12 Sep India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission: Pioneering Clean Energy Leadership and Self-Reliance
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and topic details of Green hydrogen and its role as a source of clean energy
Syllabus mapping:
GS-3: Environment: pollution and related issues. Renewable energy resources.
For Prelims:
What is Green Hydrogen, various types of Hydrogens, and what are the Key facts about the National Mission on Green Hydrogen?
For Mains:
What are the objectives of the National Green Hydrogen mission, the Significance of the mission, the challenges faced by the mission, and ways to make green hydrogen a source of renewable energy?
Why in the News?
PM Modi addresses the International Conference on Green Hydrogen virtually. He also highlited India’s Commitment to Clean Energy.

What is Hydrogen and its various forms?
Hydrogen: Hydrogen is the most fundamental element in the universe, comprising only one proton and one electron. It is the simplest and most abundant element, playing a crucial role in various chemical processes.
It can be produced and used in various forms, each with distinct methods of production and environmental impacts. Green hydrogen offers many benefits such as 1. Plentiful Supply 2. Transportable, 3. Excellent Storage, 4. Utilizes Excess Renewable Energy, 5. Energy Efficiency, 6. Readily Available.
Various forms of Hydrogen based on Production Methods
Grey Hydrogen: Produced by steam reforming of fossil fuels, emitting CO2 and contributing significantly to global warming.
Blue Hydrogen: Created through steam reforming with carbon capture and storage (CCS) to reduce CO2 emissions.
Green Hydrogen: Generated via electrolysis using renewable energy sources, producing only oxygen as a by-product.
Turquoise Hydrogen: Produced by thermally cracking natural gas into hydrogen and solid carbon.
Pink Hydrogen: Made through electrolysis powered by nuclear energy, providing low emissions.
Applications of Green Hydrogen:
1. Fuel and Feedstock Substitution: Replaces fossil fuel-derived feedstocks in key industries such as petroleum refining, fertilizer production, and steel manufacturing.
2. Decarbonizing Mobility: Powers long-haul trucks and marine vessels, reducing emissions in the transportation sector.
3. Energy Carrier for Remote Areas: Provides sustainable energy solutions for remote locations, including islands, where traditional infrastructure is challenging.
4. Storage of Renewable Energy: Stores excess renewable energy, converting it into hydrogen for later use, thus optimizing energy resource management.
5. High-Energy Density Applications: Supplies energy for high-energy-density needs such as aviation and heavy industry, where electrification is difficult.
6. Chemical Production: Serves as a clean feedstock for producing chemicals like ammonia and methanol, contributing to greener industrial processes.
National Green Hydrogen Mission
The government launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission in 2023, aiming to position India as a global leader in Green Hydrogen.

Mission Objectives:
1. Global Hub: Position India as the global hub for the production, usage, and export of Green Hydrogen and its derivatives.
2. Self-Reliance: Achieve energy self-reliance (Aatmanirbhar) through clean energy.
3. Inspiration: Serve as a model for the global clean energy transition.
4. Decarbonization: Drive significant reductions in carbon emissions across the economy.
5. Fossil Fuel Dependence: Decrease reliance on fossil fuel imports.
6. Leadership: Establish India as a leader in Green Hydrogen technology and markets.
Key components of the NGHM:
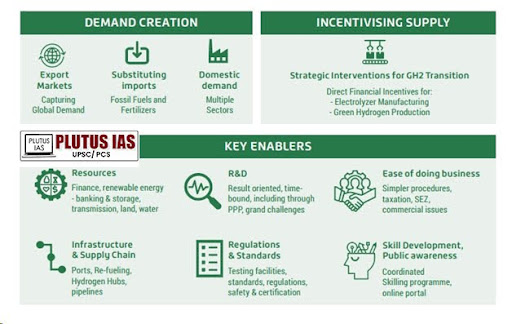
Significance of the NGHM:
Decarbonization of the Economy: The Mission aims to cut carbon emissions significantly by promoting Green Hydrogen, a zero-emission fuel.
Reduction of Fossil Fuel Dependence: The initiative seeks to reduce India’s dependence on imported fossil fuels by boosting domestic Green Hydrogen production.
Global Benchmark for Clean Energy Transition: The Mission aims to set a global benchmark for Green Hydrogen adoption, highlighting India’s leadership in clean energy.
Enhancement of Technology and Market Leadership: The initiative will drive advancements in hydrogen technologies, such as electrolysis and fuel cells, establishing India as a tech leader.
Economic Benefits: Transitioning to Green Hydrogen is expected to boost economic growth through new investments, job creation, and infrastructure development.
Environmental Benefits: The Mission will improve air quality and environmental health by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and cutting carbon emissions.

