21 Oct India’s Strategic Engagement with Africa: Highlights from President Murmu’s Visit
Posted at 21 Oct 2024
in
Current Affairs
by Ritik singh
SYLLABUS MAPPING:
GS-2 International Relation-India’s Strategic Engagement with Africa: Highlights from President Murmu’s Visit
FOR PRELIMS
What role does India play in addressing challenges faced by African nations, such as climate change and food security, as discussed during President Murmu’s tour.
FOR MAINS:
Analyze the potential impact of India-Africa partnerships on sustainable development in both regions, as highlighted during President Murmu’s visit.
Why In the News?
President Droupadi Murmu on Saturday left for home after wrapping up her three-nation visit to Algeria, Mauritania and Malawi, establishing new benchmarks in India-Africa relations. It was the first visit by an Indian Head of State to the three African nations.
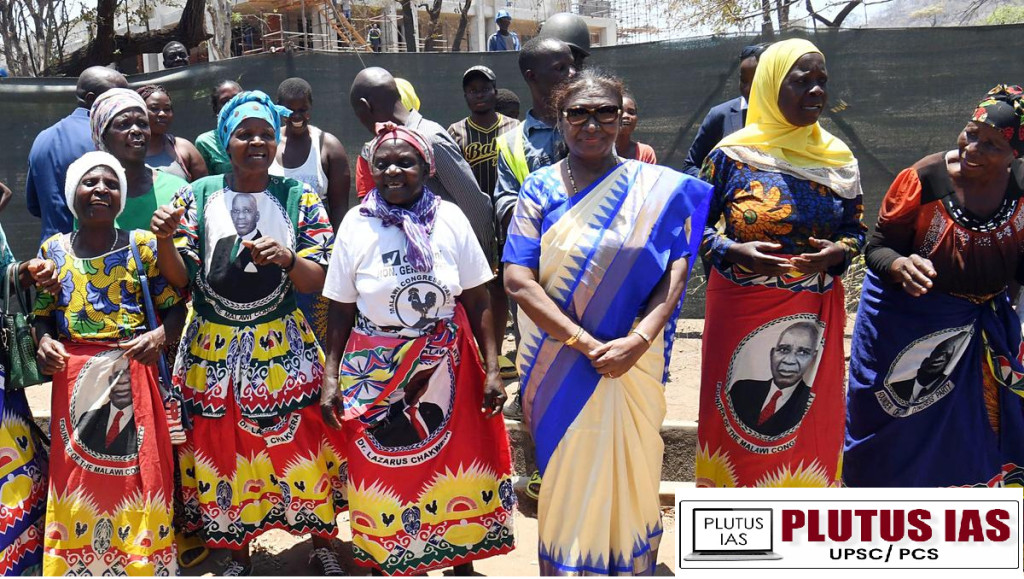

India Africa growing Cooperations:
1. Economic and Development Cooperation
Market Potential: Africa presents an untapped market for Indian businesses, especially in textiles, pharmaceuticals, automobiles, and light machinery.
Trade Growth: From 2011 to 2022, India’s total goods trade with Africa surged from USD 68.54 billion to USD 90.52 billion, reflecting a robust economic partnership. In 2022, India recorded a positive trade balance with Africa for the first time.
Infrastructure Investments: India has committed significant financial assistance through lines of credit for infrastructure projects across Africa, notably in renewable energy, roads, and railways, enhancing connectivity and development.
ITEC Program: The Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program provides training and capacity-building initiatives, helping thousands of African professionals enhance their skills in various sectors.
2. Health and Humanitarian Collaboration
Affordable Medicines: Indian pharmaceutical firms are key providers of generic medicines in Africa, improving access to essential healthcare and supporting public health systems.
Medical Assistance: India has dispatched medical teams to assist in combating diseases like HIV/AIDS, malaria, and Ebola, contributing to health infrastructure and emergency response capabilities.
Capacity Building: Initiatives like the Africa-India Health Sciences Institute aim to improve healthcare education and training for African medical professionals.
3. Defence and Security Engagement
Strategic Partnerships: India has signed MoUs with African nations along the Indian Ocean Rim, highlighting a commitment to enhance defence collaboration and maritime security.
India-Africa Defence Dialogue: The establishment of the IADD at the defence ministers’ level in 2020 and 2022 showcases India’s focus on strategic dialogue regarding security issues in the region.
