14 Aug Initiatives under National Food Security Mission (NFSM)
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “Initiatives under National Food Security Mission (NFSM)”. The topic “Initiatives under National Food Security Mission (NFSM)” has relevance in the Social Justice section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
What are Sponge Cities?
For Mains:
GS 2: Social Justice
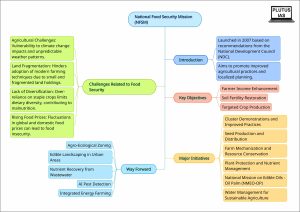
About the National Food Security Mission (NFSM)?
Challenges Related to Food Security in India?
Way Forward?
Why in the news:
In a written response in the Lok Sabha, the Union Minister of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare shared significant updates regarding the progress within the National Food Security Mission.
About National Food Security Mission (NFSM):
The National Food Security Mission (NFSM), launched in 2007 based on recommendations from the agriculture sub-committee of the National Development Council (NDC), addresses the pressing need for improved agricultural practices, technology dissemination, and localized planning.
Key Objectives:
- Targeted Crop Production: The mission aims to boost the production of essential crops like rice, wheat, pulses, coarse cereals, nutri-cereals, and oilseeds.
- Soil Fertility Restoration: Enhancing soil fertility and productivity at the individual farm level is a crucial goal.
- Income Enhancement: NFSM seeks to increase farm-level net income, thus improving the livelihoods of farmers.
Major Initiatives:
Cluster Demonstrations and Improved Practices:
- NFSM facilitates farmers through States/Union Territories to conduct cluster demonstrations that showcase optimized agricultural practices.
- These demonstrations play a pivotal role in highlighting improved techniques for crop cultivation and management.
Seed Production and Distribution:
- A key focus of NFSM is the development, production, and distribution of high-yielding crop varieties and hybrids.
- The goal is to enhance both the quality and quantity of agricultural output, contributing to food security.
Farm Mechanization and Resource Conservation:
- The implementation of modern and efficient farm machinery, coupled with the adoption of resource conservation tools, fosters enhanced agricultural practices.
- These measures optimize resource utilization and contribute to sustainable production.
Plant Protection and Nutrient Management:
- To ensure healthy plant growth, NFSM emphasizes protective measures against pests and diseases.
- Effective nutrient management and soil enhancement strategies are also promoted for improved crop productivity.
Oilseeds Production Focus:
- Recognizing the importance of oilseeds in the diet, NFSM-Oilseeds initiative focuses on boosting oilseed production to achieve self-sufficiency in edible oil.
- The initiative involves a multi-pronged approach including seed subsidies, demonstrations, training, and provision of essential resources.
National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP):
- To reduce the dependency on edible oil imports, NMEO-OP was launched in 2021.
- The mission aims to expand oil palm cultivation, increase crude palm oil production, enhance productivity, and alleviate the burden of imports.
Water Management for Sustainable Agriculture:
Per Drop More Crop (PDMC):
- Launched in 2015-16, PDMC emphasizes water use efficiency through micro-irrigation systems like drip and sprinkler irrigation.
- It also encourages the adoption of location-specific scientific techniques and modern agronomic practices.
Command Area Development & Water Management (CADWM):
- As part of the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, CADWM aims to enhance irrigation efficiency.
- This involves the construction of lined field channels and underground pipelines for last-mile connectivity.
Bureau of Water Use Efficiency (BWUE):
- The establishment of BWUE is crucial for regulating efficient water use across sectors.
- The bureau actively promotes strategies to improve water use efficiency in irrigation, industries, and domestic settings.
National Water Mission (NWM) – ‘SahiFasal’ Campaign:
- NWM launched the ‘SahiFasal’ campaign to encourage farmers in water-stressed regions to cultivate crops that align with agro-climatic conditions, are economically viable, and water-efficient.
Challenges Related to Food Security in India:
- Agricultural Challenges: India’s agricultural sector grapples with climate change impacts, unpredictable weather patterns, pest outbreaks, and soil degradation, all of which contribute to reduced crop yields and food scarcity.
- Land Fragmentation: Fragmented land holdings due to inheritance laws lead to small and uneconomical plots that hinder the adoption of modern farming techniques.
- Lack of Diversification: Overemphasis on staple crops like rice and wheat limits dietary diversity, contributing to malnutrition issues.
- Rising Food Prices: Fluctuations in global and domestic food prices can render essential food items unaffordable for vulnerable populations, leading to food insecurity.
Way Forward:
- Agro-Ecological Zoning: The implementation of detailed agro-ecological zoning maps, incorporating advanced geospatial analysis, can identify the most suitable crops for specific regions based on their natural characteristics. This approach optimizes resource utilization and minimizes the risk of crop failure.
- Edible Landscaping in Urban Areas: Encouraging urban residents to convert lawns and unused spaces into edible landscapes can significantly contribute to local food production, fostering self-sufficiency and community involvement.
- Nutrient Recovery from Wastewater: Implementing systems to extract nutrients from wastewater and organic waste, followed by their conversion into fertilizers, offers a sustainable approach to nutrient management and reduces the dependence on synthetic fertilizers.
- AI Pest Detection: The development of AI-powered cameras and sensors capable of detecting pest and disease outbreaks early can revolutionize pest management by enabling targeted interventions and minimizing the widespread use of pesticides.
- Integrated Energy Farming: The integration of agriculture with renewable energy production, such as placing solar panels above crops, serves multiple purposes: providing shade, reducing water evaporation, generating clean energy, and optimizing resource use.
In conclusion, the NFSM plays a vital role in addressing food security challenges in India by implementing a range of interventions that focus on sustainable agricultural practices, water management, and enhanced diversification.
SOURCE: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1946810
Q.1 Consider the following statements in relation to the provisions outlined in the National Food Security Act, 2013:
- Eligibility for receiving subsidized food grains is confined to families falling under the ‘below poverty line (BPL)’ category.
- The household’s senior-most woman, aged 18 years or older, is designated as the head of the household for ration card issuance.
- Expectant and breastfeeding mothers are eligible to receive a ‘take-home ration’ that ensures a daily intake of 1600 calories throughout pregnancy and for the initial six months following childbirth.
Which of the above statements is/are accurate?
(a) 1 and 2 Only
(b) 2 Only
(c) 1 and 3 Only
(d) 3 Only
Answer: B
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding NMEO-OP is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) ?
- NMEO-OP is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- NE states will not be covered under NMEO-OP due to their low potential.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: A
Q.3 Discuss the objectives, interventions, and significance of the National Food Security Mission (NFSM) in addressing food security challenges in India. Also, elaborate on the major challenges related to food security in the country and propose innovative strategies to enhance agricultural productivity and ensure sustainable food availability.



No Comments