: Strengthens criminal syndicates involved in extortion, arms, and human trafficking.
4. Social Instability: Drug addiction, especially among youth, leads to crime, unrest, and loss of human capital.
5. Economic Impact: Fuels black money, money laundering, and distorts the formal economy.
6. Digital Challenge: Use of darknet and crypto makes enforcement difficult, posing cyber-security threats.
7. Border Security Challenge: Exploits gaps in coastal and land borders, burdening security agencies.
Govt measures to combat the menace of drug trafficking
1. NDPS Act, 1985: The primary legal framework to regulate and prohibit the production, sale, and trafficking of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
2. Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB): Apex agency for coordinating anti-drug operations across states and with international agencies.
3. Narco Coordination Centre (NCORD): Multi-agency platform set up in 2016 to enhance coordination among central and state enforcement agencies.
4. National Policy on Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (2012): Aims at curbing supply and demand through strict enforcement and de-addiction measures.
5. Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA): Awareness and rehabilitation campaign launched in 2020 across 272 high-burden districts.
6. Strengthening Border Surveillance: Enhanced deployment of BSF, Assam Rifles, and coastal security to check cross-border drug smuggling.
7. Use of Technology and Intelligence Sharing: Deployment of drones, surveillance systems, and creation of a real-time intelligence sharing network among agencies.
8. International Cooperation: Bilateral treaties and collaboration with UNODC, SAARC, and neighbouring countries for joint operations and control of precursor chemicals.
9. Financial Tracking and Anti-Money Laundering: Involvement of ED and FIU to trace and seize proceeds of drug trafficking under PMLA.
Challenges in combating drug trafficking
1. Porous and Sensitive Borders: Difficult terrain along borders with Pakistan, Myanmar, and coastal areas aids smuggling.
2. Organised Transnational Networks: Drug cartels operate across countries with sophisticated logistics and safe routes.
3. Diversion of Licit Drugs: Misuse of government-approved opium cultivation and pharmaceutical drugs complicates enforcement.
4. Technological Evasion: Use of darknet, encrypted messaging, and cryptocurrency for anonymous trade.
5. Limited Inter-agency Coordination: Jurisdictional overlaps and poor coordination between central and state agencies.
6. Manpower and Capacity Constraints: Lack of trained personnel and advanced equipment in enforcement agencies.
7. Corruption and Political Nexus: Infiltration of drug money into local administration and politics weakens anti-drug efforts.
8. High Demand and Youth Addiction: Rising domestic demand, especially among youth in border and urban areas.
9. Weak International Enforcement Mechanisms: Delays in extradition, intelligence sharing, and joint operations with other countries.
Way forward
1. Strengthen Border Security: Enhance surveillance through technology, drones, and intelligence-sharing at porous borders and coastal areas.
2. International Cooperation: Strengthen ties with neighbouring countries, UNODC, and global drug control agencies for coordinated anti-trafficking operations and precursor chemical control.
3. Stricter Enforcement of NDPS Act: Regular amendments to ensure stricter penalties and faster judicial processes for drug-related offences.
4. Capacity Building of Enforcement Agencies: Train law enforcement with modern tools, techniques, and intelligence-gathering methods to combat organised crime networks.
5. Community Engagement and Awareness: Expand campaigns like Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan to raise awareness and reduce drug abuse, particularly among youth.
6. Focus on Prevention and Rehabilitation: Increase investments in rehabilitation centres, vocational training, and community-based programs for de-addiction.
7. Technological Interventions: Utilise AI and blockchain for better tracking of drug transactions, and adopt cybersecurity measures to combat darknet trafficking.
8. Strengthening Financial Monitoring: Enhance monitoring of illegal financial flows, enforce stringent anti-money laundering (AML) measures, and track drug profits through agencies like ED and FIU.
9. Public-Private Partnerships: Foster collaboration between the government, civil society, NGOs, and the private sector for sustainable solutions to drug trafficking.
Conclusion
Drug trafficking remains a critical threat to India’s national security, societal stability, and economic integrity. It involves complex transnational networks, spanning illicit drug production, distribution, and sale, while also fuelling organized crime, terrorism, and addiction. While the government has made significant strides through legal frameworks, enhanced law enforcement, international cooperation, and public awareness programs, challenges such as porous borders, technological evasion, and political nexus persist. To effectively combat drug trafficking, India must focus on strengthening border security, enhancing inter-agency coordination, and deploying advanced technologies. Furthermore, a multi-faceted approach involving stricter enforcement of existing laws, active community participation, and international collaboration is essential. By investing in rehabilitation, awareness campaigns, and financial monitoring, India can curb the growing menace of drug trafficking, ensuring a safer and more secure future for its citizens.
Prelims Questions
Q. Which of the following statements is correct about the Red Corridor in India?
1. It refers to areas affected by Left-Wing Extremism (LWE).
2. The Red Corridor spans only across the northeastern states of India.
3. The Government has launched the “SAMADHAN” strategy to tackle LWE in this region.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Answer: B
Mains Questions
Q.”Drug trafficking in India poses a severe threat to national security, social stability, and the economy. Discuss the challenges and the measures the government is undertaking to tackle this menace.”
(250 words, 15 marks)




No Comments