Joint Exercises: The first Trilateral Maritime Exercise with Tanzania and Mozambique in 2022 reflects a proactive approach to strengthening maritime cooperation and addressing security challenges.
4. Technology and Digital Initiatives
Pan African e-Network Project: Launched in 2009, this project facilitates satellite connectivity for telemedicine and tele-education, significantly impacting access to services in remote areas.
e-VidyaBharti and e-ArogyaBharti: These programs provide free tele-education and continuing medical education, enhancing learning and professional development for healthcare workers in Africa.
Digital Innovation: Initiatives promoting digital literacy and technology transfer aim to bolster Africa’s tech ecosystem, fostering entrepreneurship and innovation.
Significance of Africa for India :
1. Economic Potential: Projected GDP growth of 4% in 2023 and a bilateral trade reaching USD 98 billion in 2022-23, Africa is an attractive market for Indian businesses. The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) creates a unified market of 1.3 billion people, enhancing export and investment prospects.
2. Geopolitical Importance: Africa’s 54 nations form a significant bloc in international forums, crucial for India’s aspirations for greater global representation. India’s support for African representation in the UN Security Council and the African Union’s permanent membership in the G20 during India’s 2023 presidency highlight this strategic partnership.
3. Energy Security: Africa supplies about 15% of India’s oil demand, with key suppliers like Nigeria and Angola. The continent’s rich mineral resources are essential for India’s energy transition. Initiatives like the International Solar Alliance’s USD 2 billion funding for solar projects strengthen this energy partnership.
4. Maritime Security: Africa’s eastern coast is critical for India’s maritime interests in the Indian Ocean. Defence agreements and joint naval exercises, such as the India-Mozambique-Tanzania Trilateral Exercise, enhance regional security and protect maritime trade.
5. Cultural Connections: The 3 million-strong Indian diaspora in Africa fosters strong cultural and economic ties. Initiatives like the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas aim to leverage this community’s influence for mutual benefit.
Significance of India for Africa :
1. Economic Potential:
AfCFTA Opportunities: The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) is poised to create the largest free trade zone, providing India with opportunities to enhance bilateral trade and lift millions out of poverty.
Services Trade: There are substantial opportunities in sectors like Information Technology, mobile payment solutions, banking, and financial services, leveraging India’s expertise.
Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare: India’s success in vaccine manufacturing and telemedicine can lead to collaborative ventures in Africa’s healthcare sector, improving access to essential medicines and healthcare services.
2. Infrastructure Development
Digital Infrastructure: India’s robust start-up ecosystem it can play a vital role in enhancing Africa’s digital infrastructure, aligning with Agenda 2063 goals.
Supply Chain Facilitation: India can assist in building infrastructure for cross-border supply chains in critical sectors like food and pharmaceuticals, enhancing operational efficiency.
3. Soft Power
Cultural Influence: India’s soft power, amplified by the Indian diaspora in countries like Mauritius, fosters trust and collaboration on joint projects, enhancing India’s image in Africa.
Women’s Empowerment: By engaging with Africa’s informal labour force, particularly women, India can contribute to socioeconomic development and enhance its brand image.
4. Common Agendas
Shared Development Goals: Both regions face similar developmental challenges, facilitating a mutual understanding of issues like UNSC reform, climate change, and trade negotiations.
Capacity Building: India’s focus on capacity building and knowledge transfer aligns with Africa’s development needs, promoting sustainable growth.
5. Strategic Collaboration
Security Cooperation: India and Africa can strengthen ties in addressing security challenges, including terrorism and regional stability, enhancing peace and security across the continent.
Concern issue between Africa India- cooperation:
1. Investment Inertia
Lagging Investments: Indian investments in Africa are significantly lower than those from China and Western countries.
Challenges for Companies: Indian firms face risk perception issues, lack of local market knowledge, and competition from established players.
Example: Arcelor Mittal’s exit from a $2.2 billion iron ore project in Senegal in 2020 due to challenges faced.
2. Perception Issues of Indian Products
Quality Concerns: Some African markets perceive Indian products as inferior compared to Western or Chinese alternatives.
Notable Incident: A tainted syrup medicine imported from India led to over 60 children’s deaths in Gambia in 2022, damaging India’s reputation.
