20 Sep India’s High-Tech Revolution: Driving Global Leadership in Advanced Technology & Manufacturing
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and topic details of India’s Advancement in technologies and recent advancements.
Syllabus mapping:
GS-3: Science and Technology: Recent advancement in the field of communication and biotechnology and other science domains.
For Prelims:
What are the schemes and related facts? National Quantum Mission, National Semicorn Mission, Green Hydrogen Mission, India AI program, PM—DRIVE Scheme, etc.
For Mains:
What are the major forces behind the recent advancements in science and technology in India, What are the challenges to making India’s science and technology on par with the other developed countries and way forward?
Why in the News?
Recently, the PM of India highlighted the advancement in the science and technology field at the Semicorn India Summit 2024.

Government of India’s initiatives in recent times for the advancement of science and technology:
WISE-KIRAN: The Women in Science and Engineering-KIRAN (WISE-KIRAN) initiative aims to promote gender equity in science and technology by providing diverse opportunities for women from various backgrounds.
INSPIRE program: The Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research (INSPIRE) program seeks to attract talented youth to study basic and natural sciences and pursue research careers, thereby expanding India’s research and development base.
VAIBHAV Research Programme: This aims to connect the Indian STEMM diaspora with local institutions to foster research collaborations and innovation.
National Programme on Nano Science and Technology (NPNST): the National Programme on Nano Science and Technology (NPNST) focuses on building capacity in nanoscience research, promoting high-impact innovation, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, and enhancing India’s global competitiveness in the field of nanotechnology.

