19 Aug India’s forex reserves drop by $2.42 bn to $601.45 bn
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “India’s Forex Reserves”. The topic “India’s Forex Reserves” has relevance in the “Indian Economy” section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
What are forex reserves?
What do they constitute?
For Mains:
GS3: Indian Economy
Why in the news?
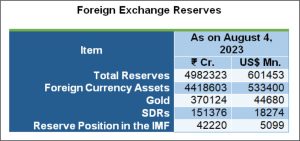
For the third consecutive week, India’s foreign exchange reserves experienced a decline, decreasing by USD 2.417 billion to reach USD 601.45 billion as of August 4th.
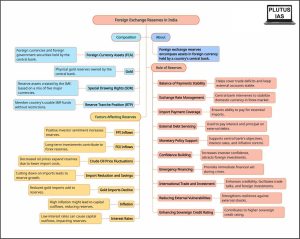
Foreign exchange reserves
- Foreign exchange reserves encompass assets in foreign currency held by a country’s central bank, comprising foreign currencies, government securities like bonds and treasury bills, and other relevant instruments.
- These reserves are pivotal for maintaining balance of payments equilibrium and are integral in evaluating a nation’s external standing within the realm of its economy.
Composition of Forex Reserves
India’s foreign exchange reserves comprises
- Foreign Currency Assets (FCA)
- Gold
- Special Drawing Rights (SDR)
-
-
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) are reserve assets on a global scale that the International Monetary Fund (IMF) generates to complement the official reserves of its member nations.
- SDRs are not a currency, but they are denominated in a basket of five currencies: the US dollar, euro, Japanese yen, Chinese renminbi, and British pound sterling.
- SDRs can be used by IMF member countries to settle payments between each other, to purchase IMF-approved currencies, or to borrow from the IMF.
-
- Reserve Tranche Position (RTP) in the IMF
-
- It is the difference between a member country’s quota and the IMF’s holdings of its currency.
- The RTP is a reserve asset that can be used by a member country without any conditions or restrictions.
Note: Foreign Currency Assets excludes
- SDR holdings of the RBI, since they are already counted under the SDR holdings
- investment in bonds issued by India Infrastructure Finance Company (UK) Limited
- amounts lent under the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) Currency swap arrangements
Role of Foreign Exchange Reserves
Foreign exchange reserves play a vital role in a country’s economic stability and growth. In the Indian context, these reserves serve multiple crucial functions:
- Balance of Payments Stability:
-
-
- Foreign exchange reserves help maintain a favorable balance of payments by covering trade deficits and ensuring the stability of the country’s external accounts.
- They act as a buffer against sudden outflows of capital, such as during financial crises or economic downturns.
-
- Exchange Rate Management:
-
-
- Reserves provide a tool for the central bank to intervene in the foreign exchange market, stabilizing the value of the domestic currency against foreign currencies.
- They prevent excessive volatility in exchange rates, which can impact trade competitiveness and investor confidence.
-
- Import Payment Coverage:
-
-
- Adequate reserves ensure the ability to pay for imports, including essential commodities like oil and machinery, even during times of economic stress.
-
- External Debt Servicing:
-
-
- Reserves are used to service external debt obligations, including interest payments and principal repayments, ensuring timely and smooth debt management.
-
- Monetary Policy Support:
-
-
- Foreign exchange reserves offer support to the central bank’s monetary policy objectives, allowing for effective management of interest rates and inflation.
-
- Confidence Building:
-
-
- Healthy reserves boost investor confidence in the economy’s stability and ability to honor financial commitments, attracting foreign investments.
-
- Emergency Financing:
-
-
- In times of emergencies like natural disasters or unforeseen events, reserves can be used to provide immediate financial support without disrupting the overall economy.
-
- International Trade and Investment:
-
-
- Strong reserves signal the country’s credibility, enhancing its position in international trade negotiations and facilitating foreign investment inflows.
-
- Reducing External Vulnerabilities:
-
-
- Ample reserves reduce a nation’s vulnerability to external shocks, ensuring it can navigate economic challenges with greater resilience.
-
- Enhancing Sovereign Credit Rating:
-
- Maintaining substantial reserves contributes to a higher sovereign credit rating, enabling the government to access global capital markets at favorable terms.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Reserves in India
Foreign exchange reserves in India are influenced by several key factors that impact the country’s economic stability and growth:
- FPI Inflows:
-
-
- Heightened Foreign Portfolio Investor (FPI) inflows contribute to an increase in the nation’s foreign exchange reserves.
- Robust FPI investments reflect positive investor sentiment and add to the forex pool.
-
- FDI Inflows:
-
-
- A surge in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows translates to larger foreign exchange reserves.
- Higher FDI indicates long-term investor confidence, bolstering the country’s economic foundation.
-
- Crude Oil Price Fluctuations:
-
-
- Given India’s oil-importing status, a drop in crude oil prices leads to an expansion of the forex reserves.
- Reduced oil costs alleviate the trade balance, supporting forex accumulation.
-
- Import Reduction and Savings:
-
-
- A reduction in imports leads to a growth in foreign exchange reserves.
- Import curtailment positively influences the trade balance, strengthening the reserves.
-
- Gold Imports Decline:
-
-
- India’s significant gold imports make their dip a noteworthy contributor to forex reserve augmentation.
- A decrease in gold imports contributes to a healthier trade balance and higher forex reserves.
-
- Inflation:
-
-
- If inflation in India is high, it can lead to capital outflows, which can deplete the forex reserves.
- This is because investors may move their money to countries with lower inflation rates.
-
- Interest rates:
-
- If interest rates in India are low, it can also lead to capital outflows.
- This is because investors may move their money to countries with higher interest rates, where they can earn more money on their investments.
Sources:
India’s forex reserves drop USD 2.42 billion to USD 601.45 billion | The Financial Express
Q1. With reference to Foreign Exchange Reserves, consider the following statements:
- India’s foreign exchange reserves comprises External Commercial borrowings along with Foreign Currency Assets.
- Foreign Currency Assets form the major component of Forex Reserves followed by Gold Reserves.
- The amounts lent under the SAARC Currency swap arrangements are included in Foreign Currency Assets.
Which of the statements given above is/are NOT correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) None
Answer: (c)
Q2. Consider the following :
- A rise in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) outflows leads to increased foreign exchange reserves.
- In the context of India, a decrease in crude oil prices results in an increase in foreign exchange reserves.
- If interest rates in India are low, it can also lead to capital outflows leading to depleting reserves.
- High inflation in India can lead to capital inflows, which can deplete the country’s foreign exchange reserves.
How many of the abovementioned statements are correct ?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All Four
Answer: (b)
Q3. “Foreign exchange reserves act as a cushion against external shocks and uncertainties.” Analyze this statement in the context of India’s economic growth and stability.



No Comments