04 Jun FPI Caution in 2025: Assessing the Shift in India’s IPO Landscape
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” FPI Caution in 2025: Assessing the Shift in India’s IPO Landscape.
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
GS-3- Economic- FPI Caution in 2025: Assessing the Shift in India’s IPO Landscape
FOR PRELIMS
Why are Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) becoming cautious in India’s IPO market in 2025? What are the major reasons behind this trend?
FOR MAINS
What lessons can Indian regulators and companies learn from the changing pattern of FPI investments in IPOs?
Why in the News?
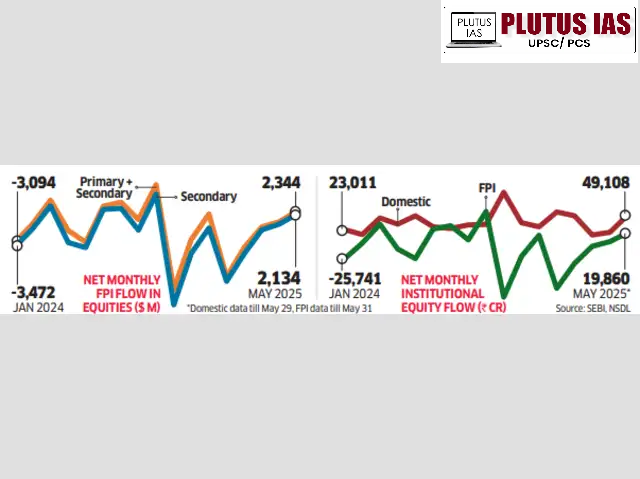
According to the ET Intelligence Group, Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) have become cautious in India’s primary market (IPOs) in 2025. They have invested just $1.8 billion (₹15,864 crore) in IPOs up to May, compared to $4 billion (₹33,487 crore) in the same period of 2024, reflecting a marked decline of over 55%.
What is Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI)?
Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) refers to investments made by foreign investors in a country’s financial assets such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Unlike Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), FPI does not involve direct control or management of companies. FPIs are typically more liquid and can be easily bought or sold on financial markets. They bring foreign capital into the economy, helping deepen capital markets and improve liquidity. However, FPIs are often more volatile and can be withdrawn quickly during times of economic uncertainty. Overall, FPI plays an important role in connecting global investors with domestic financial markets.
Reason for FPI Caution
1. High Market Volatility: Global geopolitical tensions and macroeconomic instability have increased volatility, discouraging risk-taking.
2. Interest Rate Uncertainty: Fluctuating interest rate outlooks in the US and Europe make emerging markets like India less attractive.
3. Global Risk-off Sentiment: Investors are moving away from equities and IPOs toward safer assets amid uncertain global cues.
4. Slower IPO Activity: Fewer IPOs are being launched due to subdued sentiment, reducing FPI opportunities.
5. Muted Retail Participation: Domestic retail investors have become cautious, impacting IPO subscription strength and momentum.
6. Overvaluation of IPOs: Aggressive pricing by issuers, especially in the startup space, has led to valuation concerns.
7. Poor Post-listing Performance: Several IPOs from 2024 underperformed post-listing, deterring repeat FPI investment.
8. Currency Risk: Fears of rupee depreciation reduce returns in dollar terms and increase repatriation risk for FPIs
Significance of Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) in the context of the Indian economy
1. Capital Inflows and Market Liquidity: FPI brings substantial foreign capital into India’s financial markets, enhancing liquidity and enabling smoother trading.
2. Market Development and Depth: It helps deepen and develop Indian stock and bond markets, making them more efficient and attractive to investors.
3. Price Discovery and Efficiency: Active participation of global investors through FPI facilitates better price discovery and overall market efficiency.
4. Support for Economic Growth: FPI provides companies with funds needed for expansion, infrastructure development, and business growth.
5. Foreign Exchange Stability: FPI inflows contribute to foreign exchange reserves, helping stabilize the Indian rupee and improve the balance of payments.
6. Global Integration of Financial Markets: FPI promotes integration of Indian financial markets with global capital markets, attracting further foreign investments.
7. Diversification of Capital Sources: By bringing in foreign funds, FPI diversifies India’s capital sources beyond domestic savings and investments.
8. Need for Regulation to Manage Volatility: Given its volatile nature, FPI requires strong regulatory oversight to minimize risks from sudden capital outflows that can destabilize markets.
Comparative Trends
1. 2024 IPO Boom: Record fundraising and heavy oversubscription, driven by liquidity, tech hype, and investor optimism.
2. Tech-Sector Enthusiasm: High interest in digital economy and fintech startups fuelled FPI investment in 2024.
3. 2025 Rationalisation: Market sentiment has become cautious, with emphasis shifting from quantity to quality.
