26 Aug ISRO’s Satellite Programmes
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the topic details “ISRO’s Satellite Programmes”. The topic “ISRO’s Satellite Programmes” has relevance in the “Science and Technology” section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
What are different Satellite Programmes by ISRO?
For Mains:
GS3: Science and Technology
Awareness in Space Technology
Why in the news?
The Chandrayaan-3 lander achieved a historic soft landing near the lunar south pole, marking India as the fourth nation to land on the Moon after the US, Soviet Union, and China. This success highlights ISRO’s remarkable achievements, including satellite, launch vehicle, and planetary exploration milestones. Let’s delve into Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)’s satellite programs:
ISRO’s Satellite Programmes
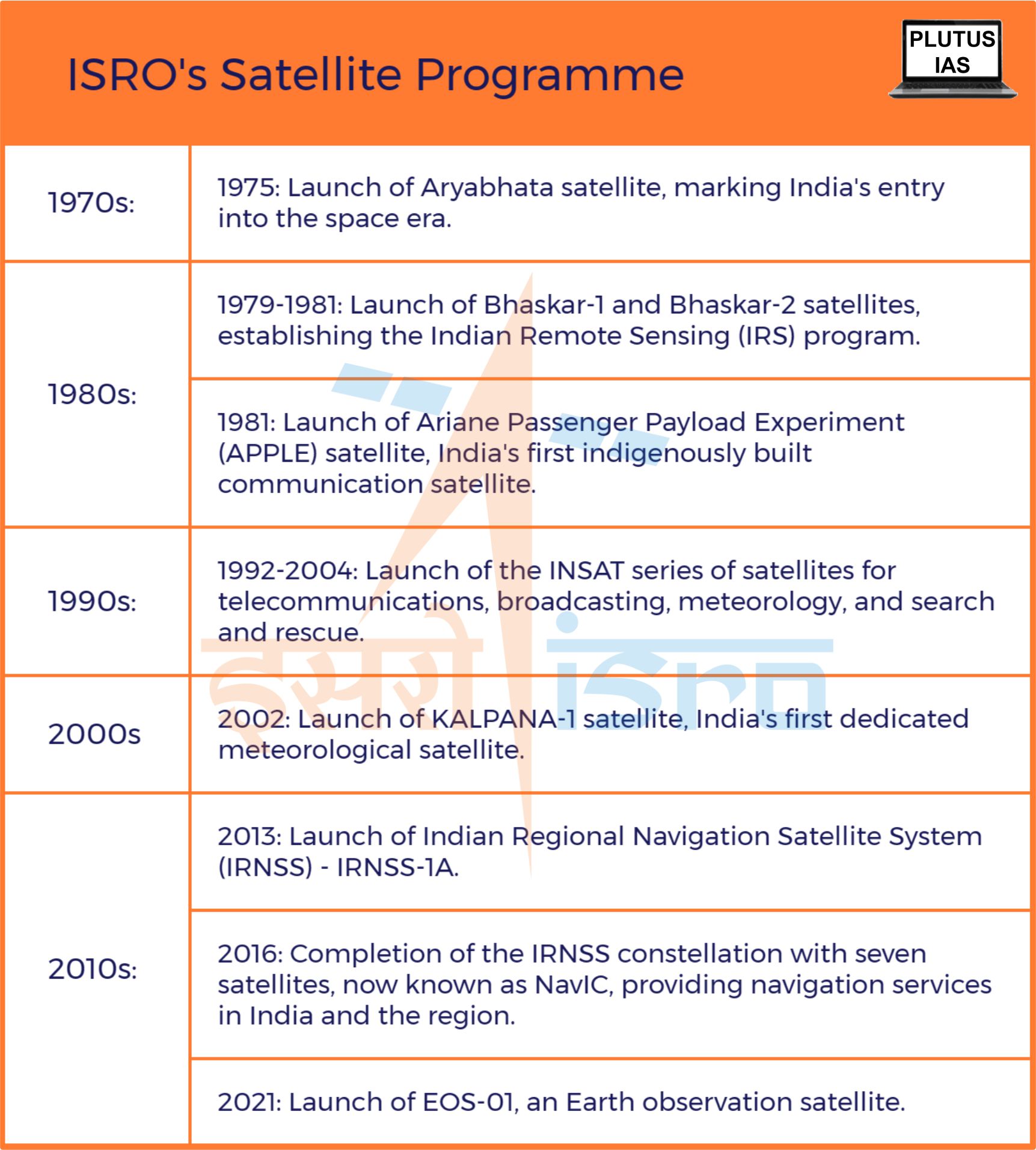
Aryabhata Satellite (1975)
- India’s entry into the space era was marked by the launch of the Aryabhata satellite on April 19, 1975.
- Weighing 360 kg, the satellite was designed by ISRO to conduct experiments in X-ray astronomy, aeronomics, and solar physics.
- It was named after the mathematician and astronomer Aryabhata. The satellite was launched from the Soviet Union on the Kosmos 3M rocket.
- Despite being deprived of power for five days, Aryabhata established the foundation for India’s space program.
Bhaskar-1 and Bhaskar-2 Satellites (1979, 1981)
- Following Aryabhata, two experimental remote-sensing satellites, Bhaskar-1 (1979) and Bhaskar-2 (1981), were launched. These satellites were instrumental in establishing the Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) Satellite system.
