31 Jul Industry in Pre-Liberalization Era
Industry in Pre-Liberalization Era
The industrial development of India during the pre-liberalization era (1947–1991) was predominantly shaped by a socialist vision with an emphasis on state control, planning, and public sector undertakings (PSUs). This period witnessed a gradual but state-dominated industrialization process aimed at achieving self-reliance, equitable distribution, and curbing the concentration of economic power. While the goals were noble, inefficiencies stemming from over-regulation, bureaucratic controls, and poor private sector participation created several challenges.
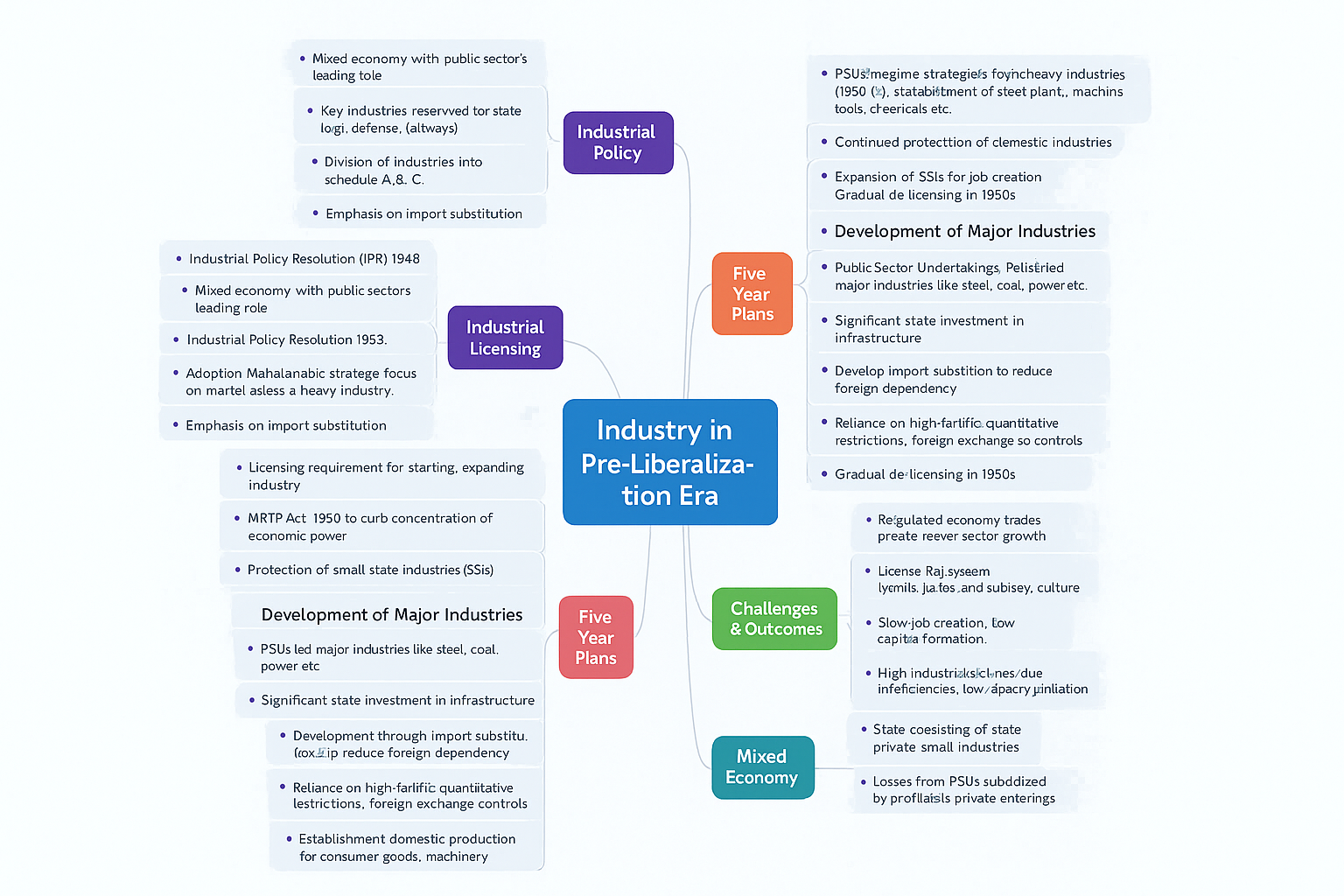
Mind Map: Industry in Pre-Liberalization Era
1. Industrial Policy Resolutions (IPRs)
1.1 Industrial Policy Resolution 1948
- Laid the foundation of a mixed economy in India
- Reserved certain sectors (like defense, railways) for the state
- Encouraged private sector but under state guidance
1.2 Industrial Policy Resolution 1956
- Core document of Nehruvian socialism
- Classified industries into Schedule A (exclusively public sector), B (joint sector), and C (private sector)
- Focused on import substitution, capital goods, and self-reliance
1.3 Industrial Policy of 1980
- Marked initial steps towards liberalization
- Encouraged modernization of industries and some deregulation
- Boosted the growth of small-scale industries (SSIs)
2. License Raj and Industrial Licensing
The term “License Raj” refers to the elaborate system of licenses, permits, and regulations that governed Indian industry prior to 1991.
