31 Jul Indian Economy After Independence in Pre-Liberalization Era
Indian Economy After Independence in Pre-Liberalization Era
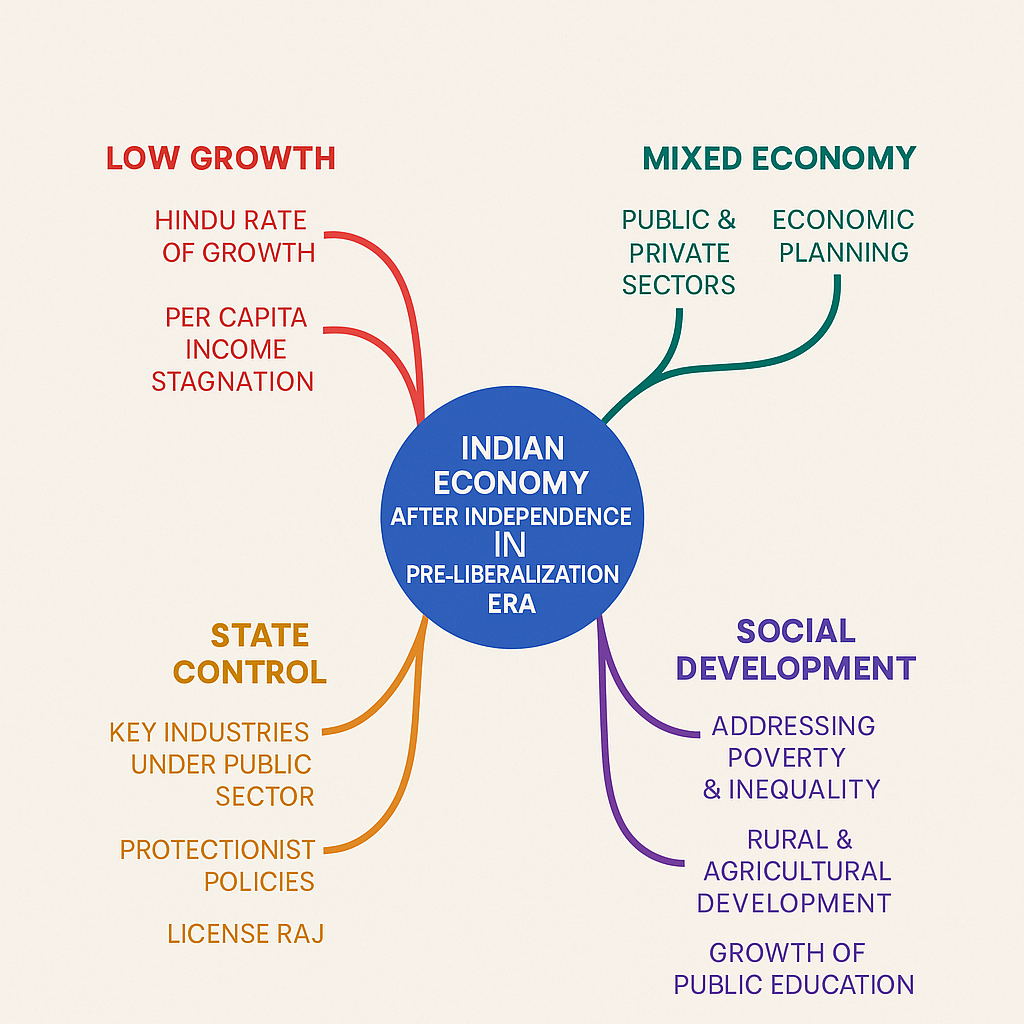
The Indian economy after independence (1947) until the economic liberalization in 1991 was shaped by a strong desire to achieve self-sufficiency, reduce poverty, and develop a modern industrial base. This period, often referred to as the Pre-Liberalization Era, was marked by the dominance of the public sector, central planning, import substitution, and a cautious approach toward foreign investment.
Infographic: Key Features of Pre-Liberalization Indian Economy
1. Historical Background
Post-1947, India faced challenges such as partition, refugee influx, poor infrastructure, low literacy, low agricultural and industrial base. These necessitated a strong role of the state in rebuilding and planning the economy.
2. Characteristics of Pre-Liberalization Indian Economy
- Planned economic development through Five Year Plans
- Dominance of public sector in key industries
- Import Substitution Industrialization (ISI)
- License-Permit-Quota Raj
- Limited foreign investment and restricted trade
3. Role of Planning Commission and Five-Year Plans
First Five Year Plan (1951-1956)
- Focus on agriculture, irrigation, and power
- Model based on Harrod-Domar growth model
Second Five Year Plan (1956-1961)
- Mahalanobis Model: Focus on heavy industries
- Rapid industrialization and expansion of public sector
Subsequent Plans
- Third Plan (1961-66): Stress on self-reliance and modernization
- Fourth Plan (1969-74): Growth with stability and equality
- Fifth Plan (1974-78): Poverty removal and self-reliance
4. Mixed Economy Model
India followed a mixed economy model combining both socialist and capitalist features. Private sector operated under significant control and the public sector was reserved for strategic and heavy industries.
5. Industrial Policy and License Raj
- Industrial Policy Resolution 1956: Established public sector dominance in core industries
- License Raj: Private enterprises required licenses to set up or expand production
- Discouraged competition and innovation, promoted inefficiency
6. Protectionism and Import Substitution
- High tariffs and quantitative restrictions on imports
- Focus on domestic production of consumer and capital goods
- Limited export competitiveness
7. Agriculture and Land Reforms
- Community Development Programme (1952), Intensive Agriculture District Programme (1960)
- Land ceiling, abolition of zamindari, tenancy reforms
- Green Revolution in 1960s: Boosted wheat and rice production but skewed regionally
8. Poverty and Inequality
- High levels of poverty throughout the period
- Limited trickle-down effect of economic growth
- Introduction of targeted programs like IRDP, Food for Work, etc.
9. Performance Indicators (1947–1991)
- GDP growth: Averaged around 3.5% annually (Hindu rate of growth)
- Per capita income growth was sluggish
- Low levels of industrial and technological innovation
Best ias coaching in hindi medium
Best mentorship programme for upsc
Best ias coaching in chandigarh
10. Criticism of Pre-Liberalization Strategy
- Excessive bureaucracy and red tape (License Raj)
- Underutilization of capacity in public sector units
- Neglect of export potential
- Limited integration with the global economy
11. Economic Crisis of 1991
By 1990-91, India faced a severe Balance of Payments crisis. Forex reserves had fallen below $1 billion, forcing India to pledge gold reserves and approach IMF for a bailout. This crisis set the stage for economic reforms and liberalization.
Mind Map: Indian Economy After Independence in Pre-Liberalization Era
Previous Year UPSC Questions (Mains)
- Discuss the role of the public sector in the Indian economy post-independence. (2020)
- Evaluate the performance of the Indian economy during the planning era. (2018)
- Explain the rationale behind import substitution industrialization in post-independence India. (2017)
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains
- Critically analyze the role of Five-Year Plans in shaping India’s economic structure before 1991.
- How did the License Raj impact entrepreneurship in India?
- To what extent did protectionism and self-reliance hinder India’s industrial and export growth?
Probable Questions for UPSC Prelims
- Which of the following was not a feature of India’s pre-liberalization economic policy?
- Under which plan was the Mahalanobis model adopted?
- Green Revolution primarily affected which of the following crops?
GS paper 4 syllabus and study plan
GS paper 3 syllabus and study plan




No Comments