- The IRS system included Earth Observation spacecraft equipped with cameras like LISS-I and LISS-II, providing imagery for applications such as agriculture, forestry, geology, and disaster management.
Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) program (Since 1988)
- The Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) program is a series of Earth observation satellites developed and operated by ISRO. The program began in 1988 with the launch of IRS-1A and has 11 operational satellites.
- The IRS satellites are equipped with a variety of sensors, including cameras, radars, and multispectral scanners. The sensors collect data on the Earth’s surface, which is then processed and used to create maps, charts, and other products.
Ariane Passenger Payload Experiment (APPLE) Satellite (1981)
- The Ariane Passenger Payload Experiment (APPLE) was India’s first indigenously built communication satellite. It was launched on June 19, 1981, by an Ariane rocket from Kourou, French Guiana. The 672 kg satellite carried a single C-band transponder and was placed in a geosynchronous orbit at 102° East longitude.
- The APPLE satellite was used to conduct experiments in telecommunications, including relaying TV programs and radio networking. It also helped ISRO to gain valuable experience in designing and operating geosynchronous satellites. The satellite was deactivated on September 19, 1983.
INSAT Series (Starting from 1992)
- The INSAT series of satellites is a constellation of geosynchronous satellites operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). The first INSAT satellite, INSAT-1A, was launched in 1982. The INSAT series is used for a variety of purposes, including telecommunications, broadcasting, meteorology, and search and rescue.
- The INSAT-2 series of satellites was launched from 1992 to 1999. These satellites were the first to be built entirely in India. They had a number of improvements over the earlier INSAT satellites, including more powerful transponders and a wider range of applications.
- The INSAT-3 series of satellites was launched from 2002 to 2004. These satellites were even more advanced than the INSAT-2 series. They had better imaging capabilities and could provide more reliable services.
- The INSAT-4 series of satellites is currently being launched. These satellites are the most advanced in the INSAT series.
KALPANA-1 Satellite (2002)
- The KALPANA-1 satellite was a major milestone in India’s space program. It was the first dedicated meteorological satellite launched by India and it helped to improve the country’s understanding of the Earth’s atmosphere and climate.
- The KALPANA-1 satellite was used to provide weather forecasts and warnings, monitor natural disasters, and study the Earth’s atmosphere. It also helped to improve the understanding of climate change. The satellite was decommissioned in 2018.
Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) / NavIC (2013)
- The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), also known as NavIC, is an autonomous regional navigation satellite system developed by the ISRO.
- The system consists of seven satellites in geosynchronous orbit, providing accurate position information service to users in India and the region extending up to 1500 km from its boundary.
- IRNSS was launched in phases, with the first satellite, IRNSS-1A, being launched in July 2013. The full constellation of seven satellites was completed in April 2016.
Benefits of India’s Satellite Program:
Communication:
- India’s satellite program has played a vital role in providing telecommunications services to millions of people across India. The INSAT series of satellites, for example, provides television and radio broadcasting, telephone connectivity, and data services to remote areas of the country.
- This has helped to improve access to information and communication, which is essential for education, economic development, and disaster management.
Remote sensing:
- ISRO’s Earth observation satellites have been used to map the country’s resources, monitor environmental changes, and track natural disasters.
- This information has been used to improve agricultural productivity, manage water resources, and plan for disaster mitigation. It has helped to protect the environment and mitigate the impact of natural disasters.
Navigation:
- ISRO’s IRNSS navigation system provides accurate positioning information to users in India and the region.
- It has found use in various applications, including facilitating navigation for vehicles, ships, and aircraft, as well as supplying timing information for telecommunications and banking.
- This has helped to improve transportation safety and efficiency, and to facilitate financial transactions.
Economic development:
- India’s satellite program has helped to boost the country’s economy by providing telecommunications, remote sensing, and navigation services to businesses and industries.
- This has helped to improve efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
National security:
- ISRO has utilized its Satellite Programmes for national security purposes, including border monitoring and tracking illegal activities.
- This has helped to protect the country from external threats and internal security challenges.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has undoubtedly carved an illustrious path in India’s journey of development and progress. From its initial milestone with the Aryabhata satellite to achieving a soft landing near the lunar south pole with Chandrayaan-3, ISRO’s achievements in satellite programs have been monumental. As India continues to aspire towards greater heights, ISRO’s contributions stand as a beacon of inspiration and a testament to the remarkable synergy of technology, determination, and national pride.
Sources: As Chandrayaan-3 lands on the Moon, the history of ISRO’s remarkable space voyage
Q1. With reference to INSAT series, consider the following statements:
- The INSAT series of satellites, managed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), comprises sun-synchronous satellites.
- These satellites play a crucial role in delivering precise position information services to users within India and the surrounding region.
- The INSAT satellite series also facilitates the transmission of television and radio broadcasts, telephone connectivity, and data services to geographically distant regions within the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) None
Answer: (c)
Q2. Consider the following pairs:
| ISRO’s Satellite Programmes | Major Applications |
|
Position information services |
|
Telecommunications, broadcasting, meteorology, and search and rescue. |
|
Agriculture, forestry, geology, and disaster management. |
How many of the abovementioned pairs are correctly matched ?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Answer: (a)
Q3. In the context of recent achievements like Chandrayaan-3, discuss the key milestones and contributions of ISRO’s satellite programmes towards India’s economic development.



No Comments