24 Jul Kalecki’s Model
Kalecki’s Model of Distribution – UPSC Economics Optional Notes
Introduction
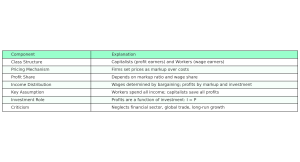
Michał Kalecki, a Polish economist and one of the pioneers of post-Keynesian economics, presented a heterodox model of income distribution that departs from neoclassical marginal productivity theory. Kalecki’s model emphasizes the role of market structure (monopoly power), class division, and investment behavior in determining the distribution of income between profits and wages. His approach is grounded in macroeconomic aggregates, especially the interaction of pricing, savings, and investment.
1. Basic Structure of Kalecki’s Economy
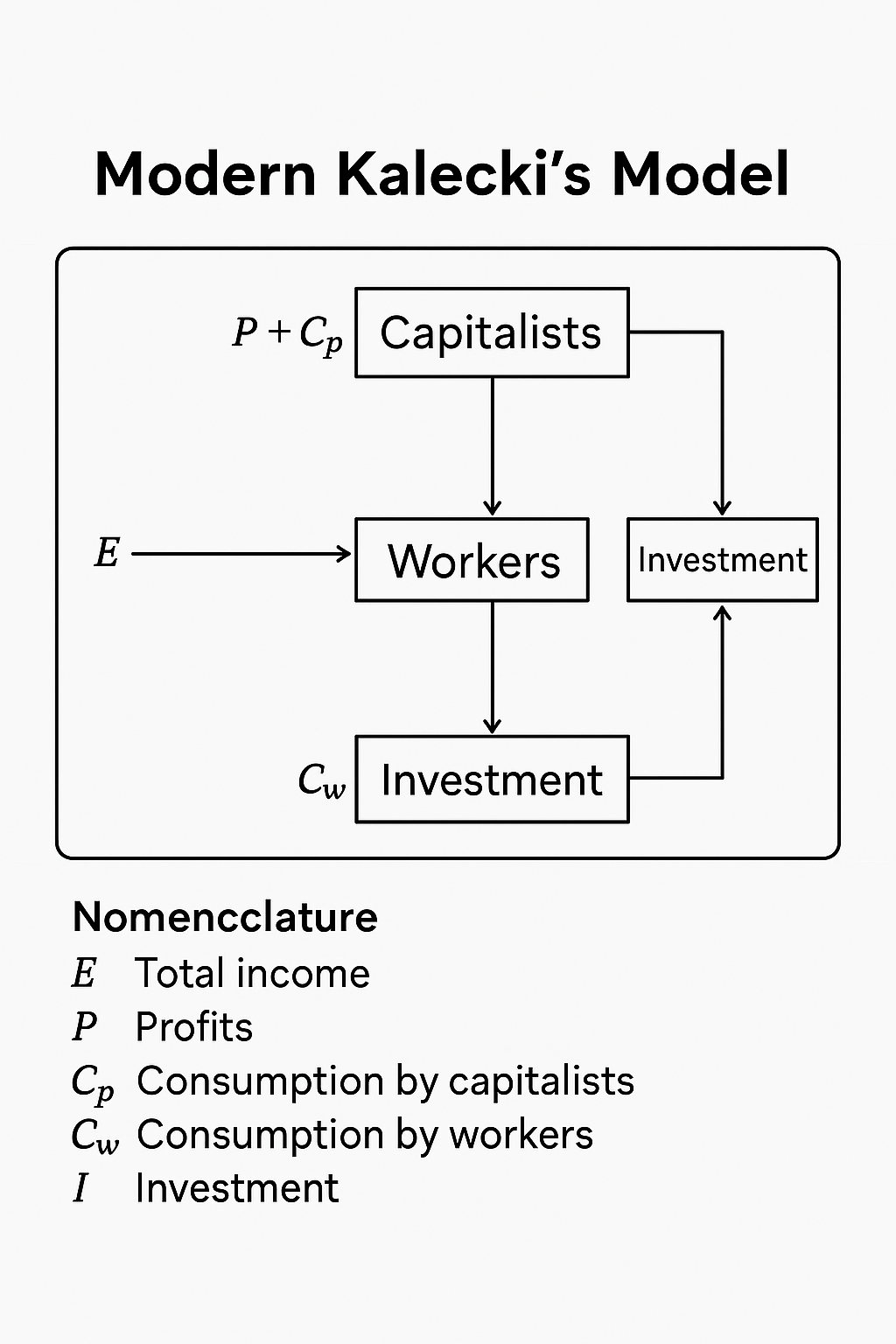
Kalecki divides society into two fundamental classes:
- Workers: Earn wages; consume all their income
- Capitalists: Earn profits; save all their income
This stark dichotomy forms the basis of his model, which sees distribution as a result of class struggle over pricing and production decisions.
