25 Jan India’s Health care: Transforming Healthcare through Digitalization
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
GS-2 Social Issue-India’s Health care: Transforming Healthcare through Digitalization
FOR PRELIMS:
Key Govt initiatives related to the digital health sector. What is National health mission
FOR MAINS
What are the key challenges in implementing digital health solutions in India, and how can they be addressed?
Why in the news?
India’s healthcare sector is undergoing a digital transformation driven by government initiatives, policy reforms, and technological advancements. With a growing population and rising healthcare demands, digital health solutions are enhancing accessibility, affordability, and efficiency. Key technologies like telemedicine, electronic health records (EHRs), and AI-driven diagnostics are helping bridge the gap between urban and rural services. The World Economic Forum highlights India’s potential to lead globally in digital health, with a focus on public-private partnerships, interoperability, and strong data governance. Initiatives like the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) and the Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS) are paving the way for a resilient digital healthcare ecosystem and could set a global benchmark.
World Economic Forum Appraisal:
India’s healthcare landscape is undergoing a digital transformation driven by government initiatives, policy reforms, and technological advancements. With a rapidly growing population and increasing demand for quality healthcare, digital health solutions are playing a crucial role in enhancing accessibility, affordability, and efficiency. Digital healthcare infrastructure in India is evolving to bridge the gap between urban and rural healthcare services, leveraging telemedicine, electronic health records (EHRs), and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven diagnostics. The recent World Economic Forum (WEF) article highlights India’s potential to become a global leader in digital health by building a resilient digital health ecosystem. The report emphasizes the role of public-private partnerships, the importance of interoperability, and the need for robust data governance frameworks. It underscores how India’s initiatives, such as the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) and the Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS), can set a global benchmark for digital healthcare transformation.
Digital Health initiatives:
1. Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM): The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) aims to create a digital health ecosystem in India, connecting healthcare providers and patients via unique health IDs. Key features include:
Health ID: A unique ID to store and share medical records.
Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): A database of registered healthcare professionals.
Health Facility Registry (HFR): A repository of healthcare facilities.
Unified Health Interface (UHI): A platform for digital health services.
Over 200,000 Ayushman Arogya Mandirs provide early diagnosis for diseases like cancer, hypertension, and diabetes. As of January 2025, 73 crore ABHA accounts have been created, with 49.15% women beneficiaries. The mission also facilitates offline account creation in areas with limited connectivity. A collaboration with IIT Kanpur will leverage AI for healthcare research, while the Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS) offers financial rewards to healthcare providers adopting digital solutions, promoting a paperless healthcare system.


2. Telemedicine and e-Sanjeevani: The e-Sanjeevani platform offers remote doctor consultations with two main modules: OPD (doctor-to-patient consultations) and AB-HWC (connecting remote Health and Wellness Centers with specialist doctors). This is particularly beneficial in rural or underserved areas.

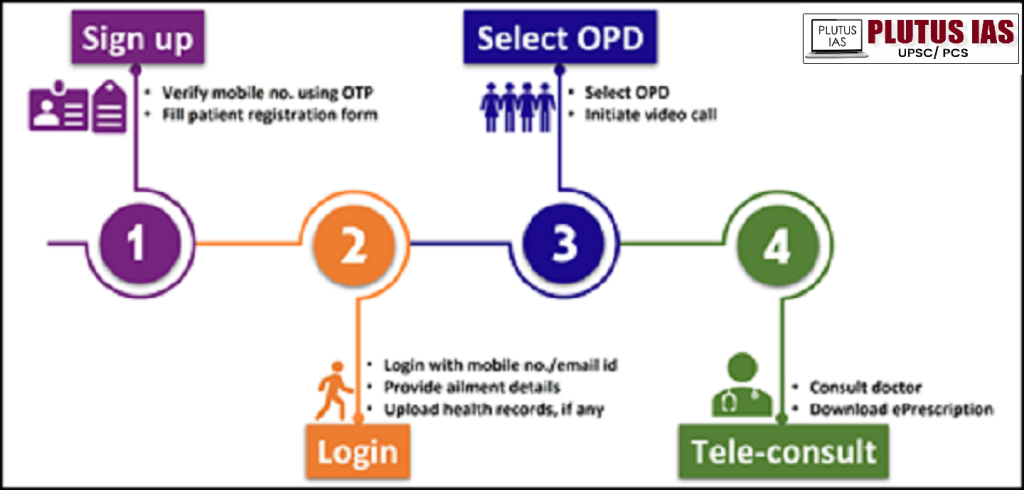
3. U-Win Portal: This platform is dedicated to digitizing vaccination services for pregnant women and children. It provides features like self-registration, automated alerts, and e-vaccination certificates and even allows users to create Ayushman Bharat Health Account IDs for themselves and their children.

