11 Jun Empowering Bharat with Technical Textiles: A Make in India Success Story
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the Topic Empowering Bharat with Technical Textiles: A Make in India Success Story
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
GS-3- Economics- Empowering Bharat with Technical Textiles: A Make in India Success Story
FOR PRELIMS
What is the National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM)?
FOR MAINS
What steps has the government taken to promote skill development in technical textiles?
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi recently highlighted the rapid transformation of India’s technical textiles sector, citing key government initiatives like the National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM) and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme. In response to a post by Union Minister Shri Giriraj Singh on social media platform X, the Prime Minister acknowledged that these initiatives are significantly boosting domestic manufacturing, fostering innovation, and enhancing exports. This growing momentum is positioning India as a global leader in the technical textiles industry.

What is a technical textile?
Technical textiles are specially engineered fabrics designed for functional purposes rather than aesthetics. They are used in various industries such as automotive, construction, agriculture, healthcare, and defence. These textiles offer properties like high strength, durability, resistance to heat or chemicals, and specialized performance like protection or filtration. Unlike traditional textiles used for clothing or decoration, technical textiles are meant to solve practical problems. Examples include airbags, crop covers, geotextiles, and medical gowns. They play a vital role in modern industry and are increasingly important for innovation and development.
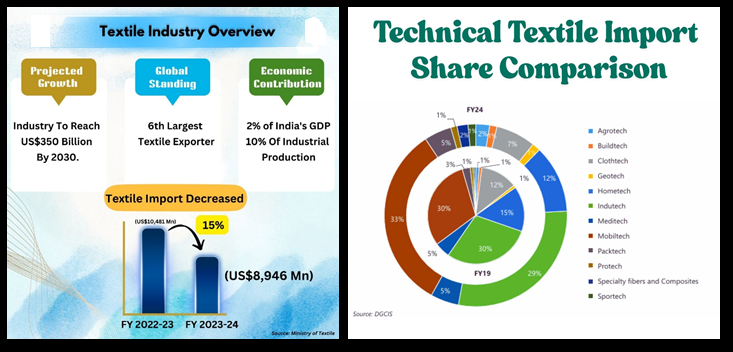
The textile technical sector in India: data
Govt initiatives: National Technical Textile Mission
1. Grant for Internship Support for Technical Textiles (GIST 2.0): Launched under NTTM, GIST 2.0 bridges the gap between industry and academia by offering hands-on learning opportunities in technical textiles. It fosters local innovation, supports the Make in India initiative and helps empower young talent to drive growth in the textile sector.
2. Grant for Research & Entrepreneurship across Aspiring Innovators in Technical Textiles (GREAT) Scheme: Launched in August 2023, the program provides funding to help translate prototypes into technologies and products for commercialization. So far, 8 startups have been granted ₹50 lakh each for innovations in medical, industrial and protective textiles. Additionally, three educational institutes, including IIT Indore and NIT Patna, received ₹6.5 crore to introduce specialised courses in geotextiles, geosynthetics, and sports textiles.
3. Skill Development Programs: To meet the growing demand in the technical textiles sector, NTTM aims to train 50,000 individuals, including undergraduate students, unskilled workers, and professionals. The initiative provides targeted skill development through 12 industry-focused courses developed by organisations like SITRA (South India Textiles Research Association), NITRA (Northern India Textile Research Association) and SASMIRA (South Ahmedabad Silk Mill and Industrial Research Association) in areas like medical, protective, mobile, and agricultural textiles.
4. Technotex 2024: Held as part of Bharat Tex 2024, showcased the strength of India’s technical textiles sector, offering a platform to explore global investment opportunities. A highlight of the event was the Innovation Zone under the National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM), spanning 693 square meters. This dedicated pavilion featured 71 cutting-edge projects, with 48 presented as prototypes and 23 through informative posters.


Technical textile application
1. Agrotech (Agricultural Textiles): Used in shade nets, crop covers, and mulch mats to improve crop yield, reduce pesticide use, and protect crops from pests and extreme weather.
2. Buildtech (Construction Textiles): Includes materials like geogrids and scaffolding nets used for concrete reinforcement, noise barriers, and structural safety in construction.
3. Clothtech (Clothing Textiles): Used in zippers, sewing threads, and interlinings to enhance the durability, functionality, and aesthetics of garments.
4. Geotech (Geotextiles): Applied in road construction, drainage, and erosion control to improve soil stability and increase the life of infrastructure projects.
5. Meditech (Medical Textiles): Includes surgical masks, gowns, wound dressings, and sanitary products that ensure hygiene, patient care, and infection control.
6. Mobiltech (Automotive Textiles): Used in seat belts, airbags, and upholstery to enhance vehicle safety, comfort, and performance.
7. Packtech (Packaging Textiles): Encompasses woven sacks, FIBCs, and jute bags used for durable, reusable, and moisture-resistant packaging of goods.
8. Indutech (Industrial Textiles): Includes filtration fabrics, conveyor belts, and insulation products that improve industrial efficiency and safety.