Reasons for the Recent boost in the science and technology Advancement:
1. The proactive policies of the governments: The initiatives like National Quantum Mission, and the National Semiconductor mission are examples of the proactive role of the Governments.
2. Skilled workforce: Due to the government’s positive approach many enthusiastic budding scientists join the hands of the Government.
3. Role of private players: Private players are working hand in hand with the government for the advancement of scientific development. For example India’s space sector. Recently private startup in Hyderabad launched its small satellite.
4. The increased allocation of funding to R&D: In the last decade, The Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD) increased from ₹601,968 million in 2010-11 to ₹1,273,810 million in 2020-21.
5. Robost of the startup culture: India has become the third largest startup economy in the world and most startups are in the domain of science and technology.
6. Global Collaborations: Partnerships with international research institutions and organizations have facilitated knowledge exchange and access to cutting-edge technologies. India is actively engaging with the International Renewable Energy Agency, and Space institutions to boost the advancement in the science field.
7. Focus on STEM Education: The NEP 2020, emphasizes science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education has created a skilled workforce equipped to tackle complex challenges.
8. Digital Transformation: The rapid adoption of digital technologies has accelerated research processes and enhanced data analysis capabilities. Digital India mission and digital Agriculture mission are boosting g the demand for new technologies.
9. Emerging Technologies: Advancements in fields such as artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and nanotechnology have opened new avenues for research and application.
10. Sustainability Initiatives: Growing awareness and initiatives focused on sustainability and climate change have spurred research in green technologies and renewable energy.
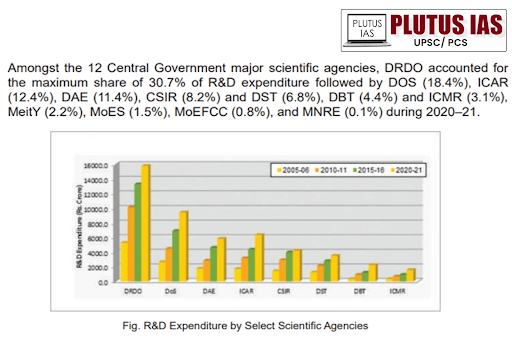
Despite the recent boost, the challenges persist these are:
1. Less GERD: The spending on gross expenditure on research and development is just approx, 1 % of India’s GDP compared to China(2%) and the US (3.5 %).
2. Lack of Formalization of Innovation: In India, most of the innovations are not patented as compared to China and the US. This limits the impact of innovation on the ground level and social benefits for society as a whole.
3. Selective domains: the present focus on innovation and research is majorly concentrated in space technology and communication technology. However, the health sector, education sector, and social welfare sector these sectors do not attract more science funding or support.
4. Infrastructure Limitations: Inadequate research facilities and infrastructure hinder the ability to conduct high-quality research and development.
5. Talent Retention: There is a brain drain as skilled researchers and professionals often seek opportunities abroad, leading to a loss of talent.
6. Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Despite the attempt from the NEP 2020 there is still a Lack of collaboration between different scientific disciplines can limit innovative solutions to complex problems.
7. Policy Implementation: Challenges in translating supportive policies into effective action can slow down progress and innovation. This is a clear example in the case of the rare diseases innovation and many other health issues.
8. Cybersecurity Threats: As reliance on digital technologies increases, so does the vulnerability to cyberattacks, affecting research data and infrastructure. The recent attack highlighted the vulnerability of the digital public infrastructure.
9. Dependency on imports: India’s most scientific advancement depends on imported raw materials and this is not sustainable for the long term, especially in the context of the border conflict with China and, the PAGER attack in Lebanon.
10. Equity in Access: Ensuring advancements in science and technology are accessible to all regions and demographics is essential but challenging.
Solutions to make scientific development for we the people of India
1. Robust Government Support: The Indian government has significantly increased its funding and support for research and development, with allocations exceeding ₹1,00,000 crore in recent budgets for science and technology initiatives.
2. International Partnerships: Collaborations with global tech giants and research institutions will facilitate technology transfer and knowledge sharing, enhancing India’s capabilities in key sectors such as artificial intelligence and biotechnology.
3. Strategic Investments: Focused investments in emerging areas like electric vehicles and renewable energy would pave the way for sustainable growth. For instance, India aims to have 30% electric vehicle penetration by 2030, which will require substantial innovation and infrastructure development.
4. Electronics Manufacturing: The government’s Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme aims to boost electronics manufacturing, with an investment target of ₹75,000 crore to attract global manufacturers and promote local production. The major domain for scientific advancement will need special attention and support.
5. Innovation-Driven Ecosystem: innovations need to be further boosted such as India’s start-up ecosystem has been thriving, with over 60,000 start-ups and a valuation exceeding $200 billion as of 2023, fostering innovation across various sectors.
6. Reducing Import Dependency: By enhancing domestic manufacturing capabilities, India is striving to reduce its reliance on imports, particularly in critical areas such as semiconductors, where the government has launched a ₹76,000 crore initiative to boost local production.
7. Nurturing Home-Grown Talent: Initiatives like the Skill India Mission aim to equip the workforce with the necessary skills, targeting over 400 million individuals by 2022 to meet the demands of the evolving tech landscape.
8. Advancements in New-Age Technologies: India is making strides in cutting-edge technologies such as 5G, IoT, and AI, with investments expected to reach $20 billion in AI alone by 2025.
9. Long-Term Growth and Increased Exports: With a target to reach $1 trillion in manufacturing output by 2025, India is positioning itself as a key player in global supply chains, enhancing its export capabilities.
10. Job Creation: The focus on expanding manufacturing and technology sectors is projected to create millions of new jobs, contributing to economic growth and stability.
Conclusion:
The recent advancement in scientific development is commendable and it helps India to achieve many milestones like internet connectivity in villages, renewable energy targets, etc. The need is to address the dependency, equity, and infrastructure challenges through a public-private partnership, equitable distribution of resources, and nurturing the scientific temper. The main objective make India a developed country by 2047 and scientific development is a major pillar in this journey the need is to harness its potential.
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 20th Sep 2024
Prelims Question:
Q. Consider the following Constitutional provisions:
1. Fundamental Rights
2. Directive Principles of State Policies
3. Fundamental Duties
4. Preamble
How many of the above provisions explicitly mention science and related topics?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. Only three
D. All four
ANSWER: B
Mains Question:
Discuss the recent advancement in the field of science and technology in India, and mention its challenges and how these developments would help to make India a developed country by 2047?
(150 words 10 marks)




No Comments