11 Oct Malaria Vaccine
This article covers “Daily Current Affairs” and the Topic details “Malaria Vaccine”. This Topic has relevance in the Science and Technology section of the UPSC CSE exam.
For Prelims:
About R21 Malaria Vaccine?
About Malaria
For Mains:
GS 3: Science and Technology
Malaria Burden Worldwide?
Global Initiatives?
India’s Initiatives?
Why in the news?
The R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine, a collaborative effort between the University of Oxford and the Serum Institute of India, utilizing Novavax’s adjuvant technology, has received a recommendation for usage from the World Health Organization (WHO) based on its compliance with essential safety, quality, and efficacy criteria.
About R21 Malaria Vaccine:
- The R21 vaccine, also known as the Matrix-M malaria vaccine, is the second vaccine ever developed for malaria.
Certified Malaria-Free Countries (since 2015):
- Nine countries have been certified as malaria-free by the WHO Director-General since 2015. These countries include Maldives, Sri Lanka, Kyrgyzstan, Paraguay, Uzbekistan, Argentina, Algeria, China (certified in 2021), and El Salvador (certified in 2021).
Malaria Burden Worldwide:
- In 2021, there were 247 million cases of malaria, compared to 245 million cases in 2020.
- In 2022, India reported over 45,000 cases of malaria.
- Approximately 80 percent of all malaria deaths in the WHO African Region occur in children under five years of age.
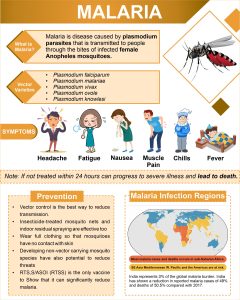
About Malaria:
- Malaria is a mosquito-borne blood disease caused by Plasmodium protozoa.
- It is spread via the bites of female Anopheles mosquitoes that are infected.
- The disease is life-threatening and is caused by Plasmodium parasites.
- Parasites initially multiply in liver cells and then attack red blood cells (RBCs).
- There are five parasite species that cause malaria in humans, with Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax posing the greatest threat.
Challenges in Developing a Malaria Vaccine:
- The parasites causing malaria are prone to mutations, which can lead to resistance to treatments.
Global Initiatives:
- The WHO has pinpointed 25 countries as part of its ‘E-2025 Initiative’ where there is the potential to achieve malaria eradication by the year 2025.
- The WHO’s Global Technical Strategy for Malaria 2016–2030 aims to reduce malaria case incidence and mortality rates by at least 40% by 2020, at least 75% by 2025, and at least 90% by 2030 against a 2015 baseline.
- WHO initiated the High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) initiative in 11 high malaria burden countries, including India.
- Implementation of the “High Burden to High Impact (HBHI)” initiative has been started in four states in India: West Bengal, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Madhya Pradesh.
India’s Initiatives:
- The Government of India has set a target to eliminate malaria in India by 2027.
- It has developed a National Framework for Malaria Elimination (2016-2030) and a National Strategic Plan for Malaria Elimination for five years.
- India shifted its focus from malaria control to elimination.
- A roadmap was established to eliminate malaria in 571 out of India’s total 678 districts by 2022.
- The Malaria Elimination Research Alliance-India (MERA-India) was formed under the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
Download plutus ias current affairs eng med 11th Oct 2023
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding malaria:
- Malaria is caused by a virus transmitted through the bites of infected Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Plasmodium falciparum is the most common parasite species responsible for causing malaria.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding the R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine:
- The R21 vaccine is a collaborative effort between the University of Oxford and the Serum Institute of India.
- It is the first vaccine ever developed for malaria.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 To what extent has the global effort to combat malaria succeeded in reducing its burden on public health, particularly in low-income countries? Analyze the key challenges that hinder malaria control and eradication




No Comments