Technical Textile Promotion in India
| Initiative/Area | Details |
|---|---|
| 1. NTTM (2020–24) | ₹1,480 crore mission to boost domestic production, R&D, education, exports of technical textiles. |
| 2. GIST 2.0 | Internship support to students bridges the industry-academia gap. |
| 3. GREAT Scheme | ₹50 lakh each to startups; ₹6.5 crore to institutes (e.g., IIT Indore, NIT Patna) for specialized courses. |
| 4. Skill Development | Target to train 50,000 individuals via 12 industry-specific courses by SITRA, NITRA, SASMIRA, etc. |
| 5. Technotex 2024 | Showcased 71 innovations (48 prototypes); platform for investment & global outreach. |
| 6. Education Support | Specialised technical textile courses have been introduced in IITs, NITs, and textile institutes. |
| 7. BIS Standards | 500+ standards developed to ensure product quality and global competitiveness. |
| 8. Make in India Focus | Encouragement for indigenous manufacturing of machinery and materials. |
| 9. Export & FDI Promotion | Support via PLI schemes, trade fair participation, and investment facilitation. |
| 10. State-Level Support | States like Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Maharashtra are offering policy and infrastructure incentives. |
Challenges in technical textiles implementation
1. Low Awareness: Limited understanding among industries, consumers, and policymakers about technical textiles and their benefits.
2. Weak Domestic Demand: Slow adoption across sectors like agriculture, construction, and healthcare restricts market growth.
3. Skill Shortages: Inadequate availability of trained personnel and limited specialised training programs.
4. High Import Dependence: Reliance on imported machinery and speciality raw materials raises production costs.
5. Insufficient R&D and Innovation: Poor industry-academia collaboration and low investment in research hinder innovation.
6. Lack of Testing Infrastructure: Few accredited labs and testing centres limit quality assurance and global competitiveness.
7. Fragmented Industry Structure: Dominated by MSMEs with limited resources for scaling, modernisation, and exports.
8. Regulatory Gaps: Delayed implementation of BIS standards and lack of mandatory usage norms in key sectors.
Way forward
1. Enhance Awareness: Conduct nationwide awareness campaigns to educate industries and end-users on benefits and applications.
2. Strengthen Skill Development: Expand industry-aligned training programs and integrate technical textiles into higher education curricula.
3. Promote Indigenous Manufacturing: Encourage domestic production of machinery and specialty fibers under Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat.
4. Boost R&D and Innovation: Increase funding and industry-academia partnerships to develop cost-effective, market-ready innovations.
5. Expand Market Demand: Introduce mandatory usage policies in public infrastructure, defence, agriculture, and healthcare.
6. Develop Testing Facilities: Establish more accredited labs for quality certification, standard compliance, and export readiness.
7. Support MSMEs: Provide financial and technical assistance to help MSMEs upgrade technology and access global markets.
8. Streamline Regulations: Fast-track implementation of BIS standards and create a single-window system for policy facilitation.
Conclusion
The technical textiles sector holds immense potential to revolutionise India’s industrial landscape through innovation, value addition, and employment generation. With strategic government interventions like the National Technical Textiles Mission, skill development programs, and startup support schemes such as GIST 2.0 and GREAT, India is steadily emerging as a global hub for technical textiles. However, challenges like low awareness, skill gaps, and weak R&D must be systematically addressed. A collaborative approach involving industry, academia, and the government will be crucial to unlocking the sector’s full potential, promoting self-reliance, and achieving sustainable economic growth.
Prelims Questions
Q. With reference to technical textiles in India, consider the following statements:
1. The National Technical Textiles Mission aims to boost both domestic consumption and exports.
2. The GREAT scheme provides funding to promote textile exports only.
3. GIST 2.0 is an initiative to support startups in the technical textiles sector.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c)1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: C
Mains Questions
Q. Technical textiles are critical to India’s aspirations for industrial innovation and self-reliance. Discuss the importance of technical textiles in India, the challenges in their implementation, and suggest a way forward.
(250 words, 15 marks)




No Comments