Challenges to the use of Green Hydrogen technology and implementation of the NGHM:
1. Safety: Hydrogen’s high flammability compared to petrol, natural gas, or propane raises safety concerns, particularly for vehicles and during transportation or storage.
2. Storage: Due to hydrogen’s low energy density, it must be stored at high pressures, low temperatures, or through chemical processes, creating challenges for compact storage in lighter vehicles.
3. Transportation: The low density of hydrogen complicates its transportation, necessitating either liquefaction at -253°C or compression to 700 times atmospheric pressure.
4. Infrastructure: The widespread use of hydrogen fuel cells in vehicles necessitates significant investment in refueling infrastructure to support users.
5. Cost of Production: The production of green hydrogen remains costly due to expensive fuel cell technology and electrolysis processes, including the use of platinum catalysts.
6. Technological Advancements: While India has made progress, there are still gaps in advanced technologies for efficient hydrogen production, storage, and utilization.
7. Skill Development: There is a shortage of skilled professionals in the emerging field of green hydrogen technology.
The Future of Green Hydrogen Technology
1. Financial support: The first step is to devote more financial resources to the private and public sectors to ensure investment in safety.
2. Role in Climate Neutrality: Green hydrogen is essential for achieving climate neutrality, It can store surplus renewable energy, decarbonize long-distance transport and heavy industry, and replace fossil fuels in various applications.
3. India Leadership: the commitment of net zero can be achieved by setting precedence, in this India can take the lead in the global south.
4. Global collaboration: India can partner with countries like Australia, Chile, Germany, Japan, and Saudi Arabia are also advancing their green hydrogen initiatives.
5. Complementary Solution: Green hydrogen will be part of a broader mix of solutions to combat climate change. In the short term focusing on the pilot projects is important. Concept of Green Highways etc.
6. Demographic Dividend: India can harness the potential of its Demography to skill these workforces to work in renewable energy including Green Hydrogen.
7. Policy support: Government initiatives like the SIGHTS program and other policies need to be consistently supported by the government so private players can invest in green energy.
Conclusion:
Green hydrogen, when produced in an environmentally friendly manner, has the potential to play a pivotal role in addressing climate change. As a zero-emission energy source, it not only offers the advantage of storing excess renewable energy but also presents a virtually limitless resource. With continued commitment and investment, green hydrogen could soon become a significant player in global decarbonization efforts and the transition to a sustainable energy future.
PRELIMS QUESTION:
Q.Consider the following Information:
| Sr | Type of Hydrogen | Sources |
| 1 | Green Hydrogen | Produced from the Natural Gas |
| 2 | Blue Hydrogen | Produced from renewable energy |
| 3 | Gray Hydrogen | Produced from vehicular emission. |
| 4 | Pink Hydrogen | Produced from animal shells. |
In how many of the given- above pairs are correctly matched?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. Only three
D. All four
ANSWER: A
MAINS QUESTION:
Green hydrogen is emerging as a key solution for decarbonizing hard-to-electrify industries and for surplus renewable energy storage. In this context, discuss the challenges and future of green hydrogen as a renewable energy source.
(250 words 15 marks)




No Comments