23 Jul Geosynclines
Geosynclines – UPSC Geography Optional Notes
Introduction
The concept of geosynclines is a foundational aspect in structural geology and tectonics, especially for understanding the origin of mountain systems. Geosynclines represent large-scale depressions in the Earth’s crust that are filled with sedimentary and volcanic materials and are later deformed into mountain belts during orogeny (mountain-building). Though the concept has undergone refinement and criticism with the advent of Plate Tectonic Theory, it remains an important historical concept in geology and geography.
1. Definition
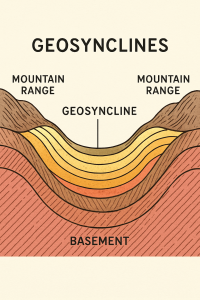
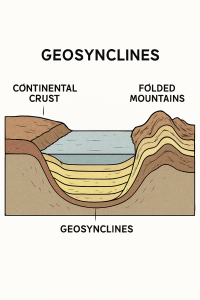
A geosyncline is a linear trough or basin in the Earth’s crust where large volumes of sediments accumulate over long geological time spans. These sediments may be derived from surrounding landmasses and can be up to several kilometers thick.
Best ias coaching in hindi medium
Best mentorship programme for upsc
Best ias coaching in chandigarh
2. Historical Development of the Concept
- James Hall & Dana (19th Century): Observed sediment accumulation leading to Appalachian mountains.
- Kober’s Theory (1921): Distinguished between ‘foredeep’ and ‘backdeep’; mountains formed due to lateral compressive forces.
- Haug’s Classification: Introduced miogeosyncline (shallow-water) and eugeosyncline (deep-water).
- Plate Tectonic Interpretation: Geosynclines are now viewed as active/passive continental margins or back-arc basins.
3. Types of Geosynclines
- Miogeosyncline: Shallow marine settings, dominated by clastic sediments, stable tectonically.
- Eugeosyncline: Deep marine troughs, volcanic and metamorphic rocks common, tectonically unstable.
- Taphrogeosyncline: Rift-like structure filled with sediments; transition to modern rift valleys.
4. Stages of Geosynclinal Development
- Initial Subsidence: Formation of a trough due to crustal sagging or rifting.
- Sediment Accumulation: Over millions of years, rivers, winds, glaciers deposit sediments.
- Compression: Caused by horizontal tectonic forces leading to folding and faulting.
- Orogeny: Crustal thickening and uplift leading to mountain building (e.g., Himalayas).
Geosynclines2
5. Examples of Geosynclines
- Tethys Geosyncline: Led to the formation of the Himalayas.
- Appalachian Geosyncline: Responsible for Appalachian mountains (USA).
- Vindhyan Basin: Partially a geosynclinal region in India with undeformed sediments.
6. Geosynclines in Modern Tectonic Context
Modern plate tectonics interprets geosynclines as tectonic settings like:
- Convergent Margins (island arcs, trenches)
- Passive Margins (continental shelves)
- Back-arc Basins and Rift Basins
The term “geosyncline” has become outdated but continues to be used in historical and regional geological literature.
Best geography optional coaching
Best geography optional teacher
7. Importance of Geosynclines
- Foundation of classical mountain-building theories
- Helps understand sedimentary basin evolution
- Relates to petroleum and mineral deposit locations
- Essential for reconstructing paleo-environments
8. Criticism of Geosyncline Theory
- Fails to explain mechanism of subsidence adequately
- No unified theory; multiple interpretations exist
- Superseded by Plate Tectonics in explaining orogeny and basin evolution
Geosynclines
9. Previous Year UPSC Questions
- 2020: Explain the concept of geosyncline and its significance in mountain building.
- 2017: Differentiate between miogeosyncline and eugeosyncline with suitable examples.
- 2015: Critically examine the relevance of geosynclinal theory in modern geology.
10. Probable Questions for Upcoming UPSC Prelims & Mains
- Discuss the stages of geosynclinal development and their role in mountain building.
- Evaluate the concept of geosyncline in the light of plate tectonics.
- Write a short note on the Tethys geosyncline and its role in Himalayan orogeny.
- What are the different types of geosynclines? Discuss with examples.
11. Conclusion
While the geosynclinal theory may have been overshadowed by the advent of Plate Tectonic Theory, its historical significance remains immense. It provided a framework to understand mountain building and sedimentary basin evolution before plate tectonics offered a more holistic model. For UPSC aspirants, it remains a crucial conceptual topic to understand the geological past and the evolution of Earth’s structural features.




No Comments