3. Diplomatic Dilemma
Regional Imbalance: India’s engagement has been criticized for focusing predominantly on East and Southern Africa, neglecting West Africa.
Trade Figures: For instance, India’s exports to South Africa alone reached $8.47 billion in 2022-23, overshadowing other regions.
4. Project Execution Predicament
Implementation Challenges: Indian development projects in Africa often face delays and execution issues.
Example: The Rivatex textile factory revival project in Kenya experienced significant delays, eroding trust.
5. Resource Rivalry
Intensified Competition: Both India and China compete for resources in Africa, particularly in the oil and gas sector.
Example: India lost a bid for oil assets in Angola to China in 2006, highlighting competitive tensions.
These points summarize the key friction areas in the India-Africa relationship, reflecting both economic and diplomatic challenges
6. Trade Barriers
Tariff and Non-Tariff Barriers: African countries often impose high tariffs and regulatory hurdles that can impede Indian exports, making market access challenging.
Complex Regulations: Differences in regulatory frameworks and standards can create obstacles for Indian businesses seeking to enter African markets.
7. Security Concerns
Regional Instability: Political instability and security issues in certain African regions can deter Indian investment and engagement.
Safety of Investments: Concerns about the safety of Indian investments in conflict-prone areas may lead to a more cautious approach.
8. Health and Safety Standards
Quality Control: Incidents of substandard products or services can harm India’s image, particularly in sectors like pharmaceuticals and construction.
Regulatory Compliance: Stricter local health and safety regulations may not always align with Indian practices, leading to challenges in compliance.
Way forward:
1. Strengthening Trade Relations
Bilateral Trade Agreements: Negotiate and implement comprehensive trade agreements that reduce tariffs and non-tariff barriers, facilitating easier access to markets.
Promotion of Indian Products: Increase efforts to promote the quality and reliability of Indian products through marketing campaigns and participation in trade fairs.
2. Enhancing Investment Opportunities
Risk Mitigation Strategies: Develop mechanisms to address risk perceptions among Indian investors, such as insurance schemes or government-backed guarantees.
Support for Local Partnerships: Encourage Indian companies to form joint ventures with local firms to leverage local knowledge and networks.
3. Increasing Diplomatic Engagement
High-Level Visits and Dialogues: Foster regular high-level diplomatic visits to strengthen ties and address mutual concerns directly.
Diversified Engagement: Expand focus beyond East and Southern Africa to include West and Central Africa, ensuring a more balanced approach.
4. Capacity Building and Knowledge Sharing
Training Programs: Implement training and capacity-building initiatives in key sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and technology.
Scholarships and Exchanges: Increase scholarships and exchange programs for African students to study in India, promoting people-to-people connections.
5. Promoting Sustainable Development
Sustainable Practices: Ensure that Indian investments prioritize sustainable and environmentally friendly practices to gain local support.
Community Engagement: Actively involve local communities in project planning and execution to address their concerns and needs.
6. Leveraging Technology and Innovation
Digital Initiatives: Collaborate on digital infrastructure projects that enhance connectivity and access to technology across Africa.
Start-up Collaboration: Encourage partnerships between Indian and African start-ups to foster innovation and share best practices.
7. Enhancing Security Cooperation
Joint Security Initiatives: Strengthen security partnerships to address common threats such as terrorism and piracy, fostering stability in the region.
Training and Capacity Building: Provide training and support for African security forces to enhance their capabilities.
8. Engaging in Multilateral Forums
Unified Voice in Global Issues: Work together in international forums to address common challenges such as climate change, trade imbalances, and global health issues.
Strengthened Alliances: Build alliances with other countries and regions to amplify their voices in discussions that impact both India and Africa.
Conclusion:
The evolving India-Africa partnership holds immense promise, but navigating the complexities of investment, perception, and regional dynamics is crucial for realizing its full potential. By focusing on mutual benefits, sustainable practices, and strategic collaboration, both regions can forge a path toward a prosperous future that addresses shared challenges and fosters growth.
Prelims Question:
Q. Which initiative aims to enhance telemedicine and tele-education access across Africa?
A. India-Africa Defence Dialogue
B. e-VidyaBharti
C . Pan African e-Network Project
D. Africa-India Health Sciences Institute
Answer: C






No Comments