21 Feb EV Batteries: Revolutions to achieve net zero emission by 2070
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and topic details of the EV Batteries: Revolutions to achieve net zero emission by 2070
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
GS-3-Science and Technology- EV Batteries: Revolutions to achieve net zero emission by 2070
FOR PRELIMS
Various types of Battery, features and mechanisms, what are the govt initiatives in battery manufacturing
FOR MAINS
Why in the news?
The Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI) signed a Programme Agreement with Reliance New Energy Battery Limited under the ₹18,100 crore PLI scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cells (ACC). This grants Reliance a 10 GWh manufacturing capacity, bringing the total allocated capacity to 40 GWh out of the 50 GWh target. The PLI scheme, aimed at boosting India’s battery manufacturing for electric vehicles and renewable energy, strengthens domestic production, reduces imports, and supports India’s green energy goals.

What are batteries?
A battery is an electrochemical device that stores and releases electrical energy through chemical reactions. It typically consists of one or more electrochemical cells, where each cell has two electrodes (an anode and a cathode) separated by an electrolyte. When the battery is discharging, chemical reactions occur at the electrodes, releasing electrons and generating an electric current. The battery can be recharged (in the case of rechargeable batteries) by reversing these chemical reactions. Batteries are categorized into two main types:
1. Primary Batteries: These can only be used once. After they are discharged, they cannot be recharged and are discarded. The reactions inside these batteries are irreversible, making them “use-and-throw” devices.
2. Secondary Batteries: These are rechargeable and can be used for many cycles of charging and discharging. The chemical reactions in secondary batteries are reversible, allowing the battery to be recharged by applying an electric current to reverse the discharge reaction.
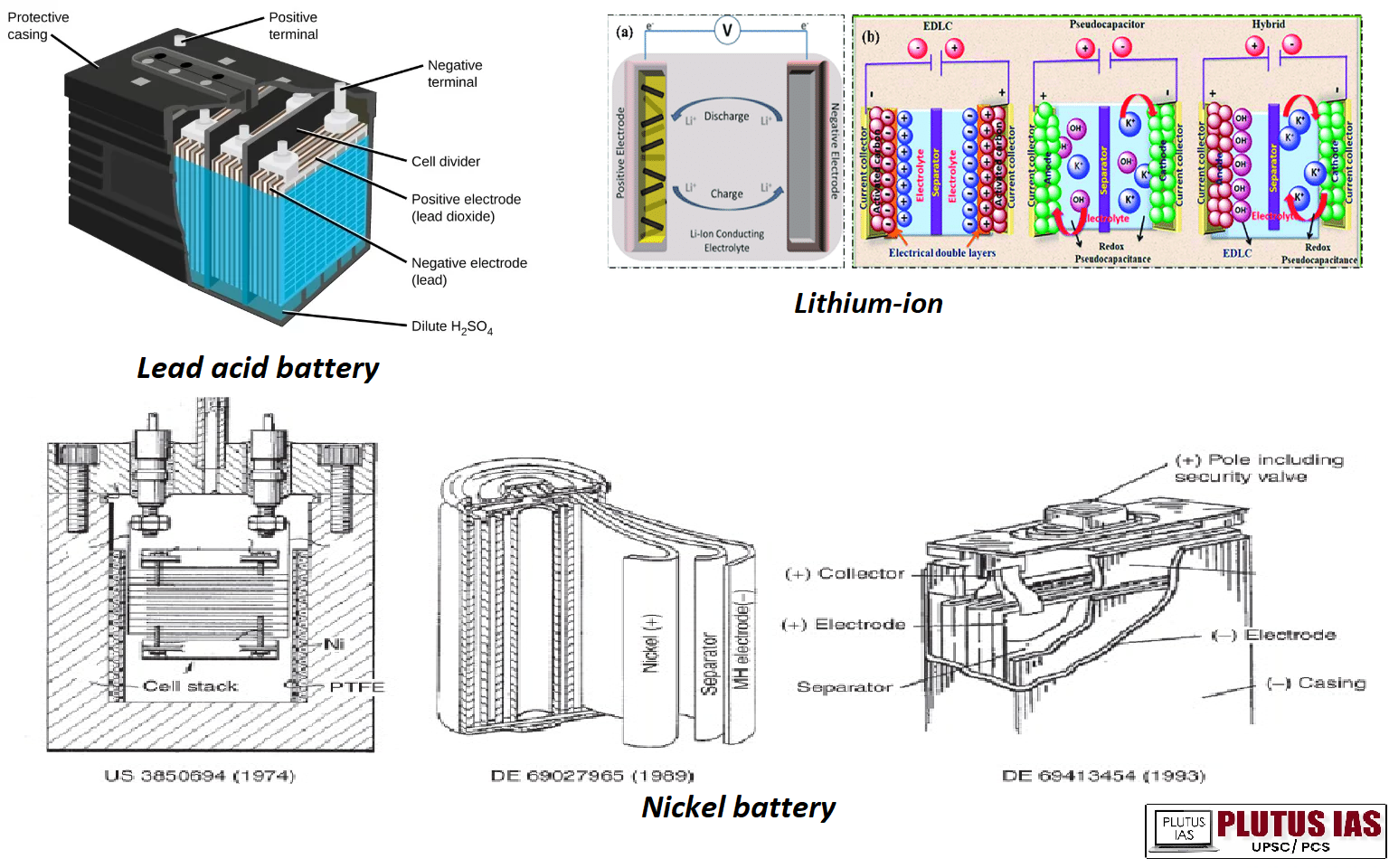
Various types of batteries and their feature:
| Battery Type | Inventor/Origin | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid Battery | Gaston Planté (1859) | – High energy-to-volume ratio, low energy-to-weight ratio – Strong surge currents – Inexpensive – Holds charge for up to 3 years |
– Automotive (car batteries) – Emergency power backup |
| Nickel-Cadmium (NiCad) Battery | – | – Fast and even discharge – Varying discharge rates – Inexpensive – Used in small electronics and toys |
– Toys – TV remotes – Small electronic devices |
| Lithium-Ion (LIB) Battery | – | – High energy capacity – No memory effect (except LFP cells) – Low self-discharge – Reversible lithium-ion flow |
– Mobile phones – Laptops – Electric vehicles |
What are the initiatives launched by the GOVT of india?