4. Profit Booking Trend: FPIs are now booking profits from earlier investments rather than investing afresh in IPOs.
5. Selective Participation: Focus has shifted to larger, stable companies with strong fundamentals.
6. Smaller IPO Pipeline: Fewer companies are listing in 2025 due to market conditions and weak investor demand.
7. Changing Investor Priorities: Shift from growth to safety due to global economic slowdown and interest rate hikes.
8. Rise in Diligence: FPIs are demanding greater transparency and stronger business models before investing.
Impact on Indian Capital Markets
1. Lower IPO Demand: Reduced FPI interest leads to under-subscription or reduced enthusiasm in IPOs.
2. Capital Raising Challenges: Startups and mid-cap companies face difficulties in mobilizing equity capital.
3. Reduced Valuations: Lack of demand pressure may force companies to lower IPO pricing, affecting valuations.
4. Shift in Investor Base: Domestic institutional investors (DIIs) are emerging as more prominent players.
5. Change in Issuer Strategies: Companies may delay or alter IPO plans based on funding availability.
6. Impact on Innovation: Slower funding may affect innovation and expansion in key sectors like tech and renewable energy.
7. Short-Term Market Correction: FPI withdrawals can increase volatility and lead to short-term corrections in equity indices.
8. Reduced Global Confidence: Persistent low participation may be seen as a signal of reduced global investor confidence.
Wider Context
1. Global Uncertainty: Economic slowdown, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical crises have impacted capital flows globally.
2. Emerging Market Impact: Similar cautious FPI behaviour seen across emerging economies, not just India.
3. US Fed Policy Effect: Hawkish signals from the US Federal Reserve influence global investment sentiment and FPI strategy.
4. Inflationary Pressures: Global inflation makes central banks cautious, leading to capital outflows from riskier markets.
5. India’s Macro Stability: Despite global uncertainty, India’s growth remains strong and inflation under control.
6. Current Account Deficit: Concerns over widening CAD and external vulnerabilities weigh on investor decisions.
7. Oil and Commodity Prices: Fluctuating global commodity prices impact India’s trade balance and investor outlook.
8. Geopolitical Realignments: Ongoing global conflicts and sanctions regimes affect long-term FPI strategy and asset allocation.
Way Forward
1. Enhance Pricing Transparency: Regulators must ensure that IPOs are fairly priced to avoid future listing losses.
2. Improve Disclosure Standards: Strengthening pre-IPO disclosures will help build investor trust.
3. Boost Corporate Governance: High governance standards attract long-term investors and reduce risk perception.
4. Strengthen Investor Education: Educating retail investors and analysts improves overall market depth.
5. Policy Stability: A predictable tax and regulatory regime encourages consistent FPI inflows.
6. Ease Compliance Norms: Streamlining procedural hurdles will improve ease of doing business for foreign investors.
7. Encourage Quality Listings: Promoting fundamentally strong companies to go public builds sustainable market growth.
8. Maintain Macro Stability: Continued economic reforms, fiscal discipline, and stable inflation will enhance India’s FPI appeal.
Conclusion
The sharp decline in Foreign Portfolio Investor (FPI) participation in India’s IPO market during 2025 reflects growing investor caution amidst global volatility, policy uncertainty, and valuation concerns. While the euphoria of 2024 was driven by liquidity and tech optimism, the current environment is marked by selective, quality-focused investing. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities for India’s capital markets. To restore FPI confidence and maintain India’s attractiveness as a long-term investment destination, policymakers, regulators, and market participants must prioritise transparency, governance, and policy predictability. With its strong macroeconomic fundamentals and reform momentum, India remains well-positioned to weather global headwinds and attract sustainable foreign capital in the years ahead.
Download Plutus IAS Current Affairs (Eng) 4th June 2025
Prelims Questions
Q. Consider the following statements regarding Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) and their role in India’s capital market in 2025:
1. FPIs have increased their investments in Indian IPOs in 2025 compared to 2024.
2. High market volatility and rupee depreciation risks have led to cautious FPI participation.
3. FPIs prefer investing in companies with strong fundamentals and robust corporate governance.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a). 1 and 2 only
(b). 2 and 3 only
(c). 1 and 3 only
(d). 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Mains Questions
Q. Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) have shown increasing caution towards India’s IPO market in 2025, marking a sharp contrast to the enthusiasm of 2024. Discuss the reasons behind this shift. What are its implications for India’s capital markets, and what policy measures can revive sustained FPI interest?
(250 words, 15 marks)




No Comments