04 Aug Health Bills
Health Bills
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “Health Bills”. The topic “Health Bills” has relevance in the Public Health section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
Facts about Health Bills?
For Mains:
GS 2: Public Health
Features about Health Bills?
Why in the news:
Two key health Bills – the National Nursing and Midwifery Commission Bill (NNMC), and the National Dental Commission Bill – were passed by Lok Sabha
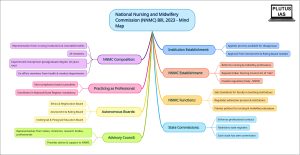
National Nursing and Midwifery Commission (NNMC) Bill, 2023:
The NNMC Bill is a healthcare legislation aimed at reforming and enhancing the nursing and midwifery professions in India. It seeks to establish the National Nursing and Midwifery Commission (NNMC) as a regulatory body for nursing and midwifery professionals by repealing the existing Indian Nursing Council Act of 1947, which is considered outdated and inadequate for the evolving needs and demands of these professions.
Key Features:
Composition:The NNMC will comprise 29 members, with the Chairperson being a highly experienced individual holding a postgraduate degree in nursing and midwifery, with a minimum of 20 years of field experience. Ex-officio members will represent the Department of Health and Family Welfare, National Medical Commission, Military Nursing Services, and Directorate General of Health Services. Other members will include nursing and midwifery professionals and representatives from charitable institutions.
Functions: The NNMC will frame policies and regulate standards for nursing and midwifery education, establish a uniform admission process for nursing and midwifery institutions, regulate these institutions, and set standards for faculty in teaching institutions.
Autonomous Boards:
- Nursing and Midwifery Undergraduate and Postgraduate Education Board: This board will be responsible for regulating education and examinations at the undergraduate and postgraduate levels for nursing and midwifery.
- Nursing and Midwifery Assessment and Rating Board:
This board will develop the framework for assessing and rating nursing and midwifery institutions.
- Nursing and Midwifery Ethics and Registration Board: This board will regulate professional conduct and promote ethical practices in the nursing and midwifery profession.
State Nursing and Midwifery Commissions:
Each state will constitute its own Nursing and Midwifery Commission with ten members, including representatives from the health department and nursing/midwifery colleges.
The functions of State Commissions include enforcing professional conduct, maintaining state registers, issuing certificates of specialization, and conducting skill-based examinations.
Establishment of Institutions:
To establish new nursing and midwifery institutions or to increase seats or postgraduate courses, approval from the Assessment and Rating Board is mandatory.
An appeals process is available to the National Commission and the Central Government in case of disapproval.
Practicing as a Professional:
Practicing nursing or midwifery in India requires enrollment in either the National or State Register. Failure to comply with this requirement may lead to penalties, including imprisonment or a fine.
Advisory Council:
- The Advisory Council will provide advice and support to the National Commission on nursing and midwifery education, services, training, and research.
- The council will include representatives from each State and Union Territory, Ministry of Ayush, University Grants Commission, National Assessment and Accreditation Council, Indian Council of Medical Research, and nursing/midwifery professionals.
The National Nursing and Midwifery Commission (NNMC) Bill, 2023, seeks to modernize and streamline nursing and midwifery education and practice in India through the establishment of a robust regulatory framework and autonomous boards. It aims to improve the quality of healthcare services and strengthen the nursing and midwifery professions, contributing to better healthcare outcomes for the country.
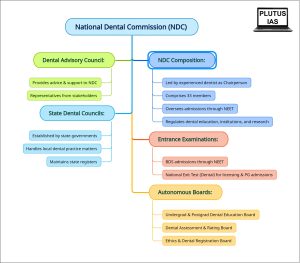
National Dental Commission (NDC):
The National Dental Commission Bill, 2023, is a healthcare legislation aimed at regulating and improving the dentistry profession in India. It focuses on establishing the National Dental Commission (NDC) as the regulatory body for dentistry and repealing the Dentists Act of 1948, which is considered outdated and insufficient to address the contemporary needs and advancements in dental education and practice.
Key Features:
- Composition: The National Dental Commission (NDC) will be composed of 33 members and will be headed by an eminent and experienced dentist.The appointment of the Chairperson will be made by the central government based on the recommendation of a search-cum-selection committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary.
- Ex-officio members of the NDC include Presidents of three autonomous Boards, Director General of Health Services, Chief of the Centre for Dental and Educational Research, AIIMS. Part-time members will include faculties of dentistry from government institutes and representatives of states and union territories.
- Functions: The primary role of the NDC will be to regulate dental education, institutions, research, and infrastructure. It will also oversee the admissions process through the National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test (NEET) for dental courses.
- Autonomous Boards: Undergraduate and Postgraduate Dental Education Board: This board will be responsible for determining education standards, developing curriculum, and granting recognition to dental qualifications at the undergraduate and postgraduate levels.
- Dental Assessment and Rating Board: This board will determine the compliance assessment procedure for dental institutions, grant permission for establishing new institutions, and conduct inspections and ratings.
- Ethics and Dental Registration Board: Responsible for maintaining online national registers of dentists/dental auxiliaries, suspending/canceling licenses, and regulating standards of conduct, ethics, and the scope of practice for dental professionals.
- State Dental Councils:Within a year of the establishment of the NDC, state governments will establish their respective State Dental Councils. These councils will be responsible for maintaining registers, handling grievances, and implementing provisions related to dental practice in their respective states.
Entrance Examinations:
- Admission to Bachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS) courses will be through NEET, which is a national-level entrance examination.
- A National Exit Test (Dental) will be introduced for licensing and postgraduate admissions in dentistry. Clearing the National Exit Test grants a license to practice dentistry, but registration in the state/national register is required before commencing practice.
Dental Advisory Council:
- The Dental Advisory Council will provide advice and support to the NDC on matters related to dental education, training, research, and equitable access to dental education.
- Ex-officio members of the NDC will also serve as ex-officio members of the Dental Advisory Council.
Q.1 Which of the following statements is/are true about the National Nursing and Midwifery Commission (NNMC) Bill, 2023?
- Each state will constitute its own Nursing and Midwifery Commission with ten members
- Practicing nursing or midwifery in India requires enrollment in either the National or State Register, and failure to comply may lead to penalties, including imprisonment or a fine.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER: C
Q.2 Which of the following statements is/are true about the National Dental Commission (NDC) Bill, 2023?
- Chairperson’s appointment will be made by the State governments based on the recommendation of a search-cum-selection committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary.
- The NDC will regulate dental education, institutions, research, and infrastructure, and oversee admissions to dental courses through the National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test (NEET).
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWER: B
Q.3 Explain the key features and objectives of the National Dental Commission (NDC) Bill, 2023. How does it aim to address the contemporary needs and advancements in dental education and practice in India?



No Comments