1. Subsidies:
PM E-DRIVE Scheme: ₹10,900 crore for subsidizing charging stations for two- and three-wheelers.
FAME-II & Advanced Chemistry Cell PLI Schemes: Incentives for EVs, batteries, and storage systems manufacturers.
2. Charging Infrastructure:
Revised guidelines from the Ministry of Power to expand public charging infrastructure.
Oil Marketing Companies to set up EV stations in cities and on highways.
3. Manufacturing Incentives:
PLI Scheme: Financial incentives for EV and battery manufacturers.
SPMEPCI (March 2024): Promotes manufacturing of electric passenger cars.
4. Other Initiatives:
Battery Swapping Policy: This policy encourages battery swapping as a viable alternative to charging, helping reduce downtime for EVs and promoting more sustainable usage of batteries.
Green Hydrogen Mission: This initiative supports the development and manufacturing of fuel cells and green hydrogen technology, which are expected to decarbonize the transportation sector.
EV-Mission: Aimed at fostering research and development in EV adoption, this mission supports the innovation of new technologies and solutions to advance the EV ecosystem in India.
5. Tax Incentives: The Indian government has reduced the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on electric vehicles and chargers, making EVs more affordable and attractive to buyers.
Why india is focusing on Ev- Batteries
1. Environmental Impact: EVs are central to reducing carbon emissions, and batteries are the heart of these vehicles.
2. Energy Security: Developing domestic battery production reduces reliance on foreign imports, ensuring a stable supply and minimizing risks from supply chain disruptions.
3. Economic Growth: A robust EV battery manufacturing industry can generate jobs, stimulate growth, and support India’s green economy.
4. Government Initiatives: Policies like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme are encouraging domestic EV battery manufacturing.
5. Technological Advancement: India aims to advance in battery technology to produce high-performance, cost-effective batteries.
6. Market Potential: With a large and growing population, India’s EV market is expected to expand, making battery production a promising sector.
Challenges to Become self-reliant in EV Batteries
1. Raw Material Dependency: India depends heavily on imports of essential materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel needed for batteries.
2. Supply Chain Complexity: Developing a local supply chain, including recycling facilities, is crucial for sustainable battery production.
3. High Initial Costs: The high upfront costs of EVs remain a barrier to adoption for many consumers.
4. Charging Infrastructure: Widespread and accessible charging infrastructure is essential to ease range anxiety and drive EV usage.
5. Technological Gaps: Lack of advanced research and development in battery technology.
6. Skilled Workforce Shortage: Insufficient expertise in battery manufacturing and engineering.
7. Regulatory Uncertainty: Inconsistent policies around battery production and recycling hinder long-term investment.
Download Plutus IAS Current Affairs (Eng) 21th Feb 2025
Conclusion
India is focusing on EV batteries to reduce carbon emissions, enhance energy security, and promote economic growth. Government initiatives like the PLI scheme for battery manufacturing and subsidies for charging infrastructure are key to boosting domestic production and reducing import dependency. Challenges such as raw material dependency, supply chain issues, and high initial costs remain. Overcoming technological gaps, workforce shortages, and regulatory uncertainty is vital for achieving self-reliance in EV battery production. With strong market potential and supportive policies, India is well-positioned to become a leader in the EV sector.
Prelims Questions:
Q. Which of the following statements are correct about India’s Electric Vehicle (EV) initiatives?
1. The government has launched the PM E-DRIVE scheme to subsidize charging stations for two- and three-wheelers.
2. The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme aims to promote the manufacturing of electric passenger cars only.
3. India’s government is actively working on a Battery Swapping Policy to reduce downtime for electric vehicles.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
Mains Questions:
(250 words, 15 marks)




No Comments