2. Kalecki’s Pricing Assumption – Markup Pricing
Firms do not set prices based on marginal cost; instead, they add a markup over average variable costs (primarily wages).
Price (P) = (1 + μ) · Unit Labor Cost
- μ = markup ratio, determined by monopoly power and union strength
This markup determines the share of profits and wages in national income.
3. Distribution Equation
Let:
- Π = Profits
- W = Wages
- Y = National Income
Then: Π/Y = μ / (1 + μ) and W/Y = 1 / (1 + μ)
Thus, income distribution is functionally determined by the degree of monopoly in the economy.
4. Role of Investment and Savings
Kalecki emphasized that total profits are determined by investment, not the other way around. The logic is:
- Workers consume all income → their spending doesn’t generate savings
- Capitalists save → savings = profits
- To maintain equilibrium, capitalist savings must equal investment
Thus, I = S = Π (Investment = Savings = Profits)
Therefore, profits are determined by investment decisions, which in turn influence distribution.
5. Kalecki’s Emphasis on Class Conflict
The markup μ is a reflection of the balance of power:
- Higher union bargaining → lower μ → higher wage share
- Greater monopoly control → higher μ → higher profit share
This aligns Kalecki’s model with a class-based, political economy framework.
6. Infographic
Kalecki Distribution_Model_Infographic
7. Mind Map
Kalecki_Distribution_Model_MindMap
8. Comparison with Kaldor
- Kaldor: Profit share depends on investment and savings rates
- Kalecki: Profit share depends on markup ratio and class power
- Kaldor assumes full employment; Kalecki allows unemployment and crisis
- Kalecki incorporates macroeconomic instability and business cycles
9. Policy Implications
- Redistribution through taxation of monopolies
- Encouraging worker bargaining power to shift income toward wages
- Regulating investment to stabilize profits and growth
10. Criticisms of Kalecki’s Model
- Too simplistic in assuming workers save nothing
- Neglects foreign trade, technology, and financial markets
- No dynamic modeling of inflation or public debt
- Doesn’t explain long-run growth trends
11. Relevance Today
- Explains profit-led growth in monopoly-dominated economies
- Useful in analyzing income inequality and wage suppression
- Applies to political economy of inflation and corporate pricing
Kalecki’s insights are widely cited in post-Keynesian, heterodox, and Marxian economics today.
12. Previous Year UPSC Questions (Economics Optional)
- UPSC 2022: “Discuss how Kalecki’s model links income distribution to investment decisions.”
- UPSC 2020: “Compare and contrast Kalecki and Kaldor’s theories of distribution.”
- UPSC 2017: “Critically examine Kalecki’s view that profits are determined by investment.”
13. Probable Questions for UPSC Prelims and Mains 2025
- Mains: “How does Kalecki’s model incorporate class conflict into distribution analysis?”
- Mains: “Explain the role of monopoly power in Kalecki’s distribution model.”
- Prelims: “In Kalecki’s model, the profit share depends on…”
- Prelims: “According to Kalecki, I = P implies…”
14. Conclusion
Kalecki’s model remains a powerful critique of neoclassical economics. By linking profits to investment, and income shares to market power and class dynamics, it presents a comprehensive framework for analyzing distribution in capitalist economies. For UPSC Economics optional aspirants, this model provides both theoretical depth and practical insight into contemporary issues like corporate profits, labor share decline, and inequality.
Best economics optional coaching for upsc




No Comments