24 Jul Duopoly
Duopoly – UPSC Economics Optional Notes
Includes Mind Map, Infographic, PYQs, and Probable Questions
Introduction
Duopoly is a special form of oligopoly where the market is dominated by only two producers or sellers. It plays a crucial role in the understanding of strategic interaction and competition under limited market players. Various models like Cournot, Bertrand, Edgeworth, and Stackelberg attempt to capture the unique features of duopolistic markets.
Definition of Duopoly
Duopoly is a market structure in which two firms control the market. Each firm must consider the reactions of its competitor when making output and pricing decisions. This leads to a situation of mutual interdependence, making game theory an essential tool in its analysis.
Best economics optional coaching for upsc
Assumptions of Duopoly Models
- Only two sellers operate in the market.
- Products may be homogeneous or differentiated.
- Firms act strategically considering rival’s actions.
- Entry of new firms is restricted.
- Demand function is known to both firms.
Duopoly Models in Economic Theory
1. Cournot Duopoly Model
Assumptions: Firms choose quantities simultaneously. Each firm assumes the rival’s output remains fixed.
Equilibrium: Occurs when neither firm wants to change its quantity, given the other’s output – called Cournot-Nash Equilibrium.
Key Insight: Price is above marginal cost, and profits are lower than monopoly but higher than perfect competition.
2. Bertrand Duopoly Model
Assumptions: Firms compete by setting prices simultaneously for identical products.
Outcome: Price competition leads to price = marginal cost, resulting in zero economic profit – similar to perfect competition.
Paradox: Two firms can mimic perfect competition under price wars.
3. Edgeworth Duopoly Model
Assumptions: Firms have capacity constraints and compete on prices.
Feature: No stable equilibrium – firms undercut each other until prices fluctuate cyclically.
4. Stackelberg Model
Assumptions: One firm acts as a leader and chooses output first; the other firm reacts.
Result: The leader firm earns a higher profit due to its first-mover advantage.
Mind Map
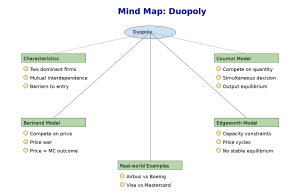
Duopoly_MindMap
Infographic – Duopoly Models Comparison
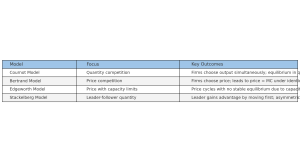
Duopoly_Infographic
Real-world Examples of Duopoly
- Airbus and Boeing: Dominate the global aircraft manufacturing industry.
- Visa and Mastercard: Dominate the global credit card processing industry.
- Coke and Pepsi: In some national markets, they form a near-duopoly in soft drinks.
Implications for Price and Output
- Price rigidity is possible under tacit collusion.
- In Cournot and Stackelberg models, quantity is the decision variable.
- Bertrand model leads to zero profits unless there is product differentiation or capacity constraints.
- Strategic interdependence is central – firms anticipate reactions.
Graphical Representations (suggested)
- Cournot Equilibrium: Reaction curves intersecting.
- Bertrand Equilibrium: Price touching marginal cost line.
- Stackelberg: Follower’s reaction curve and leader’s advantage zone.
Tip: Include these as custom images using economic graph plotting tools or in classroom slides.
Evaluation of Duopoly
- Strength: Realistic representation of many industries with 2 large players.
- Limitation: Assumptions of simultaneous moves may be too simplistic.
- Strategic Insight: Game theory helps model behavior more accurately in duopolies.
UPSC Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
- UPSC 2023: Explain the Bertrand paradox in the context of price competition in duopoly markets.
- UPSC 2021: Distinguish between Cournot and Stackelberg duopoly models with the help of reaction functions.
- UPSC 2018: What are the implications of interdependence in duopoly models? Discuss.
Probable Questions for UPSC Prelims and Mains
- Mains: “In the Bertrand model, two firms can achieve perfect competition outcome.” Examine with diagram.
- Mains: Compare and contrast the Cournot and Edgeworth models of duopoly.
- Prelims: Which of the following statements is true about Cournot Duopoly? (MCQ format)
Conclusion
Duopoly theories provide deep insights into competitive strategy, interdependence, and market outcomes. As many real-world markets mirror duopolistic structures, understanding these models is critical for UPSC aspirants, especially for those selecting Economics as their optional subject. Focus on diagrammatic clarity, logical distinctions between models, and real-life applications to maximize your score.




No Comments