- Industrial Development and Regulation Act (IDRA), 1951 made licensing compulsory for establishing new units
- MRTP Act, 1969 aimed at curbing monopoly and preventing economic concentration
- Small scale industries (SSIs) protected through reservation policies and tax concessions
3. Role of Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs)
- Established in core sectors: steel, coal, petroleum, electricity, machine tools, and fertilizers
- Major employers and contributors to infrastructure development
- Provided goods and services in strategic sectors
- Suffered from inefficiencies, bureaucratic delays, overstaffing, and low productivity
4. Five-Year Plans and Industrialization
4.1 Second Five-Year Plan (1956-1961)
- Based on Mahalanobis model
- Emphasized heavy industries like steel, iron, power
- Major state investment in PSUs
4.2 Fourth Plan to Sixth Plan (1969–1985)
- Focus shifted slightly toward agriculture and poverty alleviation
- Industrial growth slowed due to stagnation in global economy, domestic controls
4.3 Seventh Plan (1985-1990)
- Attempted liberalization by deregulating selected sectors
- Encouraged exports, technology upgradation, and modernization
5. Import Substitution Industrialization (ISI)
India adopted ISI strategy to protect domestic industries by replacing imports with local production.
- High tariff barriers and quotas on imports
- Exchange control and regulation of foreign collaboration
- Promoted backward linkages in the domestic economy
Infographic: Industrial Growth in Pre-Liberalization Era
6. Challenges of Industrial Policy
- Low industrial productivity
- Under-utilization of capacity in PSUs
- Corruption and red tape in licensing system
- Inadequate R&D and innovation
- Limited participation of private sector and foreign investment
- Stagnation in capital goods and infrastructure sector
7. Mixed Economy and Private Sector Role
While the state dominated “commanding heights” of the economy, the private sector continued in consumer goods, textiles, engineering, and services.
- Private sector faced difficulty accessing finance and imports
- Growth often hindered by excessive government interference
- Emergence of business houses like Tata, Birla, and Reliance despite restrictions
8. Outcome of Pre-Liberalization Industrial Strategy
- Industrial growth averaged 5-6% in 1950–1980 but declined during 1980s
- Failed to absorb surplus labor from agriculture
- Widening regional and sectoral disparities
- Industrial stagnation and BoP crisis led to 1991 reforms
Previous Year UPSC Mains Questions
- Discuss the impact of Industrial Policy Resolution of 1956 on India’s industrial development. (2020)
- What do you understand by License Raj? Evaluate its implications on Indian industry. (2018)
- Critically assess the performance of PSUs during the pre-liberalization era. (2016)
Probable UPSC Mains Questions for 2025
- How did import substitution affect India’s long-term industrial competitiveness?
- Was the Nehruvian industrial model successful in achieving its objectives?
- Discuss the role of Five-Year Plans in shaping industrial strategy in India before 1991.
Probable UPSC Prelims Questions for 2025
- The Industrial Policy Resolution of 1956 classified industries into how many categories?
- The MRTP Act was introduced to deal with what issue?
- Which Five-Year Plan adopted the Mahalanobis strategy?
Conclusion
India’s industrial policy during the pre-liberalization era was designed with the vision of inclusive development and self-reliance. While it created a large base of heavy industries and public sector units, it also led to inefficiencies due to over-regulation and bureaucratic controls. The structural weaknesses exposed by the balance of payments crisis in 1991 necessitated the shift towards liberalization, privatization, and globalization.
GS paper 4 syllabus and study plan
GS paper 3 syllabus and study plan




No Comments