24 Jul Marshallian and Walrasian Approaches to Price determination.
Marshallian and Walrasian Approaches to Price Determination – UPSC Economics Optional Notes
Introduction
The determination of prices in a market economy is a central issue in microeconomics. Two classical approaches—developed by Alfred Marshall and Léon Walras—explain how prices are determined through market mechanisms. The Marshallian approach focuses on partial equilibrium and individual market behavior, while the Walrasian approach addresses general equilibrium, highlighting interdependence across all markets. Understanding both approaches is crucial for aspirants of the UPSC CSE with Economics optional.
1. Marshallian Approach to Price Determination
Key Features
- Based on partial equilibrium analysis.
-

Marshall’s Equilibrium Graph
Considers only one market in isolation (ceteris paribus).
- Utilizes graphical tools like demand and supply curves.
- Incorporates time element—short run, long run, and market period.
- Stresses the role of elasticities in price adjustment.
best economics optional test series
best teacher of economics optional
Best economics optional coaching
Time Element in Marshallian Analysis
Marshall introduced the time element in price determination:
- Market Period: Supply is fixed; price is demand-driven.
- Short Run: Firms can adjust labor and raw material but not capital.
- Long Run: All inputs are variable; new firms can enter or exit.
Graphical Representation
Price is determined at the intersection of the demand and supply curves. Changes in either curve shift the equilibrium price.
2. Walrasian Approach to Price Determination
Key Features
- Based on general equilibrium analysis.
- Simultaneous determination of prices in all markets.
- Highly mathematical using sets of simultaneous equations.
- Emphasizes interdependence of markets.
- Uses the concept of tâtonnement (trial-and-error price adjustments by an auctioneer).
Walrasian Equilibrium
A Walrasian equilibrium occurs when demand equals supply in all markets simultaneously, and no agent has an incentive to change their behavior.
Assumptions
- Perfect competition.
- All agents are price takers.
- No externalities or public goods.
- Complete markets for all goods and services.
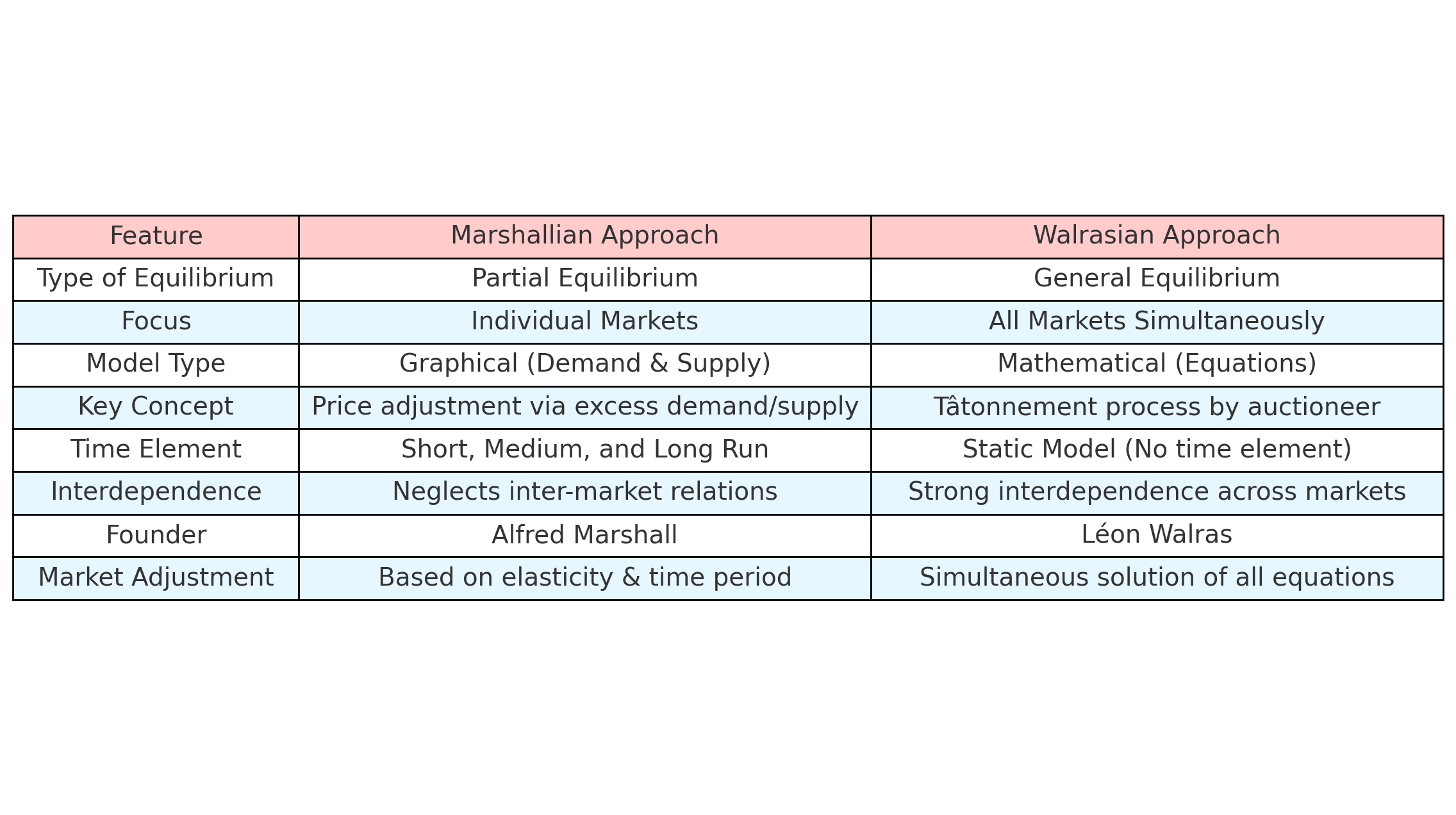
3. Comparison: Marshall vs Walras
Summary
| Aspect | Marshallian | Walrasian |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Partial Equilibrium | General Equilibrium |
| Approach | Graphical (Demand & Supply) | Mathematical (Equations) |
| Markets | Single Market in Isolation | All Markets Simultaneously |
| Founder | Alfred Marshall | Léon Walras |
| Adjustment Process | Price adjusts via demand/supply shifts | Tâtonnement process via auctioneer |
4. Relevance to UPSC CSE Economics Optional
This topic is part of Paper 1 – Microeconomics under the section “Theory of Value” in the UPSC Economics optional syllabus. A sound understanding helps in both theoretical and applied economic answer writing.
Best economics services coaching
5. Previous Year UPSC Mains Questions (Economics Optional)
- 2023: “Explain the significance of time element in Marshallian price determination.”
- 2021: “Differentiate between partial and general equilibrium. Illustrate with examples.”
- 2018: “Discuss the role of auctioneer in Walrasian equilibrium process.”
6. Probable Questions for UPSC CSE
- Mains: “Compare and contrast Marshallian and Walrasian price determination approaches. Which one better suits real-world markets?”
- Mains: “Explain the interdependence of markets in the context of Walrasian general equilibrium.”
- Prelims: “In the Walrasian model, what mechanism is used to reach market equilibrium?”
- Prelims: “Which of the following is not a feature of Marshallian partial equilibrium?”
7. Download Visual Aids
🧠 Download Mind Map on Marshallian vs Walrasian Approaches
📊 Download Infographic on Comparative Features




No Comments