31 Jan Supreme Court in India to hear Electoral Bonds petition
Supreme Court in India to hear Electoral Bonds petition
The article talks about how the Electoral Bonds in India impact the Indian Polity and Governance- Constitution that is related to daily current affairs for UPSC examination.
Relevance for Prelims: Need and Relevance of Electoral Bonds, Eligibility
Relevance for Mains: Transparency in Electoral Funding
The objective of Electoral Bonds in India
Electoral Bonds in India are financial instruments introduced in 2017 by the Indian government to encourage political funding through transparent and accountable means. These bonds are designed to be a replacement for cash donations made to political parties, which were previously the norm in India. The main objective of these Bonds is to bring more transparency to political funding and reduce the use of black money in political funding.
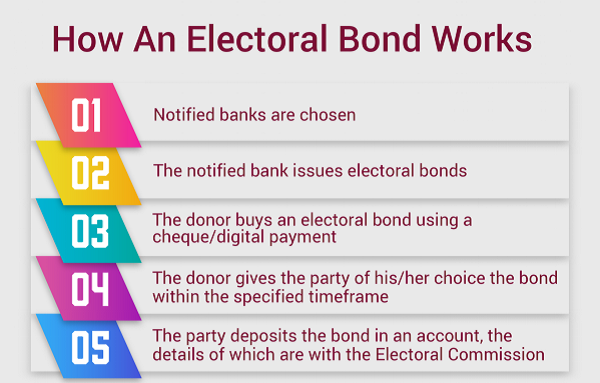
Electoral Bonds
Eligibility
- Electoral Bonds can be purchased by any citizen of India or a body incorporated in India.
- The bonds are issued by the State Bank of India (SBI) and can be bought in multiples of Rs. 1,000, Rs. 10,000, Rs. 1 lakh, Rs. 10 lacks, and Rs. 1 crore.
- These bonds can be redeemed only by recognized political parties registered with the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- The political parties can redeem the bonds within 15 days of their purchase.
The donation received through the Bonds is exempt from Income Tax under section 80GGB of the Income Tax Act, 1961. This means that the donor does not have to pay any tax on the amount donated to a political party. The political parties, on the other hand, are required to report the donations received through these bonds in their contribution report submitted to the ECI.
Criticism of the Electoral Bonds in India
One of the major criticisms of Electoral Bonds is that they do not have any provisions for disclosure of the identity of the donor. The anonymity provided by electoral bonds raises concerns about the potential misuse of these bonds by corporations or individuals with vested interests. This could lead to the influence of money on political decisions and the erosion of democratic principles.
Another criticism of these bonds is that they do not serve the purpose of reducing black money in political funding. The absence of donor disclosure provisions makes it possible for individuals and corporations to use black money to fund political parties through these bonds. This defeats the purpose of bringing transparency to political funding.
Furthermore, the requirement of a bank account for purchasing Electoral Bonds makes it difficult for small donors to participate in political funding. This exclusion of small donors from the political funding process could lead to the domination of political decision-making by a small group of individuals and corporations.
Way Forward
In conclusion, Electoral Bonds in India have the potential to bring transparency to political funding, but their current form raises several concerns. The absence of donor disclosure provisions and the requirement of a bank account for purchasing the bonds limit their effectiveness in reducing black money in political funding and promoting democratic principles. The government must take steps to address these shortcomings and improve the design of the Bonds to ensure that they serve their intended purpose.
Source:
Download the PDF Now:
Plutus IAS current affairs 31st Jan 2023
Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
Plutus IAS current affairs describe the national and international news elaborately by providing the best daily current affairs for the UPSC examination. So, Collect the daily, weekly, and monthly current affairs today for the IAS exam preparation as soon as possible.



No Comments