27 Mar Finance Bill 2023
The Finance Bill 2023
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs for UPSC“and the topic is ‘The Finance Bill 2023’ which is in news, it covers “Polity” in GS-2; “Economy” in GS-3, the following content has relevance for UPSC.
For Prelims: The Finance Bill 2023
For Mains: GS-2, Polity; GS-3, Economy
Why in news: Lok Sabha passed the Finance Bill, 2023 with 64 official amendments, including the removal of long-term tax benefits for debt funds that have stirred concerns in the fixed-income mutual fund industry that the measure would turn away investors.
About Finance Bill 2023 Key Amendments
- Mutual funds with less than 35% of their assets in domestic equity would lose the indexation benefit and will be taxed as short-term capital gains.
- Offshore financial units working in GIFT city will receive enhanced tax benefits, including a 100% income deduction over the next ten years.
- The tax on royalties or technical fees earned by foreign (non-resident) corporations has been raised from 10% to 20%.
- There is no change in the taxation of non-par savings insurance products (the 5 lakh cap remains).
- Notwithstanding representation, there will be no change in the taxation of REITS/InviTs (revenue from REITS will be taxed as ‘income from other sources rather than capital gains).
- The securities transaction tax (STT) on the selling of options has been hiked to 2,100 on a turnover of one crore, while the STT on the sale of futures contracts has been raised to 12,500 on a turnover of one crore, representing a 25% rise.
Finance Bill 2023
About Finance Bill
- The Finance Bill is a Money Bill, according to Article 110 of the Indian Constitution.
- The bill is a component of the Union Budget that specifies all of the legal changes required for the proposed tax changes by the Finance Minister.
- The Speaker of the Lok Sabha has the authority to decide whether or not the Bill is a Money Bill.
- The decision of the Speaker is final.
Features of the Bill
- Finance Bills are classified into three types:
- Finance Bill Category I,
- Finance Bill Category II, and
- The Money Bill.
- Financial bills are all money bills, but not all money bills are financial bills.
- According to Article 110, a Bill is deemed to be a Money Bill if it contains solely provisions dealing with all or all of the following:
- The imposition, repeal, remission, modification, or regulation of any tax;
- The regulation of the Government of India’s borrowing of money or the provision of any guarantee;
- The custody of the Consolidated Fund or the Contingency Fund of India, as well as the payment into or withdrawal from any such Fund;
- The appropriation of money from India’s Consolidated Fund;
- The declaration of any expense as one charged to the Consolidated Fund of India or the increase in the amount of any such expenditure;
- The receipt of money on account of the Consolidated Fund of India or the public account of India, or the holding or distribution of such money, or the audit of the Union’s or a State’s accounts;
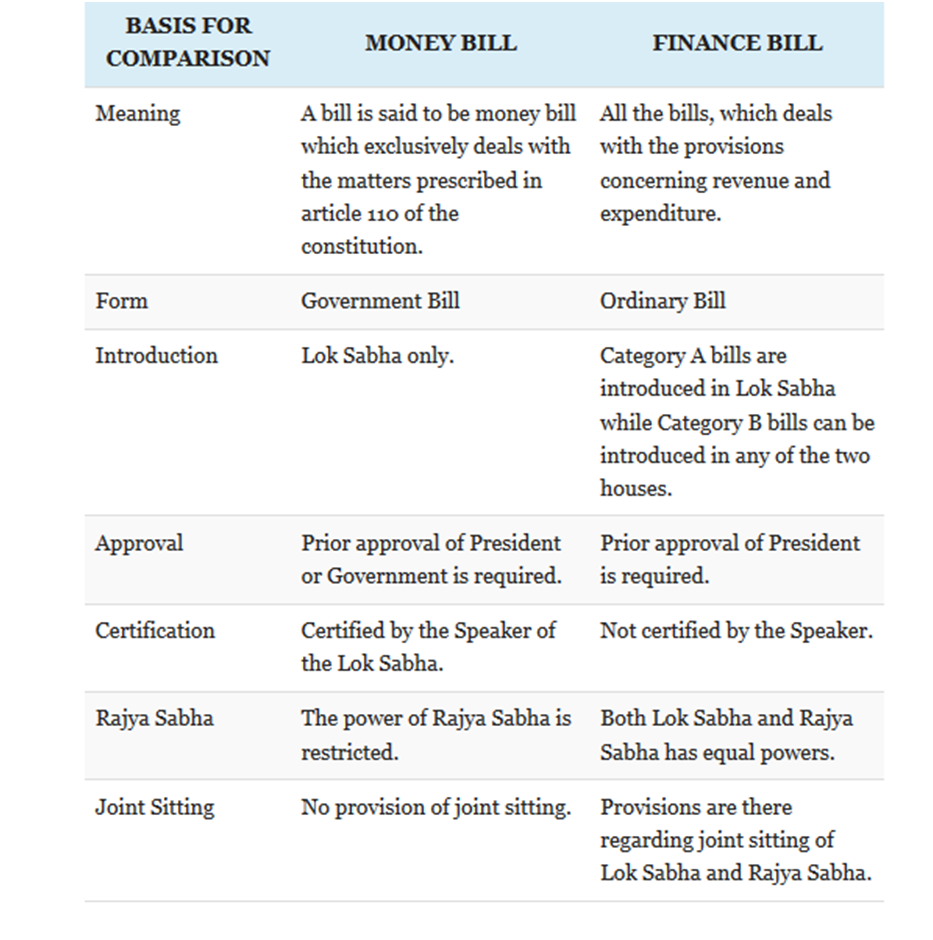
The distinction between a Money Bill and a Finance Bill
- According to Section 110 of the Constitution, a Money Bill must be introduced in the Lok Sabha.
- The bill is then sent to the Rajya Sabha for consideration.
- The Rajya Parliament has 14 days to return the Bill with suggestions.
- The Lok Sabha, on the other hand, has the option of rejecting all or any of the suggestions.
- Article 117 of the Constitution states categorically that a Bill shall not be introduced or advanced except with the President’s endorsement under certain extraordinary circumstances.
Why the Bill Required
- The Union Budget proposes numerous tax reforms for the coming fiscal year.
- The Finance Bill intends to insert adjustments into all relevant laws without the need for a separate amendment bill for each of those Acts.
- This bill overrides and amends existing legislation as necessary.
Source:
Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
If aspirants want to gain general knowledge and acquire knowledge of the national and international world, they should read daily current affairs regularly. It is crucial for every UPSC aspirant to read daily current affairs for UPSC exam preparation. Here, Plutus IAS provides the best daily current affairs for the UPSC examination. Also, collect weekly and monthly current affairs for the UPSC exam preparation.
Download the PDF Now:




No Comments