4. Aarogya Setu App: Initially developed for COVID-19 tracking, this app has evolved into a broader digital health service platform. It integrates various services like scheduling doctor appointments, receiving prescriptions, downloading vaccination certificates, and managing digital health records.

5. e-Hospital: Part of the Digital India initiative, this platform is a hospital management system for both patients and healthcare providers. It integrates services like blood bank management and hospital registrations, making healthcare more accessible online.

6. National Tele Mental Health Programme (Tele MANAS): Launched in 2022, this program aims to improve access to mental health services through teleconsultations, with more than 17.6 lakh calls handled as of January 2025.

Key policies Shaping digital Health care:
1. National Health Policy (NHP) 2017: Focuses on using digital technologies like electronic health records and telemedicine to improve healthcare accessibility and efficiency, especially in rural and underserved areas.
2. National Health Mission (NHM): Supports health infrastructure and human resources, aiming to improve access to quality healthcare for marginalized and rural populations. It provides technical and financial assistance to states for strengthening public healthcare systems.
3. Health Data Management Policy: Ensures privacy, security, and governance of digital health records, with strict protocols for patient consent, data anonymization, and secure data exchange across stakeholders.
4. National Digital Health Mission (NDHM): Aims to provide universal health coverage through a digital infrastructure, including Health IDs, Digi Doctor repositories, Health Facility Registers, and Personal Health Records. It focuses on interoperability, cybersecurity, and data exchange to ensure a secure and accessible healthcare ecosystem.

5. Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM): Strengthens primary, secondary, and tertiary healthcare infrastructure, integrating digital health technologies to enhance service delivery, research, and emergency response capacities. It’s the largest public health infrastructure initiative since 2005.
Concerns regarding digital Health care:
Way forward:
1. Strengthening Data Security & Privacy: Ensure strict compliance with data protection regulations and continually update security measures to safeguard health data. Implement advanced encryption and blockchain technologies to enhance security and maintain patient trust.
2. Bridging the Digital Divide: Increase investments in digital infrastructure, especially in rural and underserved areas, to ensure that everyone can access digital health services. Provide training programs to improve digital literacy among healthcare workers and the general population.
3. Achieving Interoperability: Promote standardized frameworks for data exchange across health systems. Ensure seamless integration between digital health services like Health IDs, EHRs, and telemedicine platforms to facilitate smooth and efficient healthcare delivery.
4. Establishing Clear Regulations: Develop comprehensive regulatory frameworks for AI-driven healthcare technologies and telemedicine, ensuring quality standards and accountability. Create transparent guidelines for AI usage and ensure consistent monitoring to guarantee patient safety.
5. Healthcare Worker Training & Support: Implement continuous training programs for healthcare professionals to effectively use digital tools and stay updated on new technologies. Provide ongoing technical support and education to ensure the proper utilization of digital health services.
6. Addressing Ethical Issues in AI: Develop ethical guidelines for AI usage in healthcare, ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI-driven decision-making. Conduct regular audits of AI systems to prevent biases and ensure equitable treatment for all patients.
7. Sustainable Investment & Funding: Ensure sustained government and private sector investments to expand and maintain digital health infrastructure. Explore innovative funding models like public-private partnerships (PPP) to ensure the long-term sustainability of digital health solutions.
Conclusions
India’s digital healthcare transformation holds immense potential to enhance healthcare accessibility and efficiency. With continued policy support, infrastructure development, and public-private collaborations, the country is poised to emerge as a global leader in digital health. Future focus areas include AI-driven diagnostics, blockchain-based health records, and enhanced cybersecurity frameworks. The Indian government’s proactive approach toward digital healthcare infrastructure and policies is shaping a more efficient and accessible healthcare system. With growing investments in digital health and technological advancements, India’s healthcare system is expected to evolve into a globally recognized model for digital transformation, setting benchmarks for other developing nations.
Prelims Question:
Q. With reference to the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), consider the following statements:
1. The ABDM aims to create a nationwide digital health ecosystem by connecting healthcare providers and patients through unique health IDs.
2. ABDM provides for the integration of AI technologies to improve the quality of healthcare services and outcomes.
3. The mission aims to provide only online consultation services, excluding physical healthcare infrastructure improvements.
How many of the above-given statements are correct?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. All three
D. None
Answer: B
Mains Question:
(250 words, 15